You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
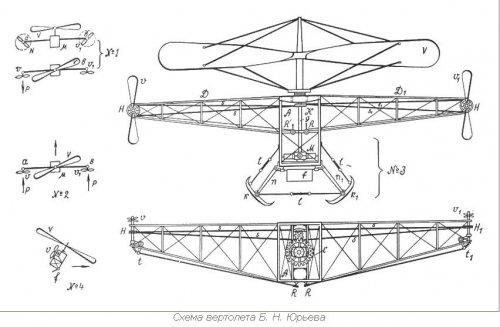
Boris Yuriev Helicopter and VTOL Projects
- Thread starter hesham
- Start date
Tophe
ACCESS: Top Secret
Do you have a date or first name, to search in the Patent database espacenet?
Tophe
ACCESS: Top Secret
According to Google, Boris Yuriev was a helicopter Russian pioneer in 1911-1912. This more complicated project may be later, 1913 to 1917?
It was in 1913-1914
Thanks, Ray))
Thanks, Ray))
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,901
- Reaction score
- 15,761
Also for Yuriev;
http://fly-history.ru/books/item/f00/s00/z0000014/st025.shtml
http://translate.google.com/translate?sl=ru&tl=en&js=n&prev=_t&hl=ar&ie=UTF-8&layout=2&eotf=1&u=http%3A%2F%2Ffly-history.ru%2Fbooks%2Fitem%2Ff00%2Fs00%2Fz0000014%2Fst025.shtml
http://fly-history.ru/books/item/f00/s00/z0000014/st025.shtml
http://translate.google.com/translate?sl=ru&tl=en&js=n&prev=_t&hl=ar&ie=UTF-8&layout=2&eotf=1&u=http%3A%2F%2Ffly-history.ru%2Fbooks%2Fitem%2Ff00%2Fs00%2Fz0000014%2Fst025.shtml
Attachments
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,147
Translated from Jean Boulet's Histoire de l'hélicoptère racontée par ses pionniers – 1907-1956:
According to Soviet author David Gai, the first helicopter to be built in the world was the 1912 Yuriev. However, that machine never flew. Here is what Eugene K. Liberatore, a historian of Russian aircraft, has to say about it:
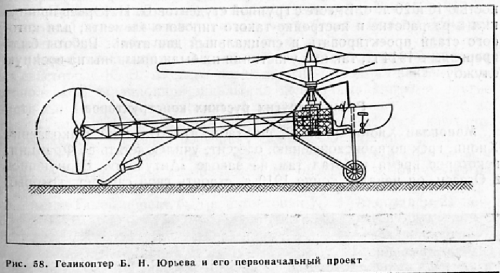
Yuriev's helicopter activities began in 1909. During that year, he proposed a design for a machine with two coaxial rotors. A 70 hp rotary Gnôme engine was fitted in the upper part of the fuselage, driving two rotors of different diameters: 9.7 m for the upper one and 3 m for the lower one. The machine featured a directional propeller with variable pitch for yaw control. It was fitted with wheels for rolling take-offs, and a parachute was planned in case of engine failure. It weighed 694 pounds.
At the end of 1909, Yuriev drew a second version. He had estimated the necessary take-off power to be 50 hp, but the absence of such an engine at his disposal prevented him from building that machine. However, a 25-30 hp Anzani engine was available at the Moscow Aero-Club. Yuriev designed a helicopter around that engine, with a two-blade main rotor (with a diameter of 8.6 m) and a tail rotor motioned by a strap.
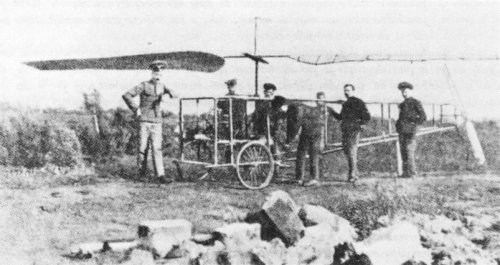
With the assistance of the Ledentoov firm, Yuriev built his prototype in 1912. He had planned for a variable pitch mechanism to be installed, but then changed his mind to gain weight. The machine weighed 445 pounds. The only known photo of the machine does not show the pilot's cabin. It was the first helicopter in the world with a single main rotor and an anti-torque tail rotor.
The helicopter was part of the ground exhibit at the 1912 Aeronautics and Automobile International Exposition in Moscow and earned Yuriev a gold medal. But during the static test phase, the rotor's axle broke. By lack of funding, Yuriev had to abandon his machine; the advent of the first World War and then the Soviet revolution put an end to all research in the field of helicopters.
According to Soviet author David Gai, the first helicopter to be built in the world was the 1912 Yuriev. However, that machine never flew. Here is what Eugene K. Liberatore, a historian of Russian aircraft, has to say about it:
Yuriev's helicopter activities began in 1909. During that year, he proposed a design for a machine with two coaxial rotors. A 70 hp rotary Gnôme engine was fitted in the upper part of the fuselage, driving two rotors of different diameters: 9.7 m for the upper one and 3 m for the lower one. The machine featured a directional propeller with variable pitch for yaw control. It was fitted with wheels for rolling take-offs, and a parachute was planned in case of engine failure. It weighed 694 pounds.
At the end of 1909, Yuriev drew a second version. He had estimated the necessary take-off power to be 50 hp, but the absence of such an engine at his disposal prevented him from building that machine. However, a 25-30 hp Anzani engine was available at the Moscow Aero-Club. Yuriev designed a helicopter around that engine, with a two-blade main rotor (with a diameter of 8.6 m) and a tail rotor motioned by a strap.
With the assistance of the Ledentoov firm, Yuriev built his prototype in 1912. He had planned for a variable pitch mechanism to be installed, but then changed his mind to gain weight. The machine weighed 445 pounds. The only known photo of the machine does not show the pilot's cabin. It was the first helicopter in the world with a single main rotor and an anti-torque tail rotor.
The helicopter was part of the ground exhibit at the 1912 Aeronautics and Automobile International Exposition in Moscow and earned Yuriev a gold medal. But during the static test phase, the rotor's axle broke. By lack of funding, Yuriev had to abandon his machine; the advent of the first World War and then the Soviet revolution put an end to all research in the field of helicopters.
Attachments
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
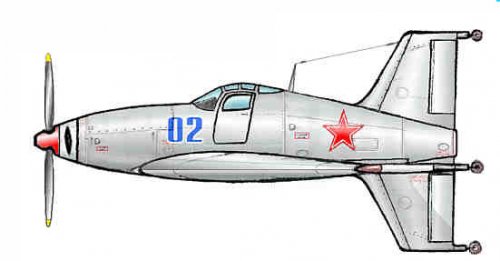
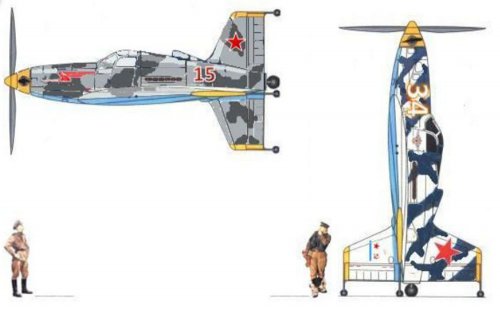
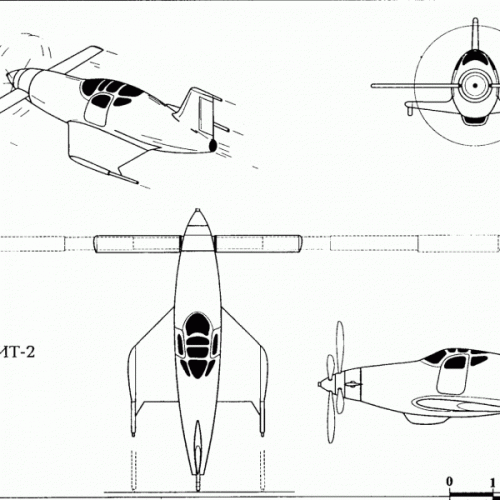
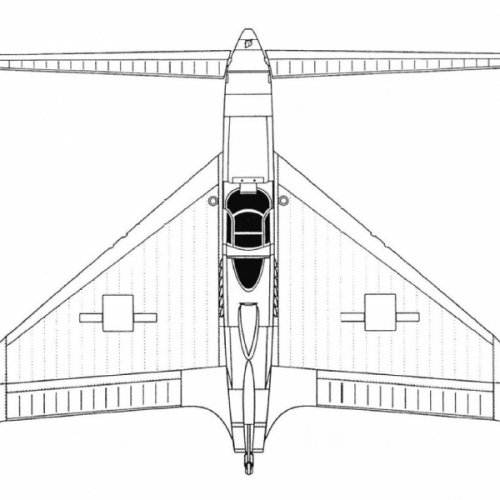
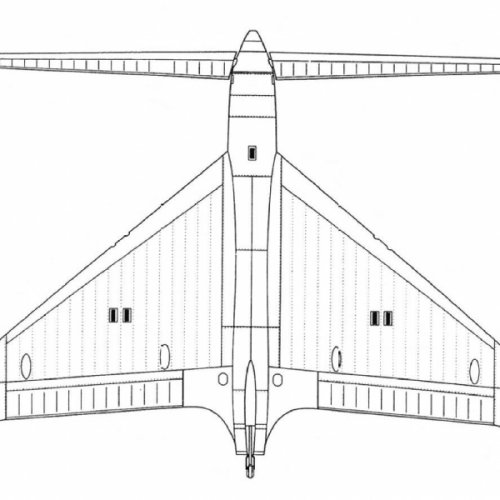
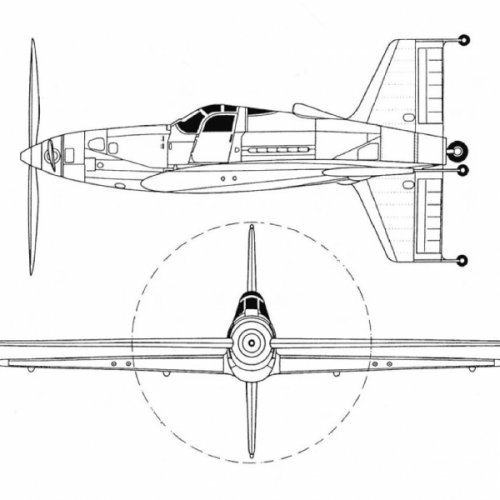
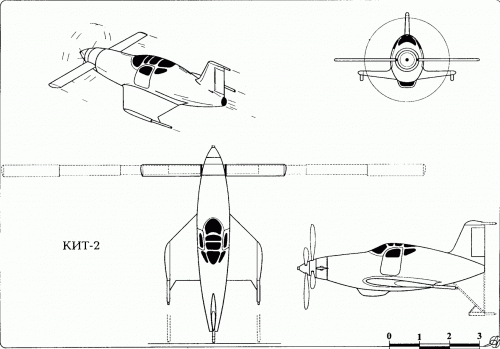
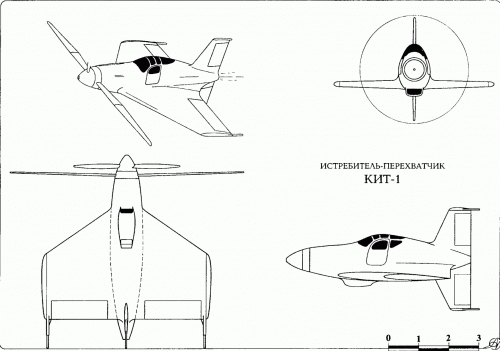
Hi! KIT-1 KIT-2. Yuriev, Kurochkin, Tyrone. Soviet VTOL aircraft. USSR, 1946
http://translate.google.fr/translate?hl=fr&sl=ru&tl=en&u=http%3A%2F%2Falternathistory.com%2Fkit-1-i-kit-2-yurev-kurochkin-tiron-sovetskie-svvp-sssr-1946-g%3Fmini%3Dcalendar%25252F2015-10&sandbox=1
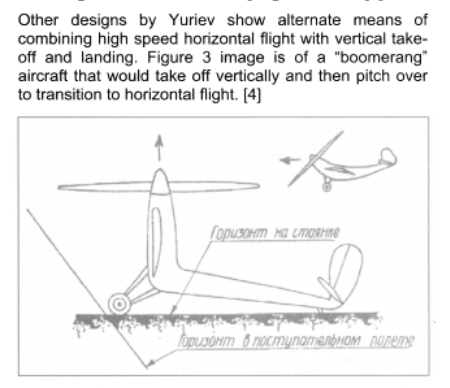
”In 1946-1947. under the leadership of BN Yuriev in VVIA engineers FP and Kurochkin VN Tiron has developed a number of projects fighters SVVP- with coaxial propellers and vertical position of the fuselage, features original layout and high design properties. According to the plan of aircraft, this machine was to have two propellers. With more who played the role of the main rotor, CIT-1 was raised "in the helicopter." At a height of 60-70 meters, he shifted to horizontal flight, and the rotor was fixed parallel to the wings. Before planting, KIT-1 took a vertical position, the rotor is spun again, and the machine gently landed on its tail.In 1946, a group of engineers, working under the leadership of BN St. George, completed the design of KIT-1 experimental aircraft. The machine has been designed on the basis of the fuselage lend-lease fighter P-63 "Cobra". The project is an experimental single KIT-1 aircraft (USSR, 1946).
Engine VK-108 - 1750 hp, The diameter of the rotor - 8 m, the diameter of the pull screws - 3.6 m., Wingspan - 3 m.
Estimated top speed - 800 nm / h., The estimated duration of the flight - 1 hour 30 minutes.
In parallel, another option designed VTOL KIT-2. In which a large screw telescopic rises after takeoff and was going to shrink in size.
Unfortunately, due to the post-war reorganization of the aviation industry, these long-term projects were not brought to the construction of prototypes. The aircraft had been diverted to the creation of conventional aircraft necessary to the national economy, and they were not able to complete the work on the car and its two modifications. ”
Larger image sourse.
http://xn--80aafy5bs.xn--p1ai/aviamuseum/aviatsiya/sssr/eksperimentalnye-samolety/proekt-eksperimentalnogo-letatelnogo-apparata-kit-1/
http://translate.google.fr/translate?hl=fr&sl=ru&tl=en&u=http%3A%2F%2Falternathistory.com%2Fkit-1-i-kit-2-yurev-kurochkin-tiron-sovetskie-svvp-sssr-1946-g%3Fmini%3Dcalendar%25252F2015-10&sandbox=1
”In 1946-1947. under the leadership of BN Yuriev in VVIA engineers FP and Kurochkin VN Tiron has developed a number of projects fighters SVVP- with coaxial propellers and vertical position of the fuselage, features original layout and high design properties. According to the plan of aircraft, this machine was to have two propellers. With more who played the role of the main rotor, CIT-1 was raised "in the helicopter." At a height of 60-70 meters, he shifted to horizontal flight, and the rotor was fixed parallel to the wings. Before planting, KIT-1 took a vertical position, the rotor is spun again, and the machine gently landed on its tail.In 1946, a group of engineers, working under the leadership of BN St. George, completed the design of KIT-1 experimental aircraft. The machine has been designed on the basis of the fuselage lend-lease fighter P-63 "Cobra". The project is an experimental single KIT-1 aircraft (USSR, 1946).
Engine VK-108 - 1750 hp, The diameter of the rotor - 8 m, the diameter of the pull screws - 3.6 m., Wingspan - 3 m.
Estimated top speed - 800 nm / h., The estimated duration of the flight - 1 hour 30 minutes.
In parallel, another option designed VTOL KIT-2. In which a large screw telescopic rises after takeoff and was going to shrink in size.
Unfortunately, due to the post-war reorganization of the aviation industry, these long-term projects were not brought to the construction of prototypes. The aircraft had been diverted to the creation of conventional aircraft necessary to the national economy, and they were not able to complete the work on the car and its two modifications. ”
Larger image sourse.
http://xn--80aafy5bs.xn--p1ai/aviamuseum/aviatsiya/sssr/eksperimentalnye-samolety/proekt-eksperimentalnogo-letatelnogo-apparata-kit-1/
Attachments
-
 KIT.jpg55.9 KB · Views: 120
KIT.jpg55.9 KB · Views: 120 -
 KIT-2_-Shema_-600x600.gif55.5 KB · Views: 97
KIT-2_-Shema_-600x600.gif55.5 KB · Views: 97 -
 KIT-1_-Shema-3_-600x600.jpg164.2 KB · Views: 88
KIT-1_-Shema-3_-600x600.jpg164.2 KB · Views: 88 -
 KIT-1_-Shema-2_-600x600.jpg164.7 KB · Views: 105
KIT-1_-Shema-2_-600x600.jpg164.7 KB · Views: 105 -
 KIT-1_-Shema-1_-600x600.jpg147.4 KB · Views: 114
KIT-1_-Shema-1_-600x600.jpg147.4 KB · Views: 114 -
 16-2-500x349.gif32.9 KB · Views: 105
16-2-500x349.gif32.9 KB · Views: 105 -
 16-1-500x351.gif31.9 KB · Views: 104
16-1-500x351.gif31.9 KB · Views: 104 -
 15-2-500x351.gif33.7 KB · Views: 122
15-2-500x351.gif33.7 KB · Views: 122 -
 %20КИТ-1%20СВВП-500x287.jpg15.8 KB · Views: 130
%20КИТ-1%20СВВП-500x287.jpg15.8 KB · Views: 130
avion ancien
The accidental peasant!
- Joined
- 6 March 2013
- Messages
- 371
- Reaction score
- 253
Is the chap on the right of the discoplane dancing the Latin Hustle? 
avion ancien
The accidental peasant!
- Joined
- 6 March 2013
- Messages
- 371
- Reaction score
- 253
..... and maybe John Travolta can be persuaded to trade in his 707 for a discoplane B)
windswords
ACCESS: Secret
- Joined
- 19 May 2009
- Messages
- 389
- Reaction score
- 217
Does anyone else see the fuselage entry door of the Bell P-39 Airacobra in the KIT design? The Soviet pilots were quite fond of the P-39 and achieved good results with it.
- Joined
- 6 November 2010
- Messages
- 5,262
- Reaction score
- 5,514
windswords said:Does anyone else see the fuselage entry door of the Bell P-39 Airacobra in the KIT design? The Soviet pilots were quite fond of the P-39 and achieved good results with it.
The P-63 was a development of the P-39, with a similar cockpit.blackkite said:The machine has been designed on the basis of the fuselage lend-lease fighter P-63 "Cobra".
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,901
- Reaction score
- 15,761
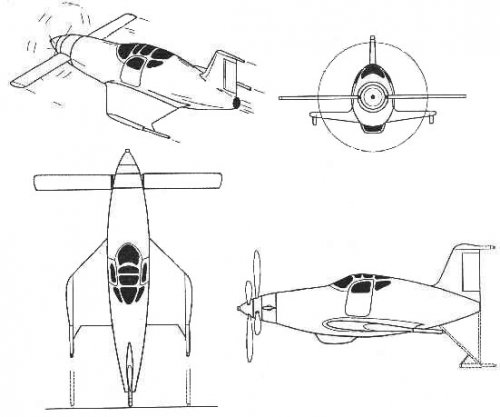
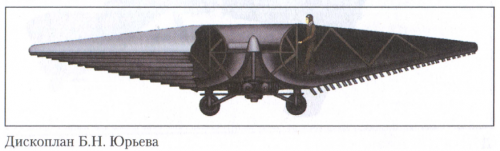
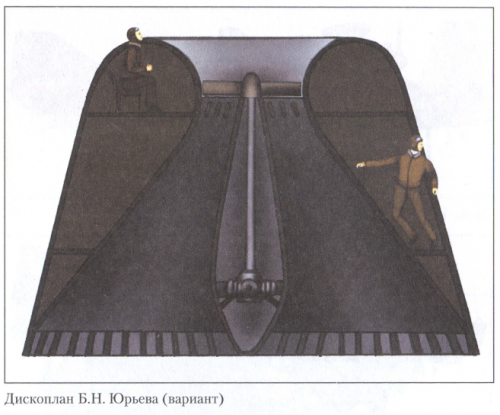
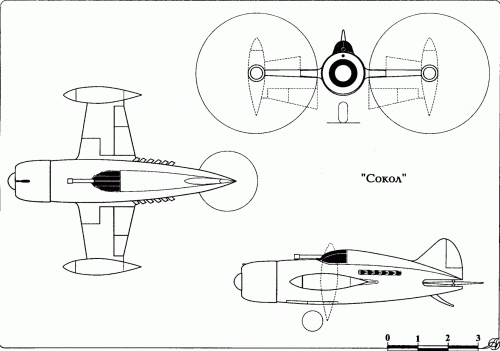
hesham said:The Yuriev Discoplane.
As we spoke about this concept,there was anther design for Yuriev called Disc Helicopter,I don't
know what the connection between them.
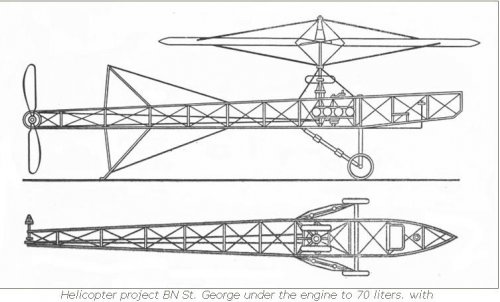
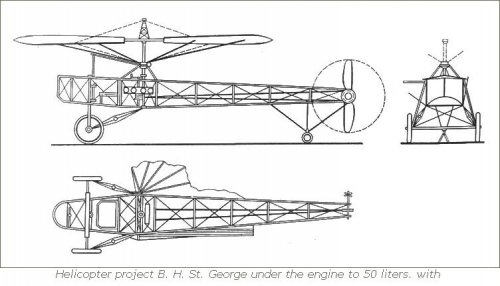
Disc Helicopter BN St. George's
In 1921, Mr .. B.N. Yuryev for the first time in the world proposed a principled
Scheme helicopter with a disk-shaped body. Known
Schemes of its two devices, which were axially symmetric
Bodies with an internal arrangement along the vertical
The axes of engines and propellers, which sucked in air
Through the air intake located on the axis from above and
Together with the engine exhaust, they threw it down under the machine,
Creating a jet stream beneath it. Inside the case was located
Compartment for the crew. Of course, the available at that time
Low-power aircraft engines were able to create
Only air cushion under the device. In our country
Apparatus of such a scheme on the eve and during the war were considered
Exotic, so work in the field of creating disc-like
Devices were not financed.
A completely different picture was observed in Germany at the end
30's - early 40's, where the idea of creating disc-like flying
The apparatus was initially picked up by individual enthusiasts,
And then work began in some firms. With the advent of
Germans of high-power piston engines, and then jet engines, began research work on the creation of vertically
Take-off aircraft disc-like
Forms - disk gyroplanes and disk helicopters (with an external
Or internal rotor arrangement), which were assumed
To use as stormtroopers. All these works
Were conducted in conditions of the strictest secrecy.
Attachments
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,901
- Reaction score
- 15,761
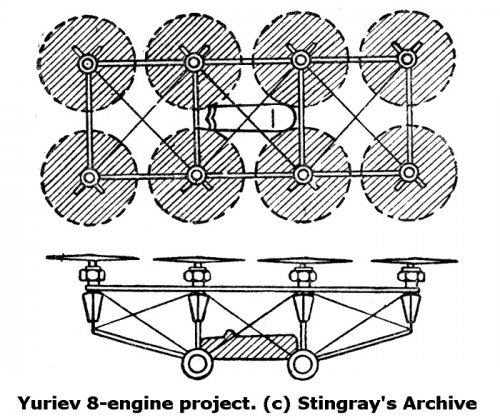
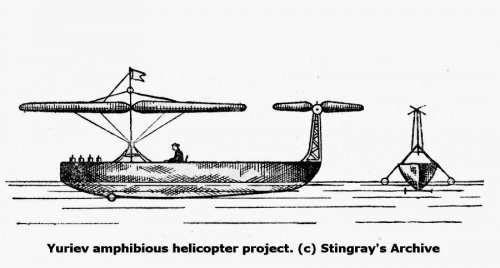
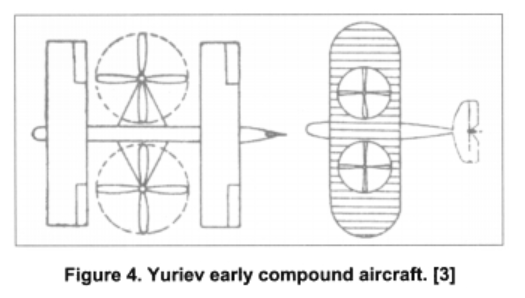
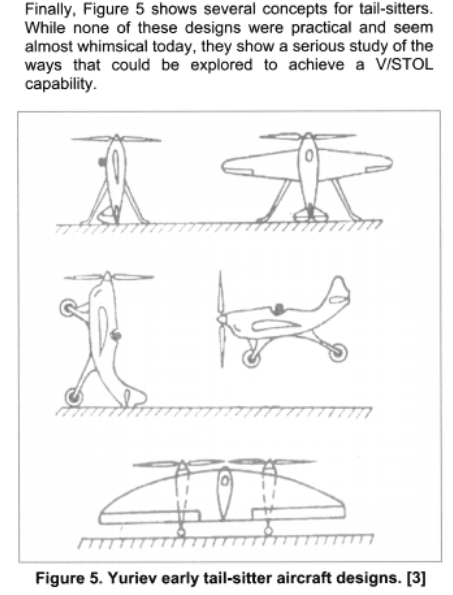
Here is some Yuriev concepts.
 www.jstor.org
www.jstor.org
Soviet Propeller V/STOL Concepts of the 20th Century on JSTOR
Since the advent of the helicopter, aviation designers have struggled to develop a practical vertical lift propulsion concept that could combine the vertical ta...
Attachments
- Joined
- 11 March 2012
- Messages
- 3,249
- Reaction score
- 3,179
Hi! KIT-1 KIT-2. Yuriev, Kurochkin, Tyrone. Soviet VTOL aircraft. USSR, 1946

КИТ-1 и КИТ-2. Юрьев, Курочкин, Тирон. Советские СВВП. СССР, 1946 г. - Альтернативная История
КИТ-1 и КИТ-2. Юрьев, Курочкин, Тирон. Советские СВВП. СССР, 1946 г. - Альтернативная Историяtranslate.google.fr
”In 1946-1947. under the leadership of BN Yuriev in VVIA engineers FP and Kurochkin VN Tiron has developed a number of projects fighters SVVP- with coaxial propellers and vertical position of the fuselage, features original layout and high design properties. According to the plan of aircraft, this machine was to have two propellers. With more who played the role of the main rotor, CIT-1 was raised "in the helicopter." At a height of 60-70 meters, he shifted to horizontal flight, and the rotor was fixed parallel to the wings. Before planting, KIT-1 took a vertical position, the rotor is spun again, and the machine gently landed on its tail.In 1946, a group of engineers, working under the leadership of BN St. George, completed the design of KIT-1 experimental aircraft. The machine has been designed on the basis of the fuselage lend-lease fighter P-63 "Cobra". The project is an experimental single KIT-1 aircraft (USSR, 1946).
Engine VK-108 - 1750 hp, The diameter of the rotor - 8 m, the diameter of the pull screws - 3.6 m., Wingspan - 3 m.
Estimated top speed - 800 nm / h., The estimated duration of the flight - 1 hour 30 minutes.
In parallel, another option designed VTOL KIT-2. In which a large screw telescopic rises after takeoff and was going to shrink in size.
Unfortunately, due to the post-war reorganization of the aviation industry, these long-term projects were not brought to the construction of prototypes. The aircraft had been diverted to the creation of conventional aircraft necessary to the national economy, and they were not able to complete the work on the car and its two modifications. ”
Larger image sourse.

Проект экспериментального летательного аппарата КИТ-1. - Российская авиация
Проект экспериментального летательного аппарата КИТ-1. :: Проект экспериментального летательного аппарата КИТ-1. Разработчик: Б.Н.Юрьев, Ф.П.Курочкин, В.Н.Тирон. Страна: СССР Проект 1946 г. В 1946-1947 годах подxn--80aafy5bs.xn--p1ai
So that's what the Russians did with all those Bell P-39 Airacobras rejected by the USAF.
Hah!
Hah!
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,901
- Reaction score
- 15,761
Hi,
 poletomania.ru
poletomania.ru
Самый первый вертолет в мире: когда появился и кто его придумал (изобретатель), история создания и развития, дата появления, в каком году и что за страна впервые изобрела летательный аппарат
Кто придумал вертолет: самые первые создатели и изобретатели в вертолетостроении, история создания и развития. В каком году были изобретены и появились вертолеты в мире — дата.
Attachments
Similar threads
-
-
-
-
Messerschmitt Courier (turbojet fighter project)
- Started by kiradog
- Replies: 8
-