A very interesting discovery.
I have always suspected that Type 985 was separate from the the NSR proposed for NIGS and I think this proves it.
Whatever system GW59 was designed around in 1955 could be considered as the first step on the path to NIGS. It has several similar features;
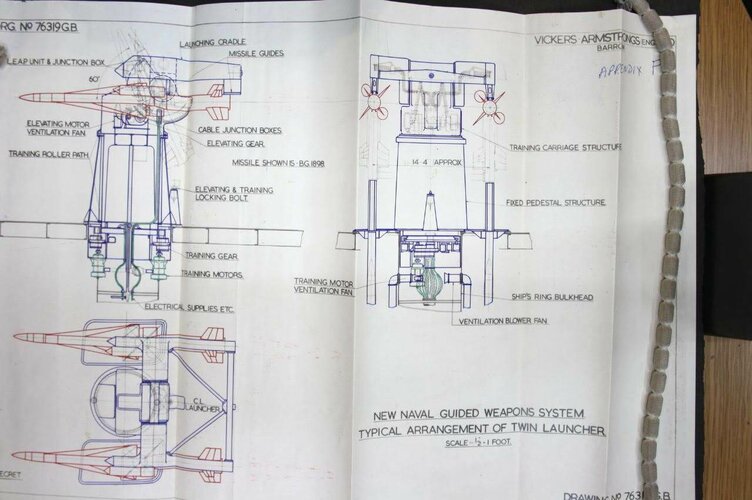
Multiple single-arm launchers - the Admiralty/ Ministry of Aviation Working Party in 1959 felt that single-arm launchers the right solution and they even discussed having separate high-angle and low-angle launchers, presumably to save power requirements for rapid elevation etc. How this would work in practice I'm not sure without a highly complicated magazine arrangement.
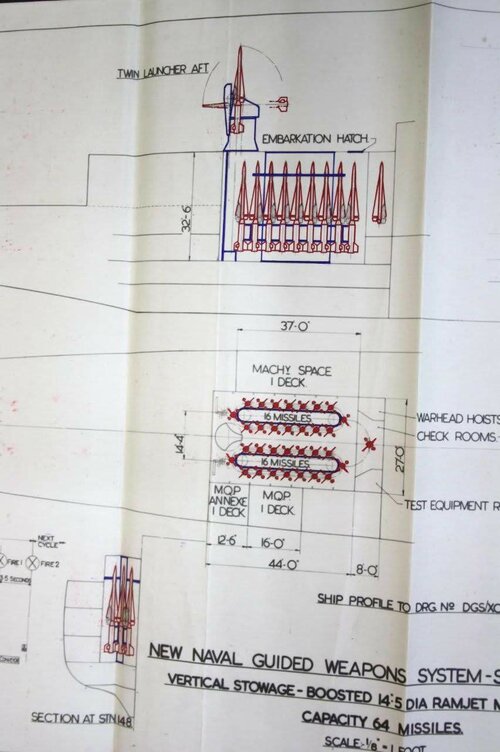
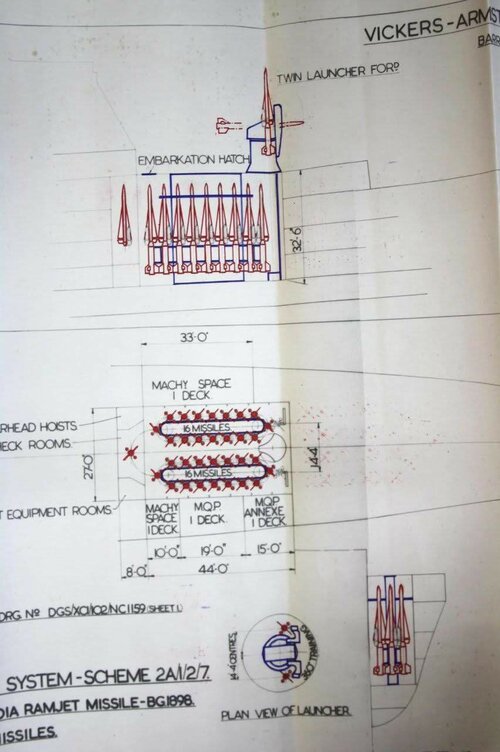
Sea Slug - GW59 only has 28 missiles (3.5 per launcher!) but the missiles seem to be Sea Slug as no other name is provided only non-Sea Slug missiles seemed to be named.
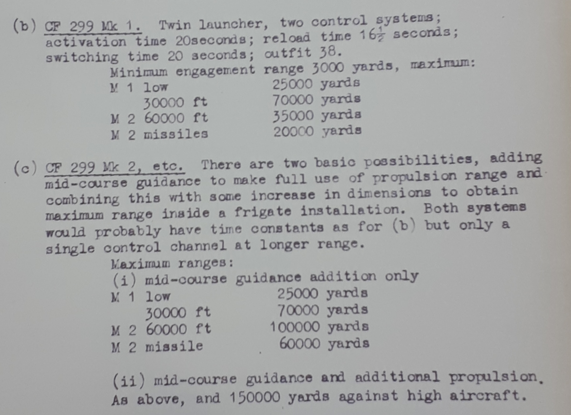
Type 985 - is a search and tracking radar, presumably one radar, sounds very similar in concept to NSR but must have been more than a speculative project in June 1955 as it was assigned a Type number. Two things stand out, the equipment weight for the ship is only 740 tons, some 300 tons lighter than the other GW designs around it and it needs a Type 992 target indication radar. So whatever the Type 985 is, its not a totally standalone system and its not very big. Maybe the Type 985 really is just a digital 984 with guidance added in?
Tonnage - interestingly GW59 is 10,500 tons and yet NIGS was meant to fit on a 6,000 ton hull, this indicates either more miniaturisation of the radar and missile for NIGS or wishful thinking in 1959! But at 540ft long, GW59 is almost County sized.
The other GW ships are interesting too;
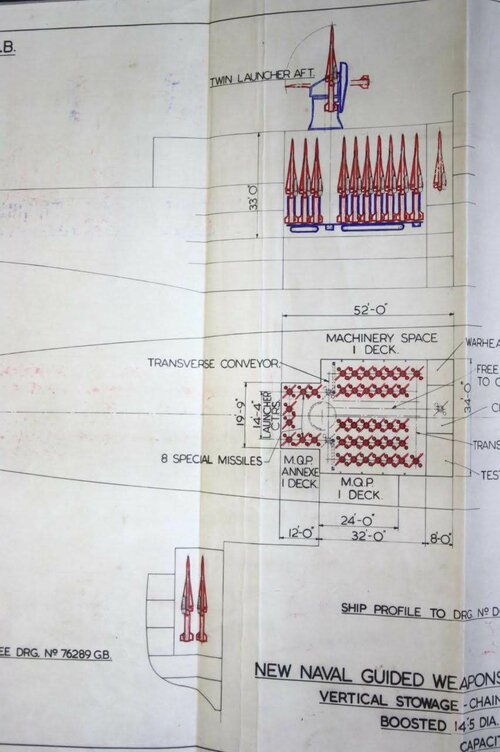
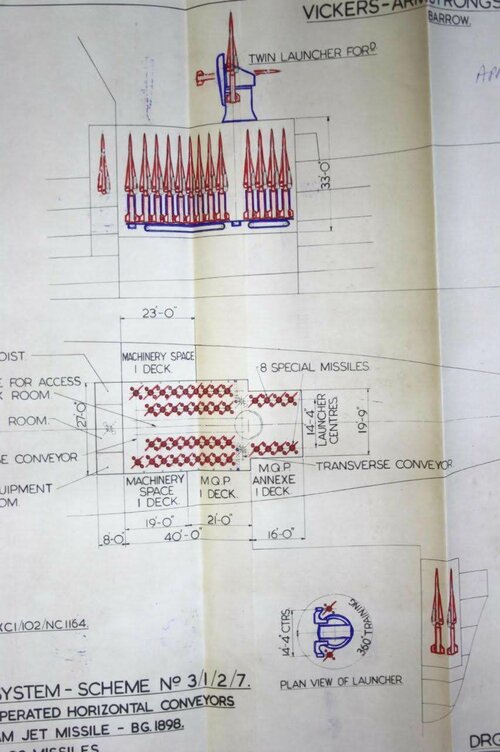
GW61 to GW 63 have the mysterious 8 launchers for 32 "R.F." missiles, 1x Trackwell radar. What is interesting is that both ships are far larger than GW59 at 15,000-16,000 tons and 610-640ft long (County was 520ft). No other radar is specified at all, not even a basic Type 974 for navigation. I find this somewhat odd as all the other designs have other radar sensors listed.
Whatever Trackwell is it must be powerful, note that Type 985 on GW985 may be a search/track radar but still needs a Type 992Q for targeting info. Trackwell seems to be able to operate without it. If this is a track/scan radar then it predates the AN/SPG-59 by at least 3 years so cutting edge indeed. At 1,090 tons equipment weight for all 3 GW designs, it seems Trackwell is a large and heavy piece of kit contributing to the weight.
GW70 to GW78 all have the Bristol 1 3/4. Nearly all have 6x T.I.A., 7 of the ships have a dedicated telemetry link, 6 of the ships have a Beacon and oddly GW 72 and GW73 only have the beacon and no T.I.A.! Regardless of the gun armament options, all of these are big and heavy ships of cruiser size.
My money is on the R.F. and Trackwell being a proto-NIGS system, it looks a capable and heavy system and close to the things the 1959 working party were talking about. Whatever 985 is, it doesn't seem quite in the same league. NIGS seems to have followed the Bristol 1 3/4 system and added illuminators too.
My questions are:
Why was Type 985 not used on any other GW ship or with the R.F. missile system and was it really just linked to Sea Slug?
What is the R.F. missile?
What is Trackwell?
What is the T.I.A tracker?
Why where the Navy looking at essentially 3 different systems at the same time (Sea Slug with 985, R.F with Trackwell, Bristol Blue Envoy with 984 & TIAs)
To answer Tzoli's question;
NIGS = New Naval Guided Weapons System