Tophe
ACCESS: Top Secret
Still from Trait d’Union #260, the last batch:
MS-2015 (no date) 1 jet
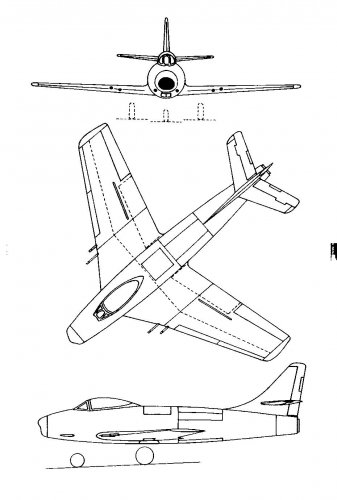
? ? ? (1945) single seat fighter, one engine of 1,700hp
Rallye bimoteur (no date) 2 engines
Convertible Roue/Air (no date) one piston engine, roadable
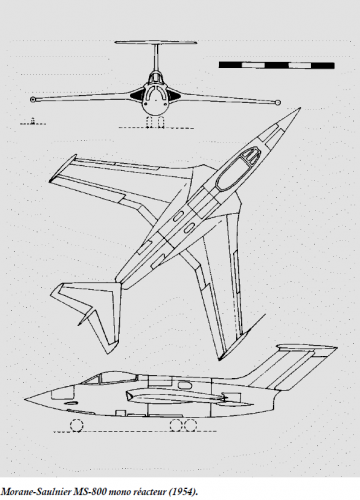
Stratodyne 01 (1955) 1 ATAR 101 jet + 1 Turbomeca Gourdon
Stratodyne 02 (1955) two ATAR E3
Stratodyne 05 (1959) flying jeep
Stratodyne A (1955) wind-tunnel model
Stratodyne B (1955) demonstrator for MS-1000
Stratodyne E1 (1955) small single-engined machine
Stratodyne E2 (1955) 2 or 3 Turbomeca Marboré jets of 400 kgp
Stratodyne E4 (1955) 2 or 3 Turbomeca Marboré jets
Stratodyne E5 (1955) two-seat trainer with 1 Orpheus jet of 2,200 kgp
MS-2015 (no date) 1 jet
? ? ? (1945) single seat fighter, one engine of 1,700hp
Rallye bimoteur (no date) 2 engines
Convertible Roue/Air (no date) one piston engine, roadable
Stratodyne 01 (1955) 1 ATAR 101 jet + 1 Turbomeca Gourdon
Stratodyne 02 (1955) two ATAR E3
Stratodyne 05 (1959) flying jeep
Stratodyne A (1955) wind-tunnel model
Stratodyne B (1955) demonstrator for MS-1000
Stratodyne E1 (1955) small single-engined machine
Stratodyne E2 (1955) 2 or 3 Turbomeca Marboré jets of 400 kgp
Stratodyne E4 (1955) 2 or 3 Turbomeca Marboré jets
Stratodyne E5 (1955) two-seat trainer with 1 Orpheus jet of 2,200 kgp