- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,407
From Aviatsiya i Kosmonautika Dec 2017
Fighter-Interceptor on the basis of the aircraft T-58M
On January 24, 1961, the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR Establish and manage a new business aircraft of the USSR Armed Forces and bomber-bomber to Su-7B, as well as "... ordered GKAT, GKRE and GKKT for further expansion of combat capabilities fighter-bombers to ensure the creation of a TTM MO USSR, coordinated with performers, navigation-aiming system and necessary modernization work Su-7B, ... " with presentation prototype modified Su-7B for joint trials in IV quarter of 1962. In the first half of the year 1962 OKB-51 together with the developers Calculation and theoretical work and coordination all elements of navigation and sighting
system (NPS) "Puma" on the modified airplane Su-7B (factory S-28).
In the 111th quarter of the design work aircraft were suspended due to lack of necessary technical characteristics new developers of the system (NII-131, NII-33 and others).
In connection with the disruption of the development time The new NPS in the USSR Council of Ministers sent a draft The decision to postpone the 11th system for 1964. At the same time, preliminary data on the structure of Puma and its functional system, a significant increase dimensions and weight (by 1200-1300 kg) with the system new deep modification of the aircraft Su-7B (factory cipher S-6).
During 1963 OKB-51 conducted theoretical and theoretical and experimental work of choice optimal design parameters. In June 1963, OKB-51 received preliminary TTT on the S-6 and jointly with the Air Force prepared a draft resolution government to establish fighter-attack aircraft S-6 with two turbojets R21F-300 (Р = 7200kgf) and NPS "Puma-6". In the second half of 1963, sketch project and built mockup S-6.
The development of aircraft systems caused The need to create a number of new products, which, due to the lack of government decrees organizations have not been accepted for development, which in turn hindered the project ктно-конструкторские work. The Air Force Commission, which reviewed the draft project and the C-6 model, put forward more high TTT to the aircraft, which led to processing theoretical and layout drawings.
In connection with the additional requirements USSR Ministry of Defense for shortening the takeoff anf landing run length, in 1964, OKB-51 launched to develop a preliminary new project of a fundamentally new fighter-attack aircraft T-58M with four additional engines RD-36-35 and the NPS "Puma". Similar task OKB-155 was assigned.
October 27, 1964 a meeting was held The Presidium of the NTS GKAT USSR, which representatives of OKB-51 and OKB-155 reported about elaboration:
- fighter aircraft - ground-attack aircraft
T-58 with two main engines R27F-300 and four lift engines RD-36-35, with a take-off weight of 22-23 tons, maximum speed of flight at the ground, equal to 1350-1400 km / h and equipped with PNS Puma;
- fighter aircraft attack aircraft E-155 with two VD-19 and wing variable geometry, with take-off mass 31-32 t, maximum speed flight near the earth, equal to 1350-1400 km / h
and equipped with the Puma
and an intermediate version of this aircraft S-28 (modified Su-7B) with a fixed wing and four additional engines RD-36-35.
NTS approved the plants in the OKB №51 and №155 study projects fighter-attack aircraft and instructed Commission composed of members of the STRP, prepare a draft resolution of the Central Committee
The CPSU and the USSR Council of Ministers on the development of the plant No. 51 on the basis of the T-58 aircraft, and Plant №155 - the project on the basis of the aircraft E-155 with a wing of variable geometry.
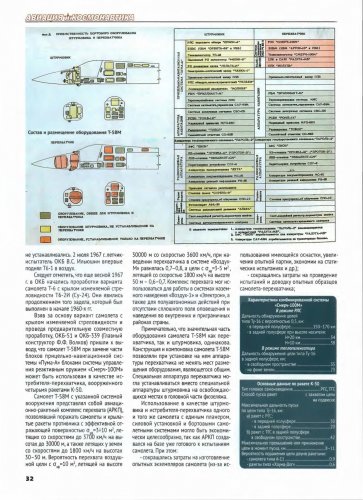
In the early stages of design It was assumed that the new machine that received code T-58M, will have a layout scheme, wing and tail of an airplane Su-15. However, as the layout is developed it became obvious that the mass-overall characteristics of "Pumas" do not fit into the dimension of the aircraft Su-15. Therefore, it was decided to the development of a new fuselage aircraft. The layout of this option was completed autumn of 1964. Chief Designer of the aircraft was appointed E.S. Felsner.
August 24, 1965, the Central Committee of the CPSU and the Council of Ministers of the USSR adopted a decision establishing on the base of the fighter-interceptor Su-15 fighter-
T-58M attack aircraft, which was assigned the code T-6.
TTT VVS to T-58M were signed Chief Commander of the Air Force Chief Marshal of the air- A.K. Vershinin on February 14, 1966, The PTS provided for the aircraft with 2хАL-21F (Р = 8900 kgf) and 4х RD-36-35 (P = 2500 kgf).
In mid-March 1966, the draft The project and model of the T-6 aircraft was considered representatives of the Air Force. In the fall of 1966, pilot production began to build two copies
T6-0 and T6-1. In addition, three more copies it was planned to build on the NAZ.
By the time the construction of T6-1 the OKB team had not only the results design calculations and windtunnel models, but also the experience of flight tests additional power plant for
experimental airplane experimental airplane T-58VD. Such the plane was converted in 1965 from the experienced interceptor T-58-1. On him in the middle of the fuselage instead of the
fuel tanks were mounted three lifting engine RD-36-35. In July 1966 his flight tests began.
A year later, on July 9, 1967, after the completion factory flight tests, pilot-and the tester Ye.S. Soloviev demonstrated a car on an aircraft parade in Domodedovo.
Construction of the first prototype T6-1 was completed in late May 1967. Temporarily on the plane were installed TRD R-27F2-300, and lifting engines not installed. On July 2, 1967, the test pilot OKB VS Ilyushin for the first time lifted T6-1 into the air.
It should be noted that as early as the spring of 1967 The design bureau in the T-6 aircraft with variable sweep wing T6-2I (Cy-24). They appeared continued to be touched, which was executed in the early 1960's. Taking as a basis the warrant of the aircraft with wing variable sweep and by conducting a joint development, OKB-51 and OKB-339 (Main co-organizer F.F. Volkov) came to the conclusion, that the T-58M aircraft when replacing part blocks of sight-navigation sPuma-A themes with control system blocks by the reactive weapon "Smerch-100M" can be used as a fighter-interceptor, armed four K-50 missiles.
The T-58M with this system Arms was an aviation-missile interception complex (ARC), allowed to hit aircraft and winged missiles with an effective counter surface area a = 3 + 10 m2, flying with speeds up to 3700 km / h at altitudes up to 30000 m, as well as flying at the ground with speeds up to 1800 km / h at altitudes 30-50 m. Probability of taking the air goals with a PE = 10 m2 flying at altitude 30000 m at a speed of 3600 km / h, with the aim of interceptor in the system "Air" Was 0.7-0.8, and the goal with the OEF = 3-5 m2, flying at a speed of 1800 km / h at altitude 50 m - 0,6-0,7. The interception complex could be used for work in terrestrial systems guidance "Vozdukh-1" and "Electron", and also for semi-autonomous actions when There is no continuous warning field and guidance in internal and cross-border areas of the country.
It is noteworthy that a significant part equipment of the T-58M aircraft as an interceptor, and the stormtrooper, is the same. Design and layout of the T-58M aircraft allowed when installing on it equipment interceptor does not change placements equipment that is common. Special interceptor equipment could set instead of special equipment for storming the ikon liberated places in the head of the fuselage.
Use as a stormtrooper and fighter-interceptor ka one and the same plane with a single glider, powerplant and airborne aircraft systems could be economically It is advisable, since the ARC was created on the basis of already ready for testing aircraft. Wherein:
- production costs were reduced
Experienced aircraft (due to time and cost of implementation decreased in batch production, in communication using the same equipment and unified technological process;
- the cost of production was cheaper aircraft by increasing the number of in the series;
- the cost of operation in connection with a reduction in the range of components products and facilities, on the supply in parts of the Air Force and Air defense;
- facilitated the development of the aircraft technical composition;
- the costs of training and training flight crew.
The ARCF consisted of:
a) a double fighter-interceptor T-58M with variable geometry wing with two engines R-27F2 -300;
b) Combined infra-red and radar control system weapon "Smerch-100M", consisting of:
- radar of quasicontinuous radiation;
thermal direction finder;
The Argon-10 computer;
- and n the combined television indusition of the system and on a high-level automatized basis monitoring;
c) missile control system weapons, consisting of K-50 missiles CSG and TGS. Also could be used guided missiles with TGS - R-8, R-8M1, P-98, K-58, K-23 and K-13, the latter were suspended on special launch devices installed in place of launchers K-50 missile systems;
d) a system of cannon armament, which included a stationary bortagasya reserve. A swiftly deployed air cannon AO-19 caliber 23mm with the rate of fire 10000-12000 per RPM / min, with ammunition 500 patrons and an electric system control of shooting. It was envisaged the possibility of setting four guns AO-19 in each spring gondola with combat 400 rounds of ammunition per each gun, rockets and cannons were suspended on four underwing suspension nodes.
The powerplant of the aircraft consisted of two R-27F2-300 engines with static thrust of 9400 kg each. Fuel in amount of 11,500 liters was located in sealed tank-compartments in fuselage and wing.
Depending on the height and speed goal, the interceptor for the attack was supposed to be to gain a reference altitude: 14 - 20 km at interception of a high-altitude target or 8 - 10 km
when intercepting a low-altitude target. On The reference height was detected, Identification and capture of the radar target "With Smerch-100M", after which the team,
you work on board, interceptor you filled the top of a hill or sight and kirovanie, eliminating the errors of guidance In the mountains is an isontal and vertical calyx planes and then launched the racket.
The maximum margin for fuel supply interception in the afternoon in the SMU in the attack in The PPP was to be 900 km.