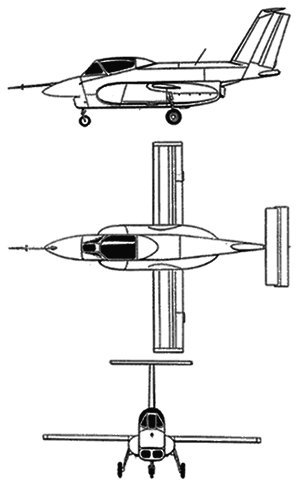
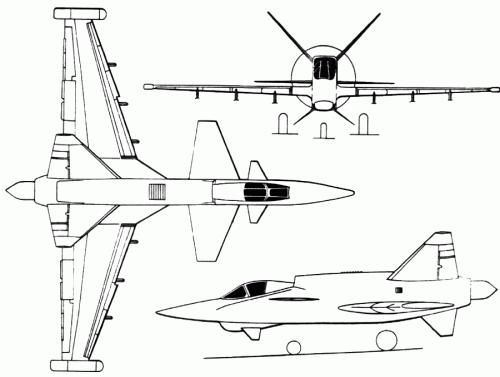
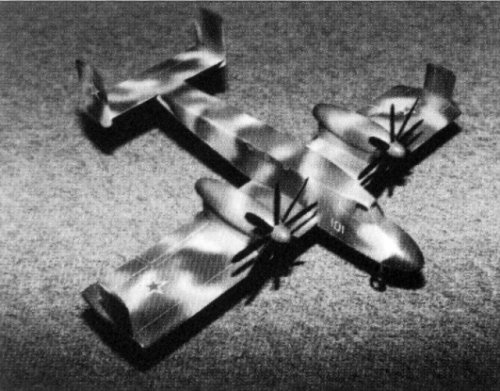
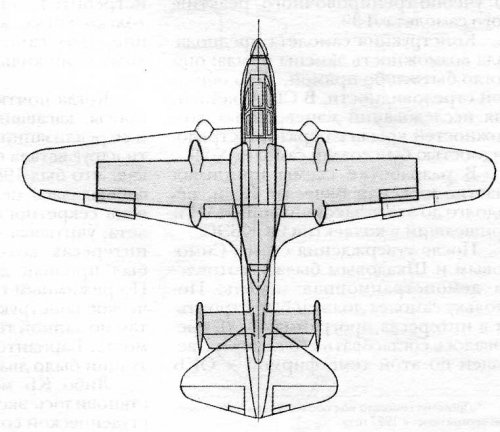
T-710 Anaconda
Crew: 2
Maximum TO Weight: 7,500 kg
Fuel Load: 1,500 kg
Cruise Speed: 720 km/h
Overland Speed: 580 km/h
Landing Distance: 500 m
Ceiling: 6,000 m
Radius of Action: 450 km with 1,000 kg load
G-limits: +5/-2.5
Engines: Two Klimov TV7-117M turboprops of 1,864 kW each
Weapons Load: 2,500 kg
Armament: Fixed gun, ASMs, guided and unguided bombs and rockets
The T-710 Anaconda was projected as an all-weather STOL strike aircraft for local conflicts, peacekeeping, FAC and transport duties. The airframe was similar to the OV-10 Bronco with tandem crew seating and twin tail booms. The cockpit was armoured with titanium and composites, the fuel tanks filled with polyurethane foam, and engine exhaust pipe nozzles mounted overwing to reduce IR signature. Triple redundant flight control system. Nine airborne troops could be accommodated in a cabin behind the cockpit, and freight could be carried on a ventral lifting platform.
T-720
Crew: 2
Normal TO Weight: 4,500 kg
Maximum Speed: 750 km/h
Maximum Range: 1,400 km
Engine: One RKBM TVD-1500 turboprop of 970 kW
Armament: Under fuselage gun pod, 8 x underwing pylons
The T-720 was projected as a lightweight combat aircraft with a six-blade pusher propeller.
(This is the 'Aeroprogress Shturmovik' in overscan's post above.)
T-730
Crew: 2
Normal TO Weight: 1,200 kg
Maximum Speed: 520 km/h
Maximum Range: 1,000 km
Engine: One Soyuz TVD-450 turboprop of 336 kW
The T-730 was projected as a very light attack aircraft and trainer. Side-by-side seating, stealth-like blended fuselage with chines, swept-forward wings, active canards, slab tailplane and twin fins. Six-blade pusher propeller.
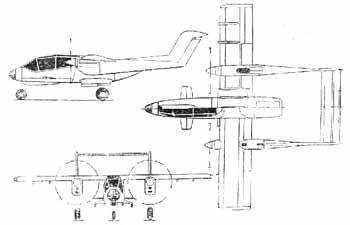
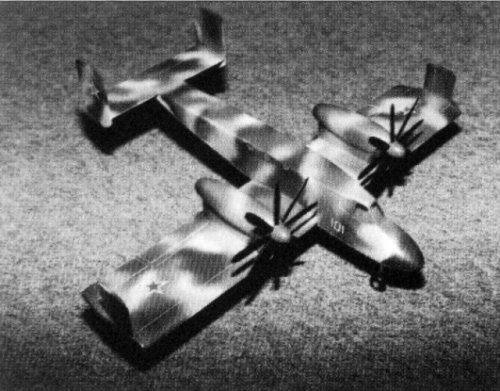
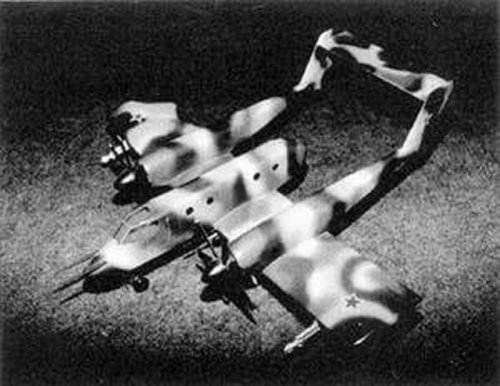
T-752 Shtyk
Crew: 2
Maximum TO Weight: 7,300 kg
Fuel Load: 1,500 kg
Maximum Speed: 740 km/h
Minimum Speed: 70 km/h
Landing Distance: 200 m
Ceiling: 6,000 m
Radius of Action: 400 km with 1,000 kg load
G-limits: +6/-3.5
Engines: Two Klimov TV7-117M2 turboprops of 1,864 kW each
Weapons Load: 2,000 kg
Armament: 12 x AAMs and ASMs, guided and unguided bombs and rockets
The T-752 was projected as an all-weather WIG strike aircraft for use in local conflicts and anti-helicopter/light aircraft missions. The tandem wing and V-tail configuration was to provide a high CG and minimum induced drag. Deflecting the high-lift devices during all flight regimes enabled effective balancing without rudders. The cockpit was armoured with titanium and composites, the fuel tanks filled with polyurethane foam, and engine exhaust pipe nozzles mounted overwing to reduce IR signature. Triple redundant flight control system. Five airborne troops or two litters with an attendant could be carried in a cargo compartment aft of the cockpit. Weapon aiming sensors mounted in the nosecone and on sidebody fairings.
Sources
- Brassey's World Aircraft & Systems Directory 1996/97













![Aeroprogress--ROKS-Aero T-710 [JAWA 1997-98 Seite 357].jpg](/data/attachments/16/16649-cdea51afc3ac040661c71f0cb52829a8.jpg)