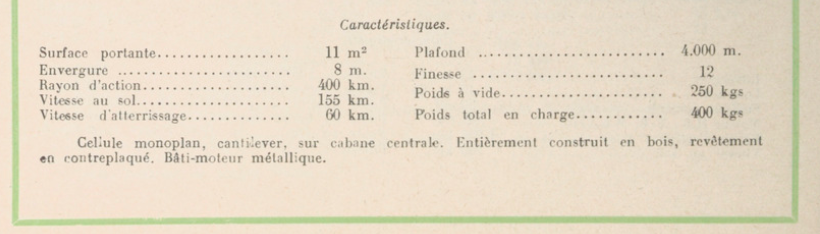
The Guerchais-Henriot T.2 was entered in the economical aeroplane contest at Orly in August 1928.
The goal of the contest was to encourage the demonstration of practical aircraft, preferably two-seaters, comfortable and capable of carrying 15-kg mail bags over 400 km non-stop, and to climb up to 1,500 m in 30 minutes with full load. No limitation was placed on engine power, but empty weight was limited at 400 kg.
Evaluation was based on a series of technical tests, which included an altitude test, a take-off and landing test, a disassembly/reassembly test, and a speed test. The qualities of takeoff, climb, seating arrangement, fireproofing, wood or metal covering of wings, assembly/disassembly, automatic engine start, dual controls, protection against rollover, visibility, comfort, protection against noise, etc., all added up to increase the aircraft's mark.
A final and decisive efficiency test consisted in a 400-kilometer closed circuit.
Once this series of tests was over, the remaining contenders had to run a series of daily 250- to 400-km legs in a 2,200-km aerial Tour de France.
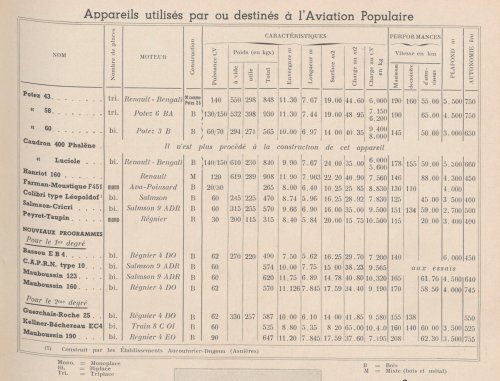
25 types were initially entered (though 25th aircraft is unaccounted for):
- 15 French aircraft: Caudron (6), Albert (4), Guerchais (1), Mauboussin (1), Leduc (1), Nessler (1), Peyret (1).
- 3 German aircraft: Klemm (2), Baumer Aero (1).
- 6 English aircraft: C.L.A. 4 (1), Avro Avian (3), De Havilland Moth (2).
10 aircraft were eventually retained:
- N°1: Caudron with 40 hp Salmson engine.
- N°3: Caudron with 60 hp Salmson engine.
- N°4: Caudron with 60 hp Salmson engine.
- N°6: Caudron with 60 hp Anzani engine.
- N°9: Klemm with 40 hp Salmson engine.
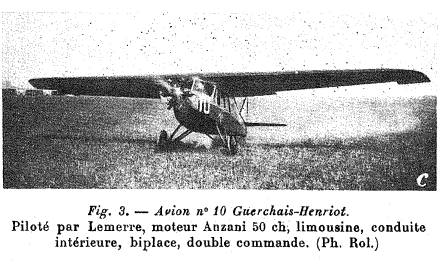
- N°10: Guerchais with 50 hp Anzani engine.
- N°14: Albert with 40 hp Salmson engine.
- N°18: Avro Avian with 85 hp Cirrus engine.
- N°20: De Havilland Moth with 85 hp Gipsy engine.
- N°25: Avro Avian with 85 hp Cirrus engine.
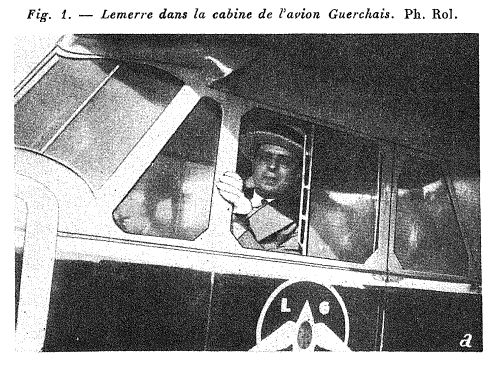
The Guerchais T.2 was a small two-seat "limousine" cabin type with dual controls, piloted by Lemerre, who aimed to prove that flying was a sport like any other andmade a point of performing his Tour de France wearing a straw hat and light gloves. It finished the contest in sixth position, behind a Caudron but ahead of an Albert and the other two Caudrons that were running.
Also see: http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php/topic,12382.0