- Joined
- 3 June 2006
- Messages
- 3,094
- Reaction score
- 3,963
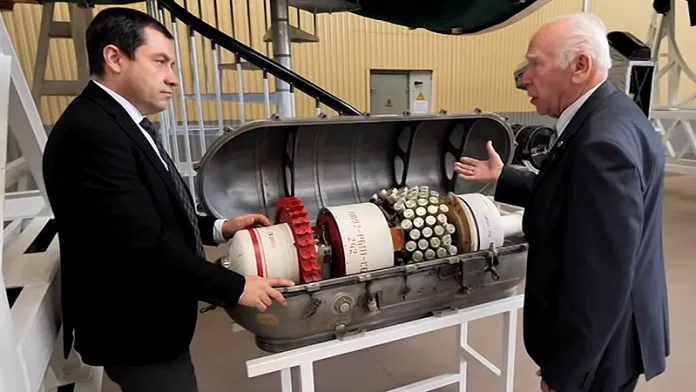
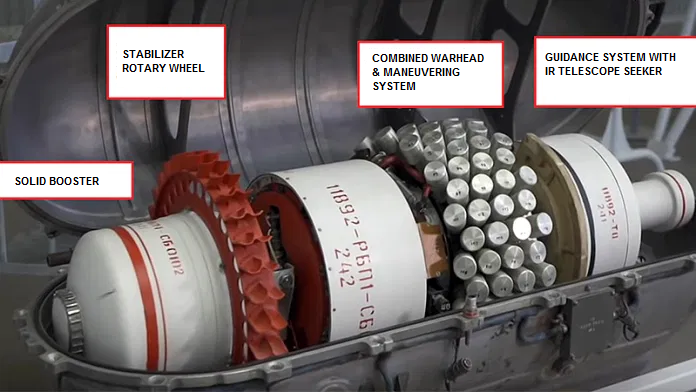
The Russian military has finally revealed the rocket-propelled grenade weapon system developed for the Almaz space station project in the 1970s.
Links:


View: https://youtu.be/0nIWMhOIK0g
See from ca.18 min onwards.
Yes, I know, that the Russian TV moderator is unpopular.
Source:

 www.thedrive.com
Dear members or mods,
www.thedrive.com
Dear members or mods,
if this post is in the false topic, please let me know, so I can delete or move this post to a more suitable topic.
Links:
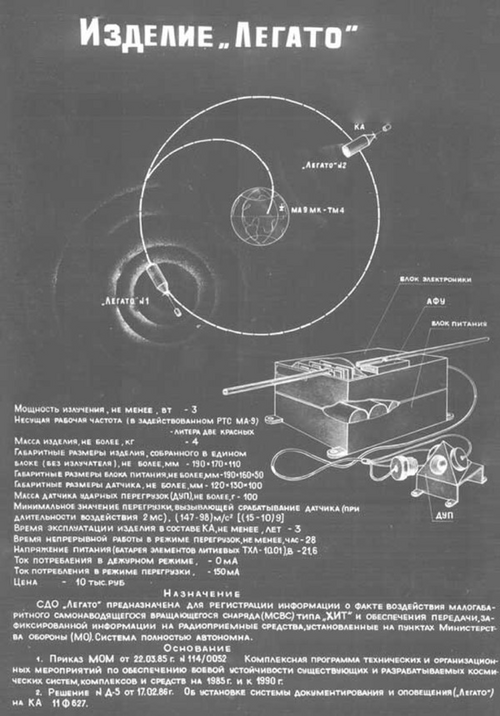
Soviet space rocket-propelled grenade revealed
Shield-2 anti-satellite missile | Story by Anatoly Zak | Editor: Alain Chabot
www.russianspaceweb.com
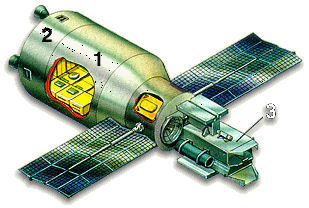
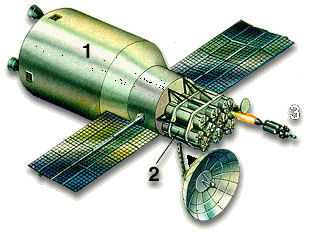
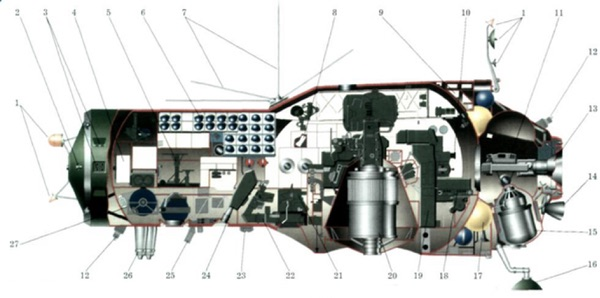
Salyut-3 (OPS-2) space station
The history of the Salyut-3 space station by Anatoly Zak
www.russianspaceweb.com
See from ca.18 min onwards.
Yes, I know, that the Russian TV moderator is unpopular.
Source:

This Is Our First Ever Look At A Top Secret Soviet Space 'Missile'
The Shchit-2 was a missile-like system designed to protect Soviet military space stations from attack.
if this post is in the false topic, please let me know, so I can delete or move this post to a more suitable topic.
Last edited: