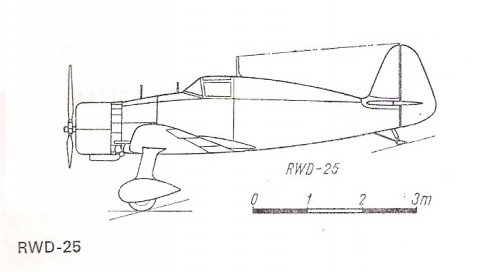
- Joined
- 28 January 2008
- Messages
- 635
- Reaction score
- 512
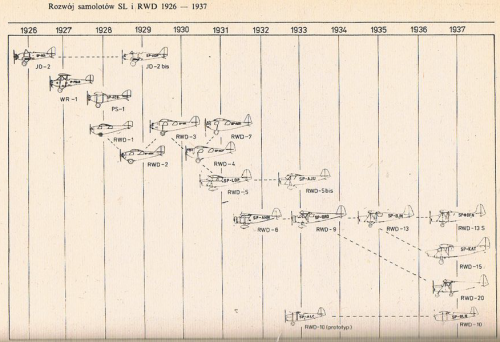
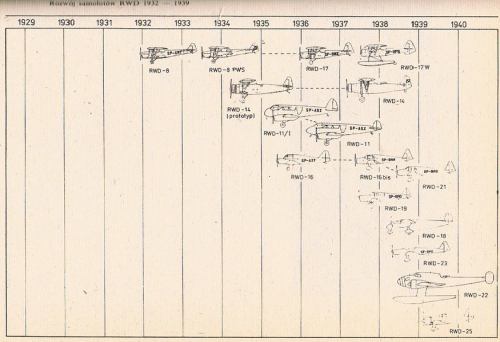
RWD was a Polish aircraft construction bureau active between 1928 and 1939. It started as a team of three young Warsaw University of Technology designers, Stanisław Rogalski, Stanisław Wigura and Jerzy Drzewiecki, whose names formed the RWD acronym. In 1933, Rogalski, Drzewiecki and Wędrychowski founded the company Doświadczalne Warsztaty Lotnicze (DWL, Experimental Aeronautical Works) in Warsaw, which became a manufacturer of further RWD aircraft.
Drzewiecki Designs
JD-1 Czarny Kot (Black Cat)
High wing glider. A heavy wooden early glider design also referred to as the SL-2 (its build number, SL – Sekja Lotnicze – University Air Section). It had a wheeled landing gear. [1925]
JD-2
A single engine wooden low-wing braced monoplane. The prototype, with a workshop number (cn) SL-4, was built in 1926 and first flown on October 4, 1926 in Warsaw. Design started in 1925 and 2 were built, including SP-ACA the second prototype (cn SL-6). Another unflown airframe (SL-5) was used for static testing. It was fitted with an Anzani 6-cylinder radial engine of 45 hp and could carry two people. [1925]
JD-2bis
A single engine low-wing braced monoplane for Aero Club use. Revised fuselage (8 inches / 20 cm longer), wing tips and fin, 2 built (SL-14/SP-ACD and SL-15/SP-ACF). One more built (SL-20/SP-ADP) the next year with an A.S. Genet (80 hp engine) replacing the Anzani 6-cylinder radial. [1929]
DK
Two seat fighter biplane project. Powered by a Lorraine W-type engine. [1926] *Project
Rogalski & Wigura Design
WR-1
This design was for a high wing, single engine, sporting aeroplane. [1927]
RW1
A high-wing braced wooden monoplane. Power came from a 45 hp Anzani 6-cylinder radial. It featured a tapering wing and was plywood covered with an unbalance rudder. [1926]
There is a possibility that these two designations (WR-1/RW1) relate to the same aircraft type.
Rogalski Wigura Drzewiecki (DWL Designs)
RWD-1
A Sports high-wing, braced, aeroplane. One ABC Scorpion II 2-cylinder air-cooled flat engine, 40 hp (53.6 kW) engine. The powerplant was horizontally opposed and suffered from extensive vibration issues. Wooden construction cantilever wing monoplane, conventional in layout. Installed with 2 seats, prototype only which was written off at the end of 1929. [1928]
RWD-2
A sporting single engine aeroplane with 2 seats. Wooden construction high-wing cantilever monoplane, conventional in layout. Fuselage rectangular in cross-section, plywood covered. Single-spar one-part wing of a trapezoid shape, covered with canvas and plywood in front. Built around a Salmson 9Ad 9-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine 46 hp (33.8 kW). A prototype and a test airframe were built. First flew May 1929. [1929]
RWD-3
This design was for a high-wing liaison two-seat aircraft. Two examples were constructed, one to fly and one for static tests. The RWD-2 sports plane was quite successful and the Polish Military of Defence ordered, in 1929, RWD to develop an enlarged variant as a liaison plane. The type was of a wooden construction with a single-engine. It had a high-wing cantilever monoplane powered with an Armstrong Siddeley Genet II 5-cylinder radial engine, 65 kW (88 hp) engine. It featured folding wings but proved to be underpowered with heavy controls. It was later donated to the Warsaw Academic Aeroclub as SP-WAA. [1930]
RWD-4
Sportsplane high-wing, 1 engine with 2 seats, 9 built. It was based upon their earlier RWD-3 design, but enlarged and fitted with more powerful inline Cirrus Hermes 4-cylinder air-cooled straight engine, 115 hp (86, kW). The folding-wing was dispensed with and had re-profiled tail surfaces. The fuel tank was fitted in the wing centre section. [1930]
RWD-5
Sportsplane and tourer with a high-wing. 1 × Cirrus Hermes IIB 4-cylinder air-cooled straight engine, 115 hp (86 kW). Fitted with 2 seats, RWD constructed 20 examples. First flight was 7 August 1931. Cantilever monoplane of composite wooden construction, it featured a tapered wing. [1931]
RWD-5bis
Touring high-wing, 1 engine with one seat. In March 1933 a special single-seat variant was built, called RWD 5bis (registration SP-AJU), powered with 130 hp Gipsy Major engine. The rear cabin was replaced with an additional fuel tank and was used on long-distance flights. It claim to fame was its transatlantic flight, being the smallest aircraft to cross the Atlantic in 1933. [1933]
RWD-5R
Sports and touring high-wing, 1 engine with 2 seats, constructed in the late 1990's as a flying replica. It flew first on 26 August 2000. [1998]
RWD-6
Competition tourer high-wing, one engine with 2 seats. Specifically designed for competitions. First flew 3 June 1932. Despite the early loss of the second example, it was a successful competition aircraft. Three built in total. [1932]
RWD-7
Sportsplane with a high-wing. Fitted with a Armstrong-Siddeley Genet II 5-cylinder radial engine. Based on the earlier RWD-2 design but with reshaped tail surfaces. It broke the FAI altitude and speed records during 1931-1932. Two seats with a cantilever wing, constructed of wood. [1931]
RWD-8
A primary trainer strutted high-wing of composite construction. One engine of a variety of types ranging from 100 hp to 150 hp with 2 seats, constructed over 550 examples, Poland’s most produced aircraft. It had a thick aerofoil built in three sections. [1933]
Sources:
Polish Aircraft 1893-1939 by Jerzy B.Cynk (Putnam, 1981)ISBN 0370000854
Polskie Samoloty Wojskowe 1945-80 by Andrjez Morgala (Wydawn. Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej, 1981) ISBN 8311064830
Drzewiecki Designs
JD-1 Czarny Kot (Black Cat)
High wing glider. A heavy wooden early glider design also referred to as the SL-2 (its build number, SL – Sekja Lotnicze – University Air Section). It had a wheeled landing gear. [1925]
JD-2
A single engine wooden low-wing braced monoplane. The prototype, with a workshop number (cn) SL-4, was built in 1926 and first flown on October 4, 1926 in Warsaw. Design started in 1925 and 2 were built, including SP-ACA the second prototype (cn SL-6). Another unflown airframe (SL-5) was used for static testing. It was fitted with an Anzani 6-cylinder radial engine of 45 hp and could carry two people. [1925]
JD-2bis
A single engine low-wing braced monoplane for Aero Club use. Revised fuselage (8 inches / 20 cm longer), wing tips and fin, 2 built (SL-14/SP-ACD and SL-15/SP-ACF). One more built (SL-20/SP-ADP) the next year with an A.S. Genet (80 hp engine) replacing the Anzani 6-cylinder radial. [1929]
DK
Two seat fighter biplane project. Powered by a Lorraine W-type engine. [1926] *Project
Rogalski & Wigura Design
WR-1
This design was for a high wing, single engine, sporting aeroplane. [1927]
RW1
A high-wing braced wooden monoplane. Power came from a 45 hp Anzani 6-cylinder radial. It featured a tapering wing and was plywood covered with an unbalance rudder. [1926]
There is a possibility that these two designations (WR-1/RW1) relate to the same aircraft type.
Rogalski Wigura Drzewiecki (DWL Designs)
RWD-1
A Sports high-wing, braced, aeroplane. One ABC Scorpion II 2-cylinder air-cooled flat engine, 40 hp (53.6 kW) engine. The powerplant was horizontally opposed and suffered from extensive vibration issues. Wooden construction cantilever wing monoplane, conventional in layout. Installed with 2 seats, prototype only which was written off at the end of 1929. [1928]
RWD-2
A sporting single engine aeroplane with 2 seats. Wooden construction high-wing cantilever monoplane, conventional in layout. Fuselage rectangular in cross-section, plywood covered. Single-spar one-part wing of a trapezoid shape, covered with canvas and plywood in front. Built around a Salmson 9Ad 9-cylinder, air-cooled, radial engine 46 hp (33.8 kW). A prototype and a test airframe were built. First flew May 1929. [1929]
RWD-3
This design was for a high-wing liaison two-seat aircraft. Two examples were constructed, one to fly and one for static tests. The RWD-2 sports plane was quite successful and the Polish Military of Defence ordered, in 1929, RWD to develop an enlarged variant as a liaison plane. The type was of a wooden construction with a single-engine. It had a high-wing cantilever monoplane powered with an Armstrong Siddeley Genet II 5-cylinder radial engine, 65 kW (88 hp) engine. It featured folding wings but proved to be underpowered with heavy controls. It was later donated to the Warsaw Academic Aeroclub as SP-WAA. [1930]
RWD-4
Sportsplane high-wing, 1 engine with 2 seats, 9 built. It was based upon their earlier RWD-3 design, but enlarged and fitted with more powerful inline Cirrus Hermes 4-cylinder air-cooled straight engine, 115 hp (86, kW). The folding-wing was dispensed with and had re-profiled tail surfaces. The fuel tank was fitted in the wing centre section. [1930]
RWD-5
Sportsplane and tourer with a high-wing. 1 × Cirrus Hermes IIB 4-cylinder air-cooled straight engine, 115 hp (86 kW). Fitted with 2 seats, RWD constructed 20 examples. First flight was 7 August 1931. Cantilever monoplane of composite wooden construction, it featured a tapered wing. [1931]
RWD-5bis
Touring high-wing, 1 engine with one seat. In March 1933 a special single-seat variant was built, called RWD 5bis (registration SP-AJU), powered with 130 hp Gipsy Major engine. The rear cabin was replaced with an additional fuel tank and was used on long-distance flights. It claim to fame was its transatlantic flight, being the smallest aircraft to cross the Atlantic in 1933. [1933]
RWD-5R
Sports and touring high-wing, 1 engine with 2 seats, constructed in the late 1990's as a flying replica. It flew first on 26 August 2000. [1998]
RWD-6
Competition tourer high-wing, one engine with 2 seats. Specifically designed for competitions. First flew 3 June 1932. Despite the early loss of the second example, it was a successful competition aircraft. Three built in total. [1932]
RWD-7
Sportsplane with a high-wing. Fitted with a Armstrong-Siddeley Genet II 5-cylinder radial engine. Based on the earlier RWD-2 design but with reshaped tail surfaces. It broke the FAI altitude and speed records during 1931-1932. Two seats with a cantilever wing, constructed of wood. [1931]
RWD-8
A primary trainer strutted high-wing of composite construction. One engine of a variety of types ranging from 100 hp to 150 hp with 2 seats, constructed over 550 examples, Poland’s most produced aircraft. It had a thick aerofoil built in three sections. [1933]
Sources:
Polish Aircraft 1893-1939 by Jerzy B.Cynk (Putnam, 1981)ISBN 0370000854
Polskie Samoloty Wojskowe 1945-80 by Andrjez Morgala (Wydawn. Ministerstwa Obrony Narodowej, 1981) ISBN 8311064830