Here is my actual listing of Vultee Aircraft's Model numbers. Little new will be added here ... but at least it will be sequential.
Vultee Aircraft Designations
Vultee Model 1 - 1933 single-engined airliner, x 25
- Model 1: 1-2 crew + 6 pax airliner prototype, x 1
-- aka Vultee V1 (orig. style) often given as 'V-1'
- V1 : 650 hp Wright SR-1820-F2; span 14.63 m
- V1-A: Production V1; 2 x crew + 8 x pax ; x 18
- V1-A: 735 hp Wright R-1820-F2; span 15.24 m
-- V1 as redesigned for American Airlines, x ~13
- V1-AD: 'D' for 'Deluxe'; executive transport; x 6
- V1-AD: 1 x 850 hp Wright R-1820-G2
Cyclone
- V1-AD Special: Exec. for Randolph Hearst, x 1
- V1-AD Special: 1 x 1,000 hp Wright R-1820-G2
- V1-AS: 'Special'; floatplane vers. to USSR, x 1
- V1-AS: 'Special'; 1 x 775 hp Wright R-1820-F52
2-10 - (??) probably not applied
Vultee AB-2 - Marketing designation for the V-12C
- AB-2: Registered V-12C, c/n 131, X18985/NX18985
Vultee Model 11 - 1935 attack Model 1 deriv.; x 175+
- Model 11: 3-seat, single-engined attack bombers
-- aka Vultee V-11 (note change in desig. style)
- V-11 : 750 hp Wright SGR-1820, span 15.24 m
-- Prototype (X14999) c/n 28; crashed & written off
- V-11-A: 2nd prototype; NX/NR/NC14980; c/n 29
-- V-11-A mod. as V-11T engine testbed for P&W
- V-11-G : 1 x 850 hp Wright R-1820-G2* engine
-- * or 1,000 hp Wright SGR-1820-G2 (tests?)
- V-11-G : 1935 2-seater; hack x 1; China x 30
- V-11-GB : 1 x 1,200 hp Wright SGR-1820-G2
- V-11-GB : USSR x 4;** Turkey x 40; Brazil x 26
-- ** + 31 x license-built BSh-1s conv. to PS-43
- V-11-GB2 : V-11-GB type variant for Brazil; x 26
- V-11-GB2F: Twin-float vers. for Brazil, not accepted
- V-11-GBT : Turkish V-11-GB variant designation
- V-11-GB : USAAC/USAAF designations in A-19 range
-- XA-19 : USAAC designation for prototype V-11-GB
-- YA-19 : USAAC desig. for 7 x V-11-GB attack a/c
-- XA-19A: 1940; 1 x 1,200hp Lycoming O-1230-1
-- Converted YA-19 testbed; enlarged, triangular fin
-- XA-19B: 1939; 1 x 1,800hp P&W R-2800-1 radial
-- Converted YA-19 airframe; USAAC serial 38-550
--- A-19 : 5 x surviving YA-19 a/c redesignated A-19
-- XA-19C: 1939; 1 x 1,200hp P&W R-1830-1/'-51
-- Converted XA-19A airframe; USAAC serial 38-555
- V-11-SBS: (Scout Bomber Seaplane) Float version
-- V-11-SBS had standard (not enlarged) tailplane
- V-11-ST : Twin-pontoon floatplane; enlarged tailfin
- V-11-T : Mod. V-11A (c/n 27, NR14980) testbed
- V-11-T : Cockpits moved aft; tall, fixed u/c legs
-- V-11-T fitted with various P&W R-2800 models
- V-11-TS: (Torpedo Seaplane) as per V-11-ST (??)
Vultee Model 12 - 1938 better streamlined evol. of V-11
- V-12 : Prototype (c/n 131, NX18985); flew Sept. 1938
- V-12 : Engine testbed at Pratt & Whitney; aka AB-2
- V-12-A: (??) hypothetical designation
- V-12-B: (??) hypothetical designation
- V-12-C: Prod'n version V-12 for Republic of China; x 26*
- V-12-C: 1 x 1,100 hp Wright R-1820-G105B
Cyclone
-- * Claimed Vultee x 1 + 25 x Chinese-assembled (??)
-- * Unlikely that CAMCO Loi-wing delivery any V-12-Cs
- V-12-D: More powerful derivative, deepened fuselage
- V-12-D: 1,600 hp Wright GR-2600
Cyclone 14; x 54
-- Some say no V-12-D were delivered; photos bely that
-- V-12-D parts to HAL Bangalore; poss. 3 x completed**
-- ** But no sign of any RAF India serials being assigned
Vultee Model 20 - (??) no details
Vultee-Stinson V-20 - S-101 with Lycoming O-435A HO6
21-31 - (??)
Vultee Model 32 - (??) no details
Vultee Model 33 - (Project) Observation-bomber floatplane
- Model 33: aka XOB-33; no other details
- Model 33: Possibly related to the Model 39 (
qv) (??)
34 - (??)
Vultee Model 35 - (Project) 1937 XP-35 twin-engined fighter
- Model 35: Single-seat, slim-fuselaged interceptor design
- Model 35: Export interceptor/fighter with non-US engines
- Model 35: 2 x 860 hp Hispano-Suiza 12Y-21; span 14.63 m
-- XP-1015: Related, enlarged, US-engined design for USAAC
-- XP-1015 to February 1937 USAAC Circular Proposal X-608
-- XP-1015: 2 x 1,150 hp Allison V-1710-C7;* span 16.46 m
-- * As quoted; 'handed' props suggest 1 x '-C7 + 1 x '-C9
-- (??) Unclear whether XP1031 had its own Model number
-- XP-236 : August 1937** Model 35 configuration variation
-- ** Note: The USAAC's CP X-608 was closed by this date
-- (??) Unclear whethe XP-236 had its own Model number
--
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/th...er-twin-engined-vultee-fighter-projects.4181/
36 - (??)
Vultee Model 37 - (??) no details
Vultee Model 38 - (Project) 1937 attack bomber
- Model 38: No other details
Vultee Model 39 - (Project) Observation-bomber
- Model 39: Poss. landplane Model 33 variant (??)
Vultee Model 40 - (Project) V.40 fighter; no details
Vultee Model 41 - (Project) Possibly XC-1031/XC1031
- Model 41: Speculatively associated with XC-1031
-- If so, low-winged side-by-side retr. u/c light a/c
--
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/question-about-vultee-xc1031.12203/#post-119614
Vultee Model 42 - (Project) single-seat fighter study
- Model 42: aka V-42; early study resulting in V-48
Vultee Model 43 - (Project) lightweight fighter concepts
- Model 43 : aka VP-43; apparently in various config's*
-- VP 43-1 : (??) hypothetical designation
-- VP 43-2 : (??) hypothetical designation
-- VP 43-3 : 1943 stratospheric lightweight fighter
-- VP-43-3 : To 1943 USAAF design directive
-- * Early VP-43 may be contemp. w/ XP-48 & XP-77
-- NB:
hesham speculated perhaps began as 'XP-1043'
Vultee Model 43 (II_ - (Project) Radio-controlled target drone
Vultee Model 44 - (Project) single-seat fighter study
- Model 44: aka V-44; early study resulting in V-48
Vultee Model 45 - (Project) single-seat fighter study
- Model 45: aka V-45; early study resulting in V-48
Vultee Model 46 - (Project) 2-engined pursuit, to CP X-608
- Model 46: Rival to XP-1015 & Lockheed Model 22/XP-38
-- NB: The Model 46 preceded the XP-236 of August 1937
- Model 46: aka Vultee XP-46 (an internal designation)
- XP-46-1: (??) hypothetical designation
- XP-46-2: Twin V-1710 in fuselage, shaft-drives to props
-- XP-46-2: Mid/blended wing, V-tail, tricycle gear
--
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/vultee-projects.1372/#post-216674
Vultee Model 46 (II) - (Project) single-seat fighter study
- Model 46: aka V-46; early study resulting in V-48
Vultee Model 47 - (Project) Attack bomber
- Model 47: no other details
Vultee Model 48 - Single-seat light fighter; aka P-48
- Model 48 : 1st prototype (NX21755); flew Sept 1939
- Model 48 : 1,200 hp P&W R-1830-S4C4-G; span 10.92 m
- Model 48 : (As flown) Long prop shaft; low-drag cowl
- Model 48 : (As mod) Cowl intake fixed; larger rudder
- Model 48 : (As mod) Conv'l cowl repl'd low-drag type
- Model 48X: 2nd prototype (NX19999); flew Feb 1940
-- Note: Model 48X originally designated as Model 61
- Model 48X: (As flown) Conv. cowl; compound dihedral
- Model 48X: (As mod) All 3 x tail surfaces enlarged
- Model 48C: Sept. 1940 prod'n prototype (NX28300) [1]
- Model 48C: 1 x 1,050 hp P&W R-1830-S3C4-G 14-cyl.
-- Model 48C to
Flygvapnet order; SE then embargoed
-- Redirected to RAF as Vanguard Mk.I fighter-trainers*
-- * Released by UK for Lend-Lease to RoChina; x 127
-- * Of 144 P-48C built, remainder to USAAF as P-66s
-- P-66 : 1 x 1,200 hp P&W R-1830-33; span 10.92 m
Vultee Model 49 - (Project) Pursuit; aka V-49 (P-49?)
- Model 49: Wright-powered; no other details
- Model 49: Possibly based on V-48
Vanguard
Vultee Model 50 - (Project) V-50 USN Scout-Bomber
- Model 50: Naval dive bomber; no other details
- Model 50: Also the basis for an advanced trainer?
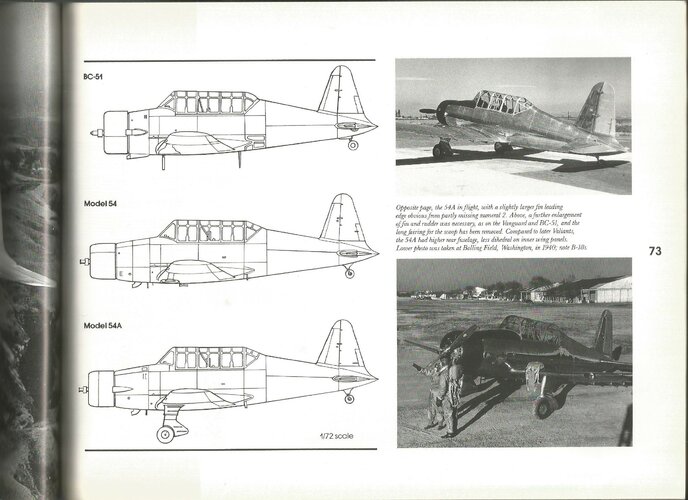
Vultee Model 51 - 1939 USAAC Basic Combat trainer, x 1
- Model 51: aka BC-51, unsuccessful comp. w/ NAA BC-2
- Model 51: All-metal const.; hydraulic flaps & main u/c
- Model 51: 1 x 600 hp Pratt & Whitney R-1340-S3H1-G
-- USAAC bought BC-51 prototype as sole Vultee BC-3
-- Palmer evolved V-51 into fixed u/c V-54 or VF-54 (
qv)
Vultee Model 52 - (Project) V-52 observation design
- Model 50: Based on V-11-GB/YA-19; no other details
52-53 - (??)
Vultee Model 54 - Advanced & basic trainer types
- Model 54 : Advanced trainer design; aka V-54
- Model 54A: aka VF-54A; fixed & faired main u/c
- Model 54B: (??) hypothetical designation
- Model 54C: (??) hypothetical designation
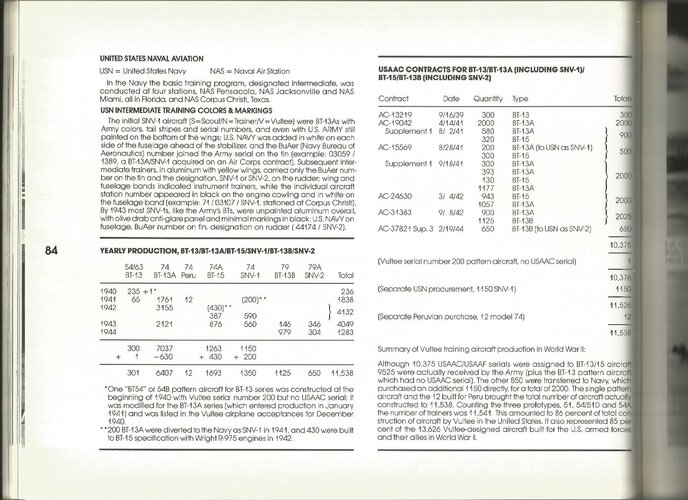
- Model 54D: USAAC/AAF BT-13 Valiant; USN SNV
-- BT-13 : 450 hp P&W R-985-T3B
Wasp Jr.; x 300
-- BT-13A: 450 hp P&W R-985-AN-1 9-cyl.; x 7,037
-- BT-13A differed in military engine; no u/c fairings
-- BT-13B: As BT-13A except 24v (not 12v); x 1,125
-- NB: BT-13B
may have been original Model 79C
-- BT-15 : 1 x 450 hp Wright R-975-11 9-cyl.; x 1,263
-- BT-15 :
May have internal desig. Model 74A (qv)
-- XBT-16: 1942 BT-13A w/ Vidal moulded fuselage
-- SNV-1 : US Navy version of the BT-13A; x 1,150
-- SNV-2 : US Navy version of the BT-13A; x 650
- NB: SNV-2
may have been the orig. Model 79A
Vultee Model 55 - (Project) 1939 USN Scout-Bomber
- Model 55: Naval dive bomber; no other details
Vultee Model 56 - (Project) 1936 fighter/light-bomber
- Model 56: Single- or 2-seat configurations
Vultee Model 57 - (Project)
Vengeance torpedo bomber
-- TBV-1 Georgia: (Project) A-31 for USN; later A-35B
-- TBV-1
Georgia: (Project) A-31 for USN; later A-35B
-- To 1939 USN VTB contest; 3-crew carrier torpedo bomber
-- Intended TBD
Devastator replacement; cancelled [3]
Vultee Model 58 - (Project) Intercontinental transport
- Model 58: Multi-engined a/c (possibly 7 x engines)
- Model 58: No other details (??)
Vultee Model 59 - (Project) no details (??)
60 - (??)
Vultee Model 61 - 1939 light fighter; re-desig. P-48X
- Model 61: Interim desig. for 2nd prototype Model 48
-- Flew Feb 1940 as prototype Model 48X (NX19999)
- Model 61: Poss. originally Model 48 alt. layout [2]
Vultee Model 62 - (Project) USAAC 2-seat basic trainer
- Model 62: Developed from the BC-51 prototype (BC-3)
Vultee Model 63 - Production USAAC BT-13
Valiant
- Model 63: Original number; relates to V-54D?
64-68 - (??)
Vultee Model 69 - (Project) Single-engined dive bomber
- Model 69 : Variant of the Model 72/A-31; aka AB-69
- Model 69 : no other details (??)
Vultee Model 70 - (Project) Single-seat single-engine pursuit
- Model 70 : To the Nov 1939 USAAC Specification XC-622
- Model 70 : Twin-boom pusher; inverted gull; tricycle u/c
- Model 70-1: 1 x (??) hp Allison (??) engine; span 40 feet
- Model 70-2: 1 x 1,800 hp Pratt & Whitney X-1800 H-24
Vultee-Stinson V-70 - Rebranding of Vultee-Stinson V-74
- Stinson V-70 : To avoid confusion with the V-74
Valiant
Vultee Model 71 - (Project) no details (??)
Vultee Model 72 -
Vengeance dive bomber, aka V-72
- Model 72: (Project) 1940 design for
Armée de l'Air
- Model 72: (Project) 1,600 hp Wright GR-2600-A5B-5
-- Initially, a twin-tailed design; span (??) m
--
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/early-vultee-v-72-Vengeance-drawing.19490/
- Model 72: 300 ordered by France, 200 taken by RAF
--
Vengeance I : Lend-Lease Northrop A-31-NO; x 200
--
Vengeance I : 1 x 1,600 hp Wright GR-2600-A5B-5
--
Vengeance IA: Lend-Lease Northrop A-31A-NO; x 200
--
Vengeance IA: 1 x 1,600 hp Wright R-2600-19
--
Vengeance II : Lend-Lease Vultee A-31-VN; x 501
--
Vengeance II : Vultee Nashville equiv. to the Mk.I
--
Vengeance III: Lend-Lease Vultee A-31A-VN; x 200
--
Vengeance III: Vultee Nashville equiv. to the Mk.IA
--
Vengeance IV: See Vultee Model 88 (below)
-- A-31 : USAAF Lend-Lease desig.; see
Vengeance I
-- XA-31A: June 1942 prototype USAAF
Vengeance
-- A-31A: Lend-Lease desig.; see
Vengeance II & III
-- XA-31B: XA-31A as 3,000 hp P&W XR-4360-1 testbed
-- YA-31C: Wright R-3350-37 testbed (some say R-3350-17)
-- For USAAF A-35 variants, see Vultee Model 88 (below)
Model 73 - Further batch of A-31 for USAAF*
- Model 73: Might this be Northrop's A-31-NOs?
-- * Obviously meaning desig. for Lend-Lease
Vultee Model 74 - Possible Model 54D variant designations
- Model 74 : Quoted as sequence for
Valiant derivatives
- Model 74 : Poss. BT-13
Valiant trainer; aka V-74
- Model 74A: Poss. BT-15
Valiant trainer; aka V-74A
Vultee-Stinson Model 74 - 1940 O-49/L-1 Vigilant liaison a/c
- Stinson Model 74: 3-seat, high-winged braced monoplane
-- YO-49: USAAC desig. for prototype Stinson Model 74
-- O-49/L-1 : 1st prod. variant; x 142; RAF
Vigilant Mk I
-- O-49/L-1 : 1 x 295 hp Lycoming R-680-9; span 15.52 m
-- O-49A/L-1A: 2nd prod. variant; x 182; RAF
Vigilant Mk II
-- O-49B/L-1B: Ambulance variant; O-49 conv'n; x 3-4
-- L-1C : Ambulance variant; O-49A/L-1A conv'n; x 113
-- L-1D : Glider tug trainer variant; L-1A conv'n; 14-21
-- L-1E : Ambulance floatplane variant; L-1 conv'n; x 7
-- L-1E : Ambulance floatplane variant; L-1A conv.; x 5
-- CQ-2 : USN target control aircraft; L-1A conv.; x 1 (?)
75 - (??) Presumably there was a Vultee Model 75 (??)
Vultee-Stinson Model 75 - 1940
Sentinel prototype
- Stinson Model 75 : Military deriv. of Stinson HW-75*
-- * Side-by-side seats; Model 75 was tandem seated
- Model 75 : Prototype leads to Model 76 = O-62/L-1
- Model 75 : 1 x 100 hp Lycoming; span 10.36 m; x 1
- Model 75A: (??) Poss. redesig. of Model 105/HW-75
-- If true, Stéphane speculates for record-keeping only
- Model 75B: 1940 tandem-seat Model 105/HW-75 deriv.
- Model 75C: Prototype re-engined w/ 125 hp Lycoming
76 - (??) Presumably there was a Vultee Model 76 (??)
Vultee Model 76 - 1940 prod'n vers. Stinson L-5
Sentinel
- Model 76 : 2nd prototype; initially with full-span slots
- Model 76 : (Modified) half-span slots & enlarged tail
- Model 76 : Modified to full L-5 standard; NX27772; x 1
Vultee-Stinson Model 76 - 1941 production
Sentinel
- Stinson Model 76 : Final prod'n version of Model 75C
- Stinson Model 76 : 185 hp Lycoming O-435; span 10.36 m
- Stinson Model 76 : 2nd prototype; init. w/ full-span slots
- Stinson Model 76 : (Mod.) Half-span slots; enlarged tail
- Stinson Model 76 : (Mod.) Full L-5 std.; NX27772; x 1
-- O-62 : Observation desig.; replaced by L-5 by delivery
-- L-5A : (Project) 1943 proposal for 24v electrical system
-- L-5B : Liaison a/c with mods for air ambulance or cargo
-- L-5C : As L-5B but w/ revisions to accept K-20 camera
-- L-5D : (Project) Variant with Ranger L-440 engine; 24v
-- L-5E : Improved low-speed control w/ drooping ailerons
-- L-5E : 185 hp Lycoming O-435-1; 12v electrical system
-- L-5E-1: Impr. STOL w/ large tires & heavy-duty brakes
-- XL-5F: 1945 L-5B conv. to L-5G standard 24v and radio
-- Used for 1948 'quiet airplane' testing at NACA Langley
-- Lycoming GO-435 HO6 driving 5-bladed prop + muffler
-- L-5G : 190 hp Lycoming O-435-11; 24v electrical syst.
-- OY-1 : USN & Marines vers. with 12v electrical system
-- OY-2 : USN & Marines vers. with 24v electrical system
-- 1948, 7 x OY-1 transf. to USCG; 1952, 1 x OY-2 to CG
77 - (??) Was there a Vultee Model 77 (as opposed to V-77)
Vultee V-77 -
Gullwing; postwar SR-10 marketing desig.
- V-77 : Refurbished Stinson Reliant military utilities*
-- NB: Stinson itself seems only to use SR-10 desig.
-- * No sign of postwar production of new-build V-77s
-- Q : Was there an earlier 'Model 77' designation?
Vultee Model 78 - Shrike; evolved into '
Swoose Goose'
- Model 78: Single-seat, pusher-propeller fighter for export
- Model 78: 1 x (??) hp Allison V-1710(-??) V12; span (??) m
- Model 78: Export market fighter; evolved into the Model 84
- Model 78: Magnesium-alloy fuselage constr.; tricycle u/c
-- At least 2 x distinct variants (poss. with sub-type suffixes)
Vultee-Stinson Model 78 - (Project) USN navigation trainer
- Stinson Model 78: Likely a proposed R3Q
Reliant variant
Vultee Model 79 - (Project) Single-engined, single-seat fighter
- Model 79 : 1 x Lycoming XH-2470 'Hyper' V12; various spans
- Model 79 : Pusher propeller with dorsal and ventral intakes
- Model 79 : Triple-boomed w/ lower boom from ventral fairing
- Model 79A: Mildly inverted-gull wing; triple tail; span 13.08 m
- Model 79B: (??) hypothetical designation
- Model 79C: Greater inverted-gull; triple tail; span 14.02 m
-- Model 79C to USN Spec. SD 112 (leading to Grumman F7F)
Vultee Model 79 (II) - (??) Possible Model of BT-13B/SNV-2
- Model 79A : Possible internal designation for USN SNV-2
- Model 79B : (??) hypothetical designation
- Model 79C : Possible internal desig'n for USAAF BT-13B
-- If true, Model 79 had come from pusher fighter (qv) [4]
Model 80 - (??) Cargo/transport aircraft; no other details
Model 81 - Model 82 - (??)
Vultee Model 83 - (Project) Derivative of Model 48 fighter
- Model 83: Supercharged variant of P-48/USAAF P-66
- Model 83: aka V-83; single-seater; no other details
Vultee Model 84 - 1943 single-seat fighter to USAAC R-40C
- Model 84 : Single-pusher; twin-booms; ducted wings; x 2
-- Scaled-up Model 78
Shrike development; aka MX-12*
-- * USAAF AMC's MX (Materiel, Experimental) designator
-- A scaled-up development of the Model V-78 Shrike
- Model 84 : 2,300 hp Lycoming XH-2470-1; span 16.41 m
- Model 84 : Ordered by USAAF as XP-54 '
Swoose Goose'
- Model 84A-84D: (??) hypothetical designations [5]
- Model 84E: (Project) Re-engined XP-68 development
- Model 84E: 1 x 2,500 hp Wright R-2160; span 16.41 m
- Model 84E:
Tornado after engine; 6-blade contra-props
Vultee Model 85 - Claimed as 1941 prototype Model 72
- Model 85:
Vengeance prototype for
Armée de l'Air
- Model 85: Is there evidence for this prototype claim?
-- If true was it for aborted twin-tailled 2nd prototype?
-- NB: Online confusion with V-85 and restricted RA-31s
Vultee Model 86 - (Project) 1942 single-seat V-72 variant
- Model 86: (??) no details; weight-reduction exercise?
87 - (??)
Vultee Model 88 - USAAF variants of export Model 72
- Model 88: Vengeance repossessed/built for USAAF
-- XA-31A: June 1942 prototype USAAF
Vengeance
A-31: Initial production variant; later renamed A-35.
-- A-31A-VN: Vultee-built; Lend-Lease a/c; x 200
-- A-31A-NO: Northrop-built; 1,600 hp R-2600-19; x 200
-- XA-31B: XA-31A as 3,000 hp P&W XR-4360-1 testbed
-- YA-31C: Wright R-3350-37 testbed (some say R-3350-17)
-- A-35A: USAAF/LL; 1,700 hp R-2600-8 or -13 or -8; x 99
-- A-35B: USAAF/LL (RAF & RAAF); 6 x .50-cal mgs; x 831
-- TBV-1
Georgia: (Project) USN A-35B; see Model 57
-- NB: TBV began as A-31 for 1939 USN VTB competition*
-- * 3-crew carrier torpedo-bomber; Douglas TBD replacement
Vultee Model 89 - Another unverified designation for XA-31
- Model 89: Improbable 'V-89' for Lend-Lease prototype [6]
Vultee Model 90 - 1944 Consolidated-Vultee XA-41 prototype, x 1*
- Model 90: Orig. dive bomber, then attack, finally testbed
- Model 90: 1 x 3,000 hp P&W R-4360-9 28-cyl., span 16.46 m
-- * 43-35124 (43-35125 and ground test airframe cancelled)
-- aka MX-312; USAAF AMC 'Materiel, Experimental' designator
-- Model 90/XA-41 became P&W R-4360 Wasp Major testbed
- (??): (Project) Late 1944 Model 90 torpedo bomber variant**
-- ** Illustrated in US Navy markings; a serious proposal (??)
Vultee Model 9? - (??) Possible desig. for early XA-44 concept*
- Model 9?: Highly speculative; Vultee may never have desig'd
-- * Later revised as unbuilt Convair Model 102 (USAF XB-53)
_____________________________
[1] The Model 48C designation
might be explained by the first prototype Model 48 and second prototype Model 48X acting to fill-in the 'A' and 'B' designation slots.
[2] This is pure speculation but, it is conceivable that, the application of this second model number to the P-48 series was based in the hope that a long-cowl Model 48 might be offered alongside a conventionally-cowled Model 61. If true, then the abject failure of the long, variable-intake cowling concept put paid to that possibility. With only conventional cowlings in the running, what was to be the Model 61 would then be re-designated as the Model 48X - a second prototype towards developing a single production type
Vanguard.
[3] The nose-up flying attitude of the
Vengeance resulted in poor pilot visibility. In truth, that characteristic alone means that the proposed TBV-1
Georgia would have produced a terrible shipboard torpedo bomber.
[4] Or vice-versa - the chronology is not at all clears. Here, Vultee may have been distinguishing between its Model 79 pusher fighter and a V-77 nomenclature for the
Valiant variants.
[5] Stéphane has speculated that the 'missing' V-84A to V-84D model numbers
might be accounted for by Vultee having redesignated the earlier pusher fighters - Models 70, 78, 79, and their derivatives - into the Model 84 sequence. This is acknowledged as purely speculative but could handily explain those 'missing' sub-type letters.
[6] No explanation is given for why the XA-31 - a straightforward USAAF Lend-Lease version of a previous export type - needed a distinct Vultee Model number (as opposed to, say, a sub-type letter added to the existing Model 72 series). Odd too that, if there was a 'V-89' applied to a Lend-Lease
Vengeance prototype; why isn't there a 'V-89A' for the June 1942 XA-31A?
_________________________________________________________