You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Seversky/Republic AP series - AP-1 to AP-100
- Thread starter lark
- Start date
Googling-around for a research about Army Air Forces Very Long Range Escort Fighters I found these interesting documents:
http://www.wwiiaircraftperformance.org/p-47/p-47.html
confirming that
AP-16a was the P-47M
and AP-16b was the P-47N-5.
About that matter, I remain in doubt regarding the designations of previous main versions of Thunderbolt, as P-47B, P-47C and P-47D...
Nico
http://www.wwiiaircraftperformance.org/p-47/p-47.html
confirming that
AP-16a was the P-47M
and AP-16b was the P-47N-5.
About that matter, I remain in doubt regarding the designations of previous main versions of Thunderbolt, as P-47B, P-47C and P-47D...
Nico
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
Thanks Nico! Had the AP-16a but AP-16b is new to me.
The first THUNDERBOLT was the AP-10, so it is likely that the early razorback versions must have been AP-10a/b/c... while AP-16 was allocated to the bubble canopy versions. Just my two cents.
The first THUNDERBOLT was the AP-10, so it is likely that the early razorback versions must have been AP-10a/b/c... while AP-16 was allocated to the bubble canopy versions. Just my two cents.
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
Also an addition to the list:
AP-71 THUNDERCHIEF - RF-105B reconnaissance version.
Don't ask me where I found it, just realized I added it to my list a while ago, but surely it must have been from the web.
AP-71 THUNDERCHIEF - RF-105B reconnaissance version.
Don't ask me where I found it, just realized I added it to my list a while ago, but surely it must have been from the web.
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
Confirmation of AP-16B (note the capital letter):
http://www.alternatewars.com/SAC/F-47N_Thunderbolt_CS_-_17_May_1950_%28Yip%29.pdf
http://www.alternatewars.com/SAC/F-47N_Thunderbolt_CS_-_17_May_1950_%28Yip%29.pdf
I have long been seeking a designation of XF-12, but could not find. But I think that designation AP-41--original XF-12 designation not true. I think that this designation should be a modification. I think name of the XF-12 should be in the range of AP-25...27 or just another designation.
Will be interesting to your thoughts on this version and what can you say about my reasons ?
Will be interesting to your thoughts on this version and what can you say about my reasons ?
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
Drawing for AP-41 proposal is dated 15 Oct. 1947, if that's of any help.
I do agree that with the YOA-15 Seabee (an RC-3 derivative) being the AP-24, it would make sense that the RC-1 and RC-2 should carry earlier numbers.
AP-17 seems too early, AP-20 more likely, but I have no information to prove this at present time.
I do agree that with the YOA-15 Seabee (an RC-3 derivative) being the AP-24, it would make sense that the RC-1 and RC-2 should carry earlier numbers.
AP-17 seems too early, AP-20 more likely, but I have no information to prove this at present time.
Hi All!
My friend Stargazer2006, first draft of the YOA-15, submitted by the military at the end of 1944 or at the beginning of 1945, was soon the development of RC-1 than the RC-3. First flight of the RC-1---30 November 1944 and first flight of the RC-3---1 December 1945.
You can see more information about this in wikipedia: Republic RC-3 Seabee.
If XP-72(Model AP-19) development began in late 1941 and early 1942, the development of AP-20 began no earlier than 1942, and the launch of the XF-12 began in late 1943 to early 1944 (By the way at the same time work began the RC-1 Thunderbolt Amphibian).
I think that XF-12 should be or AP-20 or AP-25...or we have not known the designation.
But if these two planes began to develop around the same time that the factory should be marked with one after the other.
My friend Stargazer2006, first draft of the YOA-15, submitted by the military at the end of 1944 or at the beginning of 1945, was soon the development of RC-1 than the RC-3. First flight of the RC-1---30 November 1944 and first flight of the RC-3---1 December 1945.
You can see more information about this in wikipedia: Republic RC-3 Seabee.
If XP-72(Model AP-19) development began in late 1941 and early 1942, the development of AP-20 began no earlier than 1942, and the launch of the XF-12 began in late 1943 to early 1944 (By the way at the same time work began the RC-1 Thunderbolt Amphibian).
I think that XF-12 should be or AP-20 or AP-25...or we have not known the designation.
But if these two planes began to develop around the same time that the factory should be marked with one after the other.
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
nugo said:first draft of the YOA-15, submitted by the military at the end of 1944 or at the beginning of 1945, was soon the development of RC-1 than the RC-3. First flight of the RC-1---30 November 1944 and first flight of the RC-3---1 December 1945.
Thanks for the correction, nugo.
nugo said:If XP-72 (Model AP-19) development began in late 1941 and early 1942, the development of AP-20 began no earlier than 1942, and the launch of the XF-12 began in late 1943 to early 1944 (By the way at the same time work began the RC-1 Thunderbolt Amphibian).
I think that XF-12 should be or AP-20 or AP-25...or we have not known the designation.
But if these two planes began to develop around the same time that the factory should be marked with one after the other.
This makes a lot of sense. If we consider that RC-1 was designed before RC-2, then logically RC-1 could be #20 and RC-2 could be #25 or maybe #26.
But as I was writing these lines it dawned on me that they just couldn't be AP-... because the "A" signified "Army". So that's one possible reason why our search for "AP-20" and "AP-25" has been unsuccessful so far...
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
Ultimate online reference on the Seabee is http://www.seabee.info
According to the author, "The prototype [RC-1] had secretly been under development since January 1944," so it makes me wonder if AP-24 was not simply the sole designator for both the RC-1 and YOA-15...
And of course, let's not forget the possibility that the RC- list was created OUTSIDE the AP- list precisely to reflect the commercial status of the projects. In that case, there would be NO AP- type designator for them...
According to the author, "The prototype [RC-1] had secretly been under development since January 1944," so it makes me wonder if AP-24 was not simply the sole designator for both the RC-1 and YOA-15...
And of course, let's not forget the possibility that the RC- list was created OUTSIDE the AP- list precisely to reflect the commercial status of the projects. In that case, there would be NO AP- type designator for them...
AP-47 - mixed-power ground support airplane proposal:
http://retromechanix.com/article/fighters/republic-ap-47-mixed-power-ground-support-airplane-proposal-1948/
Regards
http://retromechanix.com/article/fighters/republic-ap-47-mixed-power-ground-support-airplane-proposal-1948/
Regards
Hi All!
more...
XF-12---Model AP-2? or ?, beginning of the development in late 1943 or early 1944.
JB-2-----Model AP-22 or AP-2?, beginning of the development/construction in the second half of 1944.
MX-773---Model AP-3? (or AP-2?), beginning of the development in late 1945 or early 1946.
AP-41---development of the XF-12 (4xR-4360 VDT (maybe)), beginning of the development in 1947.
Information from the past:
New additions for the Republic Projects list.
Model AP-22 - Drone (apparently a version of the V-1 flying bomb).
AP-24 - Amphibious aircraft with XO-425-7 Franklin air-cooled engines, 1945.
AP-38 - Cargo and Personnel Land-based Transport.
AP-41 - The original proposal for the XF-12 Rainbow, drawing dated 15.10.47.
My friend overscan, if you can say about the sources of the AP-22 and AP-38?
more...
XF-12---Model AP-2? or ?, beginning of the development in late 1943 or early 1944.
JB-2-----Model AP-22 or AP-2?, beginning of the development/construction in the second half of 1944.
MX-773---Model AP-3? (or AP-2?), beginning of the development in late 1945 or early 1946.
AP-41---development of the XF-12 (4xR-4360 VDT (maybe)), beginning of the development in 1947.
Information from the past:
New additions for the Republic Projects list.
Model AP-22 - Drone (apparently a version of the V-1 flying bomb).
AP-24 - Amphibious aircraft with XO-425-7 Franklin air-cooled engines, 1945.
AP-38 - Cargo and Personnel Land-based Transport.
AP-41 - The original proposal for the XF-12 Rainbow, drawing dated 15.10.47.
My friend overscan, if you can say about the sources of the AP-22 and AP-38?
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,421
Nugo, the source is research by the author Tony Buttler as stated.
Another archive mystery? This time from Republic Aviation.
Just came across a long lost July 1944 Republic Aviation file book of Organization Charts, and there was a loose note page tucked in. So the info MAY of MAY NOT be from Republic, and could have been placed in there, much later.
It SHOULD have been easy to track down the design because it had FIVE engines (two tractor props at the front of each outer pod, and two smaller Pusher prop engines at the trailing edge of each wing-outside of each of the two pods. Then it had a four blade pusher prop engine at the rear of the short center pod. The general layout being similar to a P-38 shape with the twin-boom and twin tail. and center pod. Also very remarkable for being a giant sized airliner or troop transport, having (at least) 15 passenger windows on the inside and outside of each of the pods. The short center pod having fewer windows for two decks high. Do these unique features sound familiar to anyone? I have tried various Internet searches but came up empty. It was developed at LEAST to the model stage,
FIVE engines with 3 pusher, two tractor propellers
Very large size resembling giant P-38 general config./shape
airliner or troop transport
"possibly" from Republic.
Just came across a long lost July 1944 Republic Aviation file book of Organization Charts, and there was a loose note page tucked in. So the info MAY of MAY NOT be from Republic, and could have been placed in there, much later.
It SHOULD have been easy to track down the design because it had FIVE engines (two tractor props at the front of each outer pod, and two smaller Pusher prop engines at the trailing edge of each wing-outside of each of the two pods. Then it had a four blade pusher prop engine at the rear of the short center pod. The general layout being similar to a P-38 shape with the twin-boom and twin tail. and center pod. Also very remarkable for being a giant sized airliner or troop transport, having (at least) 15 passenger windows on the inside and outside of each of the pods. The short center pod having fewer windows for two decks high. Do these unique features sound familiar to anyone? I have tried various Internet searches but came up empty. It was developed at LEAST to the model stage,
FIVE engines with 3 pusher, two tractor propellers
Very large size resembling giant P-38 general config./shape
airliner or troop transport
"possibly" from Republic.
Steve Pace
Aviation History Writer
- Joined
- 6 January 2013
- Messages
- 2,266
- Reaction score
- 225
FANTASTIC...thanks Stephane! -SP
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
The North American/Republic MX-1764 aircraft project;
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php/topic,5660.msg45459.html#msg45459
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php/topic,5660.msg45459.html#msg45459
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,421
From Tony Buttler
Republic Project List
The following are known project numbers.
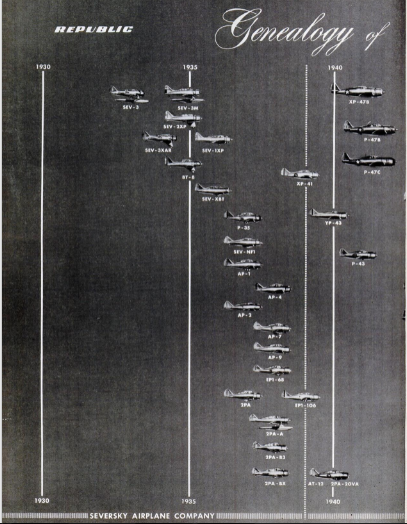
AP-1 Modified P-35 for trials 1937
AP-2 Lost out in 1937 pursuit competition. Featured flush retracting gear.
AP-3 Proposal with liquid cooled Allison V-1710 engine – abandoned in favour of AP-4.
AP-4 Adaptation of P-35. Order of 13 aircraft in March 1939 (YP-43) delivered in September 1940 as P-43 Lancer.
AP-4J 1400hp Pratt & Whitney R-2180-1 powered proposal. 80 ordered Sept 13, 1939 as P-44 Rocket. Order cancelled.
AP-4L Proposal with 2000hp R-2800-7-also not constructed. Some sources use the name "Warrior" instead of "Rocket".
AP-5 Single seat fighter.
AP-6 Single seat fighter.
AP-7 Speed record aircraft. In 1938 Major Seversky used this aircraft to establish a new transcontinental speed record.
AP-8 Never completed. Formed the basis for the AP-9
AP-9 Entrant in 1939 Air Corps fighter competition based on AP-8. Used improved airfoil. Air Corps turned proposal down in favour of Bell XP-39.
AP-10 Response to Air Corps circular proposal 39-770. Design submitted in August 1939 for a light weight fighter to be powered by a Allison V-1710 liquid cooled engine. Army placed an order as XP-47. XP-47A stripped version of XP-47. Contract signed January 1940. September 1940 all work on XP-47 and XP-47A was terminated. Full scale wind tunnel model handed over to Langley Field for testing. In same month contract placed for XP-47B - later to become the Thunderbolt.
AP-12 Republic answer to R40C. Highly streamlined design with engine behind the cockpit driving tractor contraprop in the nose via long shaft. Illustrations showing the design as the "Republic Rocket".
AP-16B F-47N version of Thunderbolt.
AP-18 Development of AP-12 "Rocket". Intended powerplant Wright R-2160. Design ordered as XP-69 in July 1941. Scale mock-up June 1942. Final configuration had long bubble cockpit. Cancelled 1943.
AP-19 = XP-72.
AP-21a Appears to be North American XT-28.
AP-22 Unmanned flying bomb drone project based on German V-1. Loon?
AP-23 Straight wing fighter project, 19.9.44. Became XF-84 Thunderjet fighter bomber prototype first flown 28.2.46.
AP-23X Preliminary design - March 1947 - for a sweptwing F-84. Not accepted by Air Force Material Command.
AP-23M Final sweptwing proposal . On the 10th November 1949 ordered as the YF-96.
AP-24 Amphibious aircraft with XO-425-7 Franklin air-cooled engines, 1945.
AP-31 Proposal for high performance research aircraft and day interceptor, 1.46. Competition won by Convair XP-92 but AP-31 design ordered as prototype XF-91 Thunderceptor. XF-91 first flew 9.5.49 but no production.
AP-41 XF-12 Rainbow initial proposal dated 15.10.47.
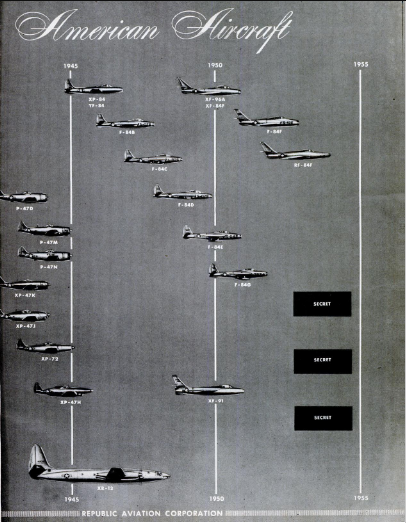
AP-42 Heavy USAF bomber, c1944/45. Follow up/replacement design for B-47.
AP-44A Mach 3 all-weather high altitude interceptor, early 1948.
AP-46 Development of F-84F fitted with turboprop engine as XF-84H and first flown 22.7.55. Apart from wing and cockpit, pretty well all new aircraft. No production.
AP-47 Mixed-power ground support airplane proposal, 9.48. Radial piston engine, jet in rear fuselage, general configuration fairly similar to Ryan Fireball.
NP-48 Proposal for US Navy interceptor based on XP/XF-91, c9.48. Probably to OS-113.
NP-49 Proposals for US Navy interceptor with V-tail & underwing engine nacelles, c9.48. Probably to OS-113.
NP-50 Naval bomber, late 1940s. Competitor in OS-111 competition won by Douglas A3D.
NP-52 Twin-engine anti-submarine aircraft, early 1950s.
AP-54 Single engine swept wing all-weather interceptor fighter study with F-91-style wing and large tip fittings, late 1949/1950. One of submissions to ‘1954 Interceptor’ requirement MX1554.
AP-55 Twin-boom inverted V-tail lightweight fighter/interceptor project, early 1950. Later believed in competition with Lockheed F-104. Several versions drawn, one also as submission to ‘1954 Interceptor’ requirement MX1554, none built.
AP-57 ‘1954 Interceptor’ proposal and full development into Mach 3 XF-103, 1951. Three prototypes ordered but project cancelled 8.57 before had flown.
AP-?? All Weather Fighter-Bomber Study to MX1764, c1950/51.
AP.60 Four engine turboprop bomber aircraft based on XF-12 Rainbow. 1949.
AP-63 Swept wing fighter bomber, 1951 onwards. Numerous layouts covered by designation. Eventually design AP-63-31 built as F-105A Thunderchief to WS.306A. First example flew 22.10.55.
AP-71 RF-105B/RF-105C version of Thunderchief.
AP-75 Long range interceptor to WS.202A, c5.54.
AP-76 Study to requirement won by NAA X-15. Also in competition with Douglas project.
AP-85 Two-seat swept-wing development of F-84F Thunderstreak, c1955.
AP-95 ASM ballistic missile to fit inside F-105 weapons bay.
AP-96 Man in space vehicle.
AP-99 Strategic ASM ballistic missile.
AP-100 V/STOL fighter-bomber proposal with three large lift fans mounted in centre of wide fuselage, 1959/60.
AP-106 Parametric studies for VTOL aircraft.
TFX Believed Republic undertook Tactical Fighter studies to TFX requirement, 12.61. Competition won by General Dynamics/Grumman F-111.
FX Proposals for new fighter, 1965 onwards. One possibly designated FH-100. Studies included v-g wings but final fixed-wing proposal of 1968 rejected for McDonnell Douglas design that became F-15.
FR-150 V/STOL fighter design proposed for Sea Control Ship, 30.12.71. Lost to Rockwell XFV-12A.
AP-183 Helicopter.
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
Hi,
I don't know what was this designation for Seversky ?,a SEV-4 ?,or it is misprint ;
http://books.google.com.au/books?id=XGd6GwAACAAJ&dq=SEVERSKY+SEV-4&hl=en&sa=X&ei=UXATVL6WKcWOO6O6gEA&ved=0CBwQ6AEwAA
I don't know what was this designation for Seversky ?,a SEV-4 ?,or it is misprint ;
http://books.google.com.au/books?id=XGd6GwAACAAJ&dq=SEVERSKY+SEV-4&hl=en&sa=X&ei=UXATVL6WKcWOO6O6gEA&ved=0CBwQ6AEwAA
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,151
Most likely a typo. Not only the designation SEV-4 is not known to have been used, but the number in these early designations indicated the number of seats (SEV-3 for three, SEV-6 for six, etc.) so it is very unlikely that the SEV-1XP could have been a "SEV-4"...
burunduk
I love the history of airplanes
- Joined
- 1 January 2007
- Messages
- 128
- Reaction score
- 118
Dear Colleagues!
According to the "Army air forces statistical digest, World War II", published 12.1945, tab. 75, p.117
USAAC purhased from Republic during 1940-1945
272 P-43
9006 P-47
AND 160 "others": 151 in 1940 and 9 in 1941.
60 "others" may be easily found: they are P-35A, or EP1-106, the second part of Swedish order, requisitioned by USAAC 24.10.1940.
But what are 100 more? I have no idea. Couldn't you help me?
According to the "Army air forces statistical digest, World War II", published 12.1945, tab. 75, p.117
USAAC purhased from Republic during 1940-1945
272 P-43
9006 P-47
AND 160 "others": 151 in 1940 and 9 in 1941.
60 "others" may be easily found: they are P-35A, or EP1-106, the second part of Swedish order, requisitioned by USAAC 24.10.1940.
But what are 100 more? I have no idea. Couldn't you help me?
Bazinga
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 14 December 2012
- Messages
- 292
- Reaction score
- 406
Silencer1
That now I am the Ruler of the Queen's Navee!
- Joined
- 3 August 2009
- Messages
- 897
- Reaction score
- 582
From the Cradel Aviation Museum (it's real gold mine for Seversky/Republic aircraft):
Collection of P-44 images - https://cdm16694.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/p16694coll109/search/searchterm/P-44
Including quite unusual, with jettisonable upper wing:


Collection of P-44 images - https://cdm16694.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/p16694coll109/search/searchterm/P-44
Including quite unusual, with jettisonable upper wing:


- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
From the Cradel Aviation Museum (it's real gold mine for Seversky/Republic aircraft):
Collection of P-44 images - https://cdm16694.contentdm.oclc.org/digital/collection/p16694coll109/search/searchterm/P-44
Including quite unusual, with jettisonable upper wing:
And we have them here;
Silencer1
That now I am the Ruler of the Queen's Navee!
- Joined
- 3 August 2009
- Messages
- 897
- Reaction score
- 582
Thank you, hesham!
I was too fast and unattentive, placing this images here. Please, someone, transfer these images to above mentioned thread or delete them here.
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
Attachments
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
From Tony Buttler
Republic Project List
The following are known project numbers.
AP-183 Helicopter.
My dear PaulMM,
please can you ask my dear Tony,is he sure about that ?.
- Joined
- 3 September 2006
- Messages
- 1,475
- Reaction score
- 1,472
Just like the Hillson FH-40 Slip wing on Hurricanes.Including quite unusual, with jettisonable upper wing
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,421
Why, do you have a reason to doubt him?From Tony Buttler
Republic Project List
The following are known project numbers.
AP-183 Helicopter.
My dear PaulMM,
please can you ask my dear Tony,is he sure about that ?.
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
Why, do you have a reason to doubt him?
Yes I have,but wanting to know if he is sure about it was a helicopter ?.
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
Why, do you have a reason to doubt him?From Tony Buttler
Republic Project List
The following are known project numbers.
AP-183 Helicopter.
My dear PaulMM,
please can you ask my dear Tony,is he sure about that ?.
From the Spangenberg index,
I think it was an aircraft and not helicopter,I know the Republic Helicopter Division was responsible for it,but it
also designed a VTOL aircraft,so it is not related to those projects;
Attachments
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
I know this topic for Republic AP series,but I want to talk about Seversky Sev sequence,instead off
open new thread;
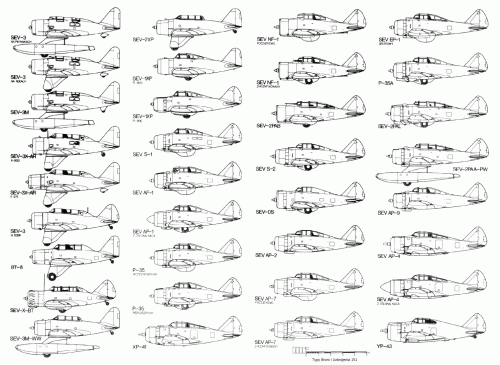
SEV-3 was a three-seat low-wing amphibian monoplane,on floats,powered by one 420 hp Wright J-6 Whirlwind
radial engine,
SEV-3XAR
was a landplane trainer
SEV-3XLR
was a landplane
SEV-3M-WW
was an amphibian for the Colombian Air Force, six built (only four delivered to Colombia), with Wright Whirlwind engines.
BT-8
was a landplane basic-trainer for the United States Army Air Corps, developed from SEV-3XAR
SEV-X-BT
was a multi-discipline trainer version of the BT-8 with retractable undercarriage. The sole SEV-X-BT lost in competition to the North American BT-9 and was reportedly scrapped for spares to service the Seversky 2PA
SEV-1 was a single seat low-wing all metal construction fighter,powered by one 850 hp Wright R-1850-G5 engine,
SEV-1XP
was a single-seat fighter prototype, aka SEV-S1
SEV-2XP
was a two-seat fighter prototype
SEV-DS
for Shell Oil Company / James Doolittle
SEV-X-BT
was a two-seat basic trainer
SEV-4 ? may it was a twin engined low-wing attack bomber project,could be with four-seat
SEV-5 was a five-seat amphibian project,developed from SEV-3,with a maximum speed of 200 m.p.h.
SEV-6A was a six-seat amphibian project,a large version of SEV-3,with two floats
SEV-6L was a six-seat landplane large version of SEV-6A,project only
SEV-7 was a single seat fighter,developed from SEV-1XP,powered by one 850 P & W R-1830-9 engine,had
speed of 465 km/h
SEV-8 ? may it was an executive light transport low-wing monoplane,clearly based on its earlier fighters,powered by
one 1200 hp engine and had a retractable tricycle
SEV-9 ? may it was a large twin hull transatlantic high-wing flying boat monoplane project,powered by eight 2,000 h.p. (2,300 for take-off) liquid-cooled engines are specified, giving a total of 16,000 h.p.. with 18.400 for take-off. The two nose units and the central one aft will each consist of two engines driving one airscrew, while the outboard ones will be single engines. The nacelles will, like the rest of the interior, be supercharged, and mechanics will have access to the engines in flight,could accommodated
100 to 120 passenger
SEV-10 ? may it was a mid-wing stratosphere heavy fighter project,powered by two buried engines,would have driven
four propellers,and had a twin tail fin,and fitted with 22 machine gun
SEV-11 ? may it was a mid-wing torpedo bomber monoplane for the competition VB-VT (SD-119-3),project only
- To be continued
open new thread;
SEV-3 was a three-seat low-wing amphibian monoplane,on floats,powered by one 420 hp Wright J-6 Whirlwind
radial engine,
SEV-3XAR
was a landplane trainer
SEV-3XLR
was a landplane
SEV-3M-WW
was an amphibian for the Colombian Air Force, six built (only four delivered to Colombia), with Wright Whirlwind engines.
BT-8
was a landplane basic-trainer for the United States Army Air Corps, developed from SEV-3XAR
SEV-X-BT
was a multi-discipline trainer version of the BT-8 with retractable undercarriage. The sole SEV-X-BT lost in competition to the North American BT-9 and was reportedly scrapped for spares to service the Seversky 2PA
SEV-1 was a single seat low-wing all metal construction fighter,powered by one 850 hp Wright R-1850-G5 engine,
SEV-1XP
was a single-seat fighter prototype, aka SEV-S1
SEV-2XP
was a two-seat fighter prototype
SEV-DS
for Shell Oil Company / James Doolittle
SEV-X-BT
was a two-seat basic trainer
SEV-4 ? may it was a twin engined low-wing attack bomber project,could be with four-seat
SEV-5 was a five-seat amphibian project,developed from SEV-3,with a maximum speed of 200 m.p.h.
SEV-6A was a six-seat amphibian project,a large version of SEV-3,with two floats
SEV-6L was a six-seat landplane large version of SEV-6A,project only
SEV-7 was a single seat fighter,developed from SEV-1XP,powered by one 850 P & W R-1830-9 engine,had
speed of 465 km/h
SEV-8 ? may it was an executive light transport low-wing monoplane,clearly based on its earlier fighters,powered by
one 1200 hp engine and had a retractable tricycle
SEV-9 ? may it was a large twin hull transatlantic high-wing flying boat monoplane project,powered by eight 2,000 h.p. (2,300 for take-off) liquid-cooled engines are specified, giving a total of 16,000 h.p.. with 18.400 for take-off. The two nose units and the central one aft will each consist of two engines driving one airscrew, while the outboard ones will be single engines. The nacelles will, like the rest of the interior, be supercharged, and mechanics will have access to the engines in flight,could accommodated
100 to 120 passenger
SEV-10 ? may it was a mid-wing stratosphere heavy fighter project,powered by two buried engines,would have driven
four propellers,and had a twin tail fin,and fitted with 22 machine gun
SEV-11 ? may it was a mid-wing torpedo bomber monoplane for the competition VB-VT (SD-119-3),project only
- To be continued
Last edited:
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,904
- Reaction score
- 15,778
I know this topic for Republic AP series,but I want to talk about Seversky Sev sequence,instead off
open new thread;
SEV-3 was a three-seat low-wing amphibian monoplane,on floats,powered by one 420 hp Wright J-6 Whirlwind
radial engine,
SEV-3XAR
was a landplane trainer
SEV-3XLR
was a landplane
SEV-3M-WW
was an amphibian for the Colombian Air Force, six built (only four delivered to Colombia), with Wright Whirlwind engines.
BT-8
was a landplane basic-trainer for the United States Army Air Corps, developed from SEV-3XAR
SEV-X-BT
was a multi-discipline trainer version of the BT-8 with retractable undercarriage. The sole SEV-X-BT lost in competition to the North American BT-9 and was reportedly scrapped for spares to service the Seversky 2PA
SEV-1 was a single seat low-wing all metal construction fighter,powered by one 850 hp Wright R-1850-G5 engine,
SEV-1XP
was a single-seat fighter prototype, aka SEV-S1
SEV-2XP
was a two-seat fighter prototype
SEV-DS
for Shell Oil Company / James Doolittle
SEV-X-BT
was a two-seat basic trainer
SEV-4 ? may it was a twin engined low-wing attack bomber project,could be with four-seat
SEV-5 was a five-seat amphibian project,developed from SEV-3,with a maximum speed of 200 m.p.h.
SEV-6A was a six-seat amphibian project,a large version of SEV-3,with two floats
SEV-6L was a six-seat landplane large version of SEV-6A,project only
SEV-7 was a single seat fighter,developed from SEV-1XP,powered by one 850 P & W R-1830-9 engine,had
speed of 465 km/h
SEV-8 ? may it was an executive light transport low-wing monoplane,clearly based on its earlier fighters,powered by
one 1200 hp engine and had a retractable tricycle
SEV-9 ? may it was a large twin hull transatlantic high-wing flying boat monoplane project,powered by eight 2,000 h.p. (2,300 for take-off) liquid-cooled engines are specified, giving a total of 16,000 h.p.. with 18.400 for take-off. The two nose units and the central one aft will each consist of two engines driving one airscrew, while the outboard ones will be single engines. The nacelles will, like the rest of the interior, be supercharged, and mechanics will have access to the engines in flight,could accommodated
100 to 120 passenger
SEV-10 ? may it was a mid-wing stratosphere heavy fighter project,powered by two buried engines,would have driven
four propellers,and had a twin tail fin,and fitted with 22 machine gun
SEV-11 ? may it was a mid-wing torpedo bomber monoplane for the competition VB-VT (SD-119-3),project only
- To be continued
I complete it,any corrections or additions are welcome.
Last edited:
- Joined
- 25 July 2007
- Messages
- 4,299
- Reaction score
- 4,196
I would suggest that Seversky's earlier SEV series probably deserves its own thread. But here goes ...
SEV-1XP - 1935 '1-seat Experimental Pursuit' conversion
- SEV-1XP: All-metal; single-engine low-wing monoplane
- SEV-1XP: SEV-2XP rebuilt after 18 June 1935 accident
- SEV-1XP: X18Y; single-seater; semi-retr. main gear
- SEV-1XP: 1 x 850 hp Wright R-1820-G5; span 10.97 m
-- AP-1 : Redesignation of revised SEV-1XP prototype
-- AP-1 leads to USAAC P-35; EP-1; Swedish EP-106/J 9
- SEV-DS : Civil SEV-1XP NX1291 for Shell Oil Company
- SEV-DS : 'Doolittle Special'; for pilot Jimmy Doolittle
- SEV-S1 : 'Special'; 1937 racer for Jacqueline Cochran*
- SEV-S1 : 1 x 900 hp P&W R-1830-13 14-cyl. radial
- SEV-S1 : 'Executive' (due to buried 2nd seat) [1]
-- * So, SEV-1XP (now NR18Y) converted to AP-1 standard
-- Seversky S-1: Revised later designation for SEV-S1
- SEV-S2 : 1937 civilian racer for Frank Fuller; reg. 70Y
- SEV-S2 : 1939 re-eng; 1,200 h.p. P&W R-1830-SC-8
-- Seversky S-2: Revised later designation for SEV-S2
SEV-2XP - 1935 '2-seat Experimental Pursuit' conversion
- SEV-2XP: All-metal; single-engine low-wing monoplane
- SEV-2XP: From the Seversky II X, in turn from SEV-3X
-- Seversky II X: Single-seater, open-cockpit monoplane
-- II X: 735 hp Wright GR-1670-A1 14-cyl.; span 10.97 m
-- II X: Alexander Kartveli design; conv. into SEV-2XP
- SEV-2XP: II X airframe conv.; 2-seat fighter prototype
- SEV-2XP: USAAC Material Division pursuit submission
-- SEV-2XP damaged 18 June 1935; conv. into SEV-1XP
- SEV-2PA : 2-seater 'Convoy Fighter' offered for export
- SEV-2PA : 1 x 850 hp Wright R-1820-G2 Cyclone
- SEV-2PA : Rebuilt SEV-X-BT X189M; drooping ailerons
- SEV-2PA-A: Amphibian; Soviet 'Convoy Fighter'; x 1
- SEV-2PA-A: 1 x 1,000 hp Wright XR-1820* Cyclone
-- * Some sources claim an 850 hp Wright R-1820-G2
- SEV-2PA-A: Tested as NX1307; no license production
- SEV-2PA-L: Landplane; Soviet 'Convoy Fighter'; x 1
- SEV-2PA-L: 1 x 1,000 hp Wright R-1820-G3 Cyclone
- SEV-2PA-L: Prototype marked simply as 'R' ('Russian')
- SEV-2PA-B: 1938 SEV-2PA demonstrator; reg. NX2586
- SEV-2PA-B: aka SEV-1-68/EP-1-68 (suggesting 1 seat?)
- SEV-2PA-B3: Imperial Japanese Navy landplane; x 20
- SEV-2PA-B3: IJN designation A8V1; Allied code 'Dick'
- SEV-2PA-BX: European demonstrators; NX2586/'2587
- SEV-2PA-204A: Dive-bomber for SE; aka EP-106 x 52**
- SEV-2PA-204A: 1,065 hp P&W R-1830-45; span 12,50 m
-- ** Only 2 x SEV-2PA-204A delivered; Flygvapnet B 6
- SEV-2PA-204A: Embargoed SE a/c to US Army Air Corps
-- AT-12 : Guardsman; USAAC advanced trainer***
-- *** Actually empl. as base commanders' transports
SEV-3 - 1933 3-seat, single-engined low-wing monoplane
- SEV-3 : Flew in June 1933; amphibious floatplane gear*
- SEV-3 : 1 x 420 hp Wright J-6-9 Whirlwind; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3 : Michael Gregor & Alexander de Seversky design
-- * Built by EDO Aircraft Corporation, College Point, NY [2]
-- Registered NX/NR2106 (c/n 301) for 1935 Thompson race
- SEV-3 : (Project) 'Sportsman' transport; portside door
- SEV-3L : 1934 SEV-3 rebuild; landplane military trainer
- SEV-3L : 1 x 350 hp Wright R-975E 9-cyl.; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3XAR: SEV-3 rebuild; simplified trousered main u/c
- SEV-3XAR: Later conv. back into amphibian as SEV-3M
- SEV-3XAR: 1934 Army Air Corps basic trainer submission
-- BT-8 : 2-seat USAAC basic trainer; x 30 (c/n 7-36)**
-- BT-8 : 1 x 400 hp P&W R-985-11 9-cyl; span 10.97 m
-- ** An additional 5 x BT-8 airframes ordered as spares
- SEV-X-BT: Refined SEV-3XAR; trainer demonstrator; x 1
- SEV-X-BT: 1 x 550 hp Pratt & Whitney S1H1-G Wasp
-- SEV-X-BT basic trainer: Fixed main u/c; span 12.50 m
-- SEV-X-BT advanced trainer/combat type: span 10.97 m
- SEV-X-BT: (N)X189M; shorter-span wings; retr. main u/c
-- SEV-X-BT prototype lost USAAC competition to NAA BT-9
- SEV-3M : X2106 c/n 301; high-powered SEV-3XAR conversion
- SEV-3M : (Initial) 1935 speed-record amphibian (230.4 mph)
- SEV-3M : 1 x 710 hp Wright SR-1820 Cyclone; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3M : (Later) 1936 landplane; sold Rep. Spain via Mexico
- SEV-3M-WW: 1934 export amphibian fighter for Colombia; x 3
- SEV-3M-WW: 1 x (??) hp Wright J-6 Whirlwind; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3M-WW: c/n 37-39; begun by Kirkham Engineering [3]
- SEV-3XLR: (??) landplane; online, Wiki references only
- SEV-3XLR: (??) suggests 'Experimental Long Range' (??)
SEV-4 - (??) hypothetical designation; no evidence
- SEV-4 : Possibly twin-engined attack bomber project
-- https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/seversky-twin-engine-bomber.42051/#post-617130
-- SEV4XP : [sic]; Typo for 'SEV-1XP' racer, R18Y
-- SEV 4-1XP: [sic]; Typo for SEV-1XP
SEV-5 - (Project) 1936 Sky Yacht civil floatplane
- SEV-5 : 1+4 pax float transport; derived from SEV-3
SEV-6 - (Project) 1936 single-engined civil transport
- SEV-6 : Low, SEV-3-like wings w/ broader fuselage
- SEV-6A: Amphibian; twin float gear as per SEV-3
- SEV-6L: Landplane; presumably trousered main u/c
- SEV-6 : 2 crew (pilot/radio op); 4 pax in rear cabin
-- https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/seversky-sev-6-sky-yacht-project.20301/
SEV-7 (I) - (Project) 1936 10-seat transport aircraft
- SEV-7 : (I) 2+8* pax civilian passenger floatplane
-- * Note deviation from seat number-based system
SEV-7 (II) - Re-engined SEV-1XP prototype X18Y; x 1
- SEV-7 : (II) Refined SEV-1XP; leads to AP-1 & P-35
- SEV-7 : (II) 1 x 738 hp* P&W R-1830-9 Twin Wasp
-- * Under-performing; should have produced 950 hp– AP-4B: (??)
__________________________________________________
By this stage, the SEV number system has clearly drifted away from its origin. There is a very slight possibility that a typo on the number of seats has been repeated regarding the first SEV-7 project. But the erstwhile AP-1 was most definitely a single-seater.
Beyond this point, SEV designations are pure speculation. The SEV-7 fighter demonstrator itself was redesignated as AP-1. Was Seversky Aircraft moving on to another designation system. Or was this Republic trying to distance itself from association with its founder?
__________________________________________________
[1] The Executive was later applied to a range of vaguely related design - beginning by applying then-current advanced aerodynamic techniques (taken from the fighter series) and later culminating in a variant with a tricycle landing gear.
[2] EDO's chief engineer was another ex-Tzarist pilot, the Russian-born Boris V. Korvin-Kroukovsky.
[2] This likely the source of some confusion. Many sources claim 6 x SEV-3Ms. This likely stems from SEV-3M work having begun on the three airframes by Kirkham Engineering Company at Farmingdale on Long Island. When funding dried up, work halted. Seversky Aircraft Corporation then opened its own facility at Farmingdale and completed the Colombian order using those Kirkham-built components.
__________________________________________________
If we choose to speculate further, hesham, remember that you have twice proposed SEV-8 as possible designations for unbuilt Seversky projects. So, reflecting that, an entry might be as follows:
SEV-8 - (??) hypothetical designation; no evidence
- SEV-8 : Possibly 1936 low-wing twin-engine bomber
-- https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/seversky-twin-engine-bomber.42051/
- SEV-8 : Possibly low-wing executive light transport
- SEV-8 : 1 x 1,200 hp engine; retractable tricycle u/c
As for the SEV-9 and SEV-10, always a bit dodgy applying 'designations' to design patents.
SEV-1XP - 1935 '1-seat Experimental Pursuit' conversion
- SEV-1XP: All-metal; single-engine low-wing monoplane
- SEV-1XP: SEV-2XP rebuilt after 18 June 1935 accident
- SEV-1XP: X18Y; single-seater; semi-retr. main gear
- SEV-1XP: 1 x 850 hp Wright R-1820-G5; span 10.97 m
-- AP-1 : Redesignation of revised SEV-1XP prototype
-- AP-1 leads to USAAC P-35; EP-1; Swedish EP-106/J 9
- SEV-DS : Civil SEV-1XP NX1291 for Shell Oil Company
- SEV-DS : 'Doolittle Special'; for pilot Jimmy Doolittle
- SEV-S1 : 'Special'; 1937 racer for Jacqueline Cochran*
- SEV-S1 : 1 x 900 hp P&W R-1830-13 14-cyl. radial
- SEV-S1 : 'Executive' (due to buried 2nd seat) [1]
-- * So, SEV-1XP (now NR18Y) converted to AP-1 standard
-- Seversky S-1: Revised later designation for SEV-S1
- SEV-S2 : 1937 civilian racer for Frank Fuller; reg. 70Y
- SEV-S2 : 1939 re-eng; 1,200 h.p. P&W R-1830-SC-8
-- Seversky S-2: Revised later designation for SEV-S2
SEV-2XP - 1935 '2-seat Experimental Pursuit' conversion
- SEV-2XP: All-metal; single-engine low-wing monoplane
- SEV-2XP: From the Seversky II X, in turn from SEV-3X
-- Seversky II X: Single-seater, open-cockpit monoplane
-- II X: 735 hp Wright GR-1670-A1 14-cyl.; span 10.97 m
-- II X: Alexander Kartveli design; conv. into SEV-2XP
- SEV-2XP: II X airframe conv.; 2-seat fighter prototype
- SEV-2XP: USAAC Material Division pursuit submission
-- SEV-2XP damaged 18 June 1935; conv. into SEV-1XP
- SEV-2PA : 2-seater 'Convoy Fighter' offered for export
- SEV-2PA : 1 x 850 hp Wright R-1820-G2 Cyclone
- SEV-2PA : Rebuilt SEV-X-BT X189M; drooping ailerons
- SEV-2PA-A: Amphibian; Soviet 'Convoy Fighter'; x 1
- SEV-2PA-A: 1 x 1,000 hp Wright XR-1820* Cyclone
-- * Some sources claim an 850 hp Wright R-1820-G2
- SEV-2PA-A: Tested as NX1307; no license production
- SEV-2PA-L: Landplane; Soviet 'Convoy Fighter'; x 1
- SEV-2PA-L: 1 x 1,000 hp Wright R-1820-G3 Cyclone
- SEV-2PA-L: Prototype marked simply as 'R' ('Russian')
- SEV-2PA-B: 1938 SEV-2PA demonstrator; reg. NX2586
- SEV-2PA-B: aka SEV-1-68/EP-1-68 (suggesting 1 seat?)
- SEV-2PA-B3: Imperial Japanese Navy landplane; x 20
- SEV-2PA-B3: IJN designation A8V1; Allied code 'Dick'
- SEV-2PA-BX: European demonstrators; NX2586/'2587
- SEV-2PA-204A: Dive-bomber for SE; aka EP-106 x 52**
- SEV-2PA-204A: 1,065 hp P&W R-1830-45; span 12,50 m
-- ** Only 2 x SEV-2PA-204A delivered; Flygvapnet B 6
- SEV-2PA-204A: Embargoed SE a/c to US Army Air Corps
-- AT-12 : Guardsman; USAAC advanced trainer***
-- *** Actually empl. as base commanders' transports
SEV-3 - 1933 3-seat, single-engined low-wing monoplane
- SEV-3 : Flew in June 1933; amphibious floatplane gear*
- SEV-3 : 1 x 420 hp Wright J-6-9 Whirlwind; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3 : Michael Gregor & Alexander de Seversky design
-- * Built by EDO Aircraft Corporation, College Point, NY [2]
-- Registered NX/NR2106 (c/n 301) for 1935 Thompson race
- SEV-3 : (Project) 'Sportsman' transport; portside door
- SEV-3L : 1934 SEV-3 rebuild; landplane military trainer
- SEV-3L : 1 x 350 hp Wright R-975E 9-cyl.; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3XAR: SEV-3 rebuild; simplified trousered main u/c
- SEV-3XAR: Later conv. back into amphibian as SEV-3M
- SEV-3XAR: 1934 Army Air Corps basic trainer submission
-- BT-8 : 2-seat USAAC basic trainer; x 30 (c/n 7-36)**
-- BT-8 : 1 x 400 hp P&W R-985-11 9-cyl; span 10.97 m
-- ** An additional 5 x BT-8 airframes ordered as spares
- SEV-X-BT: Refined SEV-3XAR; trainer demonstrator; x 1
- SEV-X-BT: 1 x 550 hp Pratt & Whitney S1H1-G Wasp
-- SEV-X-BT basic trainer: Fixed main u/c; span 12.50 m
-- SEV-X-BT advanced trainer/combat type: span 10.97 m
- SEV-X-BT: (N)X189M; shorter-span wings; retr. main u/c
-- SEV-X-BT prototype lost USAAC competition to NAA BT-9
- SEV-3M : X2106 c/n 301; high-powered SEV-3XAR conversion
- SEV-3M : (Initial) 1935 speed-record amphibian (230.4 mph)
- SEV-3M : 1 x 710 hp Wright SR-1820 Cyclone; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3M : (Later) 1936 landplane; sold Rep. Spain via Mexico
- SEV-3M-WW: 1934 export amphibian fighter for Colombia; x 3
- SEV-3M-WW: 1 x (??) hp Wright J-6 Whirlwind; span 10.97 m
- SEV-3M-WW: c/n 37-39; begun by Kirkham Engineering [3]
- SEV-3XLR: (??) landplane; online, Wiki references only
- SEV-3XLR: (??) suggests 'Experimental Long Range' (??)
SEV-4 - (??) hypothetical designation; no evidence
- SEV-4 : Possibly twin-engined attack bomber project
-- https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/seversky-twin-engine-bomber.42051/#post-617130
-- SEV4XP : [sic]; Typo for 'SEV-1XP' racer, R18Y
-- SEV 4-1XP: [sic]; Typo for SEV-1XP
SEV-5 - (Project) 1936 Sky Yacht civil floatplane
- SEV-5 : 1+4 pax float transport; derived from SEV-3
SEV-6 - (Project) 1936 single-engined civil transport
- SEV-6 : Low, SEV-3-like wings w/ broader fuselage
- SEV-6A: Amphibian; twin float gear as per SEV-3
- SEV-6L: Landplane; presumably trousered main u/c
- SEV-6 : 2 crew (pilot/radio op); 4 pax in rear cabin
-- https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/seversky-sev-6-sky-yacht-project.20301/
SEV-7 (I) - (Project) 1936 10-seat transport aircraft
- SEV-7 : (I) 2+8* pax civilian passenger floatplane
-- * Note deviation from seat number-based system
SEV-7 (II) - Re-engined SEV-1XP prototype X18Y; x 1
- SEV-7 : (II) Refined SEV-1XP; leads to AP-1 & P-35
- SEV-7 : (II) 1 x 738 hp* P&W R-1830-9 Twin Wasp
-- * Under-performing; should have produced 950 hp– AP-4B: (??)
__________________________________________________
By this stage, the SEV number system has clearly drifted away from its origin. There is a very slight possibility that a typo on the number of seats has been repeated regarding the first SEV-7 project. But the erstwhile AP-1 was most definitely a single-seater.
Beyond this point, SEV designations are pure speculation. The SEV-7 fighter demonstrator itself was redesignated as AP-1. Was Seversky Aircraft moving on to another designation system. Or was this Republic trying to distance itself from association with its founder?
__________________________________________________
[1] The Executive was later applied to a range of vaguely related design - beginning by applying then-current advanced aerodynamic techniques (taken from the fighter series) and later culminating in a variant with a tricycle landing gear.
[2] EDO's chief engineer was another ex-Tzarist pilot, the Russian-born Boris V. Korvin-Kroukovsky.
[2] This likely the source of some confusion. Many sources claim 6 x SEV-3Ms. This likely stems from SEV-3M work having begun on the three airframes by Kirkham Engineering Company at Farmingdale on Long Island. When funding dried up, work halted. Seversky Aircraft Corporation then opened its own facility at Farmingdale and completed the Colombian order using those Kirkham-built components.
__________________________________________________
If we choose to speculate further, hesham, remember that you have twice proposed SEV-8 as possible designations for unbuilt Seversky projects. So, reflecting that, an entry might be as follows:
SEV-8 - (??) hypothetical designation; no evidence
- SEV-8 : Possibly 1936 low-wing twin-engine bomber
-- https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/threads/seversky-twin-engine-bomber.42051/
- SEV-8 : Possibly low-wing executive light transport
- SEV-8 : 1 x 1,200 hp engine; retractable tricycle u/c
As for the SEV-9 and SEV-10, always a bit dodgy applying 'designations' to design patents.
Similar threads
-
-
-
RARE 16mm Films Republic Aviation AP-100 VTOL Fighter
- Started by Orionblamblam
- Replies: 8
-
CAB - Cantieri Aeronautici Bergamaschi, Caproni ...
- Started by Apophenia
- Replies: 11
-
AN/APS-20E Tri-Band radar
- Started by A_Random_Guy
- Replies: 0