You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
MiG-29 and its modifications
- Thread starter lancer21
- Start date
Does it mean that the guidance commands are sent over wires to JDAM-ER in these MiG-29s? Is the avionics upgrade difficult to implement given the confined spaces in the MiG-29? Is there a possibility of wireless programming target's coordinates to JDAM-ER?
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,628
- Reaction score
- 14,304
I think it's a kludge to have a western GPS to tell the JDAM where it's starting from, when the MiG doesn't have the right data bus. Think of it as a babelfish, able to turn the Russian/Ukrainian data into something that the JDAM can read.Does it mean that the guidance commands are sent over wires to JDAM-ER in these MiG-29s? Is the avionics upgrade difficult to implement given the confined spaces in the MiG-29? Is there a possibility of wireless programming target's coordinates to JDAM-ER?
- Joined
- 25 July 2007
- Messages
- 4,299
- Reaction score
- 4,196
... Ukraine's MiG-29s and Su-27s do not have the kind of integrated GPS/INS capability and a NATO-compatible data bus that is needed for JDAM-ER. So, the fixture at the end of the pylon could be a GPS antenna that feeds key information into the bombs before they are released. Mounting it on the protrusion would help ensure it has a clear line of sight to the satellite constellation and is not shadowed by the aircraft's wing structure.
Which version of the Kh-31 is used with Egyptian MiG-29Ms? Even Jane's is uncertain if these are Kh-31AD ASM or Kh-31PD ARM.
Ainen
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 25 August 2011
- Messages
- 1,277
- Reaction score
- 1,714
Interesting if they considered integration of western fire control/defensive avionics.Good old mig-29. It has moxy. The Ukrainians are doing the best they can with these old birds. Thry are still providing good service to the nations that fly them.
The war is two years old by now - a lot could be done in that time.
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,628
- Reaction score
- 14,304
Requires keeping a couple of planes back to do the fitting and testing, plus however long it takes to install the Western parts on the existing planes. A super-simplified setup with the NATO data bus set up in the pylon with some translation software to turn whatever the Russian avionics say into NATO-standard for the JDAM to land on makes more sense than a total refit.Interesting if they considered integration of western fire control/defensive avionics.
The war is two years old by now - a lot could be done in that time.
Besides, how long do we think Ukraine will have any MiG29s in service?
Worthy of Tufte—that visual aid.An interesting comparison of the size of the MiG-29 and the Su-27.
View attachment 707206
As far as the hump…what hump?
aonestudio
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 11 March 2018
- Messages
- 2,964
- Reaction score
- 7,493
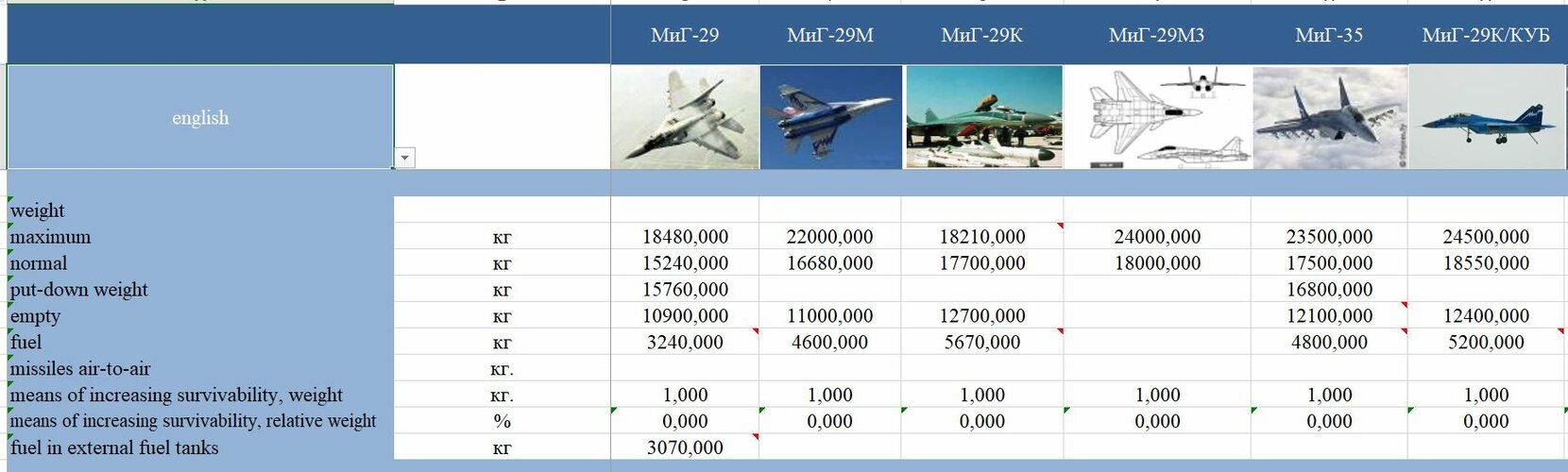
By chance does anyone have reliable empty weight figures for the Mig-29M (any version) Mig-29k (any version) and SMT?
Attachments
Life of Tyo
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 23 January 2022
- Messages
- 71
- Reaction score
- 231
Life of Tyo
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 23 January 2022
- Messages
- 71
- Reaction score
- 231
Full photo
 vk.com
vk.com
VK.com | VK
Attachments
This radome looks smaller than usual one. Perhaps thhis is the same bort?That is interesting, judging by the radome perhaps this example is testing the AESA radar. Or maybe even a production MiG-35 sporting same?
EDIT: it also shares the same wide HUD.
Last edited:
I have questions about numbers in @paralay post.
MiG-29K, that was converted from 9.15 have MTOW 18.2t. Also 5.6t fuel. Compared to 22t MTOW of 9.15 and 4.6t of fuel.
How come it has less MTOW and where additional 1t of fuel came?
Also, why MIG-35 has 400kg less fuel than 29K? And smaller MTOW.
MiG-29K, that was converted from 9.15 have MTOW 18.2t. Also 5.6t fuel. Compared to 22t MTOW of 9.15 and 4.6t of fuel.
How come it has less MTOW and where additional 1t of fuel came?
Also, why MIG-35 has 400kg less fuel than 29K? And smaller MTOW.
Deck planes are always heavier. From +500 kg for Rafal-M to 2300 kg for Su-27K
Some hard data as per Russians at Aero India
- crew - 1 or 2
- take off wt 17500 kg normal
-maximum-23500kgs
-max landing wt - 16800 kgs
-max combat load 6500 kgs
-max speed at sea level-1400km/hr
-at high altitude- 2100km/hr
-max altitude- 17500 mtr
-max g load - 9.0
max range 2000 km
with 3 drop tanks-3000km
with 3 drop tanks +one mid air refueling - 6000 kms
Engine RD 33 MK or thrust vectoring RD 33 MKV WITH 9000Kgf
life engine - 4000 hrs
1st overhaul-1000 hrs
quadrapole redundant three axis digital fly by wire control
Zhuk AE muli mode active phased array radar detection range more than 140 km ( 250 km??) with upto 30+targets on track while scan mode operation
integrated in flight refueling system
OLS UEM forward looking optronic search and track system with IR TV Laser range finder cum target illumination channel
cockpit information management system
upper air intake eliminated
fuel capacity 1.5 times compared to mig 29
10 weapon hard points and may come with Kh 31 anti ship missile,RVV AE,Integrated Gsh 301 with ammo 150 rounds,KAB 500TV guided bombs,KH 35 anti ship missile,Kh 31P anti radiation missile,
three multifunctional colour LCDs and wide angle HUD,four MFDS in second cockpit if incorporated.
VK 100 turbine starter
MIL STD 1553 B compliant multiple data bus
Full HOTAS capability
OLS UEM forward looking IRST SYSTEM
OLS K 360 degree look down IRST
thrust vectoring plus/minus 20 degree all aspect (more than su-30 mki)
Attachments
Last edited:
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,628
- Reaction score
- 14,304
That's probably due to having to fly off a ski-jump carrier. Can't get enough speed up on the carrier deck to safely take off at 22000kg, but can safely take off at 18,200kg.I have questions about numbers in @paralay post.
MiG-29K, that was converted from 9.15 have MTOW 18.2t. Also 5.6t fuel. Compared to 22t MTOW of 9.15 and 4.6t of fuel.
How come it has less MTOW and where additional 1t of fuel came?
As to the extra fuel, they probably found a few new spots to store fuel. My personal suspicion is that the new avionics take up less volume, so MiG was able to add another structural bay to hold fuel instead of avionics.
thrust-to-weight ratio of at least 1 - takeoff from the "first technical position" (95 meters)
thrust-to-weight ratio of less than 1 - takeoff from the "second technical position" (180 meters)
such a takeoff is possible at any speed of the ship
thrust-to-weight ratio of less than 1 - takeoff from the "second technical position" (180 meters)
such a takeoff is possible at any speed of the ship
Ainen
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 25 August 2011
- Messages
- 1,277
- Reaction score
- 1,714
Actually it looks like the first time we see "full" mig-35.That is interesting, judging by the radome perhaps this example is testing the AESA radar. Or maybe even a production MiG-35 sporting same?
Wing feels new.
aonestudio
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 11 March 2018
- Messages
- 2,964
- Reaction score
- 7,493
It's an ersatz. This implementation doesn't provide full munition capabilities, as plane doesn't have proper WCS and essentially is a glorified truck. You could arm Su-22 or MiG-23 for the same result.Ironic how the Mig's best days for exports potential are canceled by the Kremlin's leaders policies.
Who wouldn't have bought cheap Migs with AMRAAM, Harm, Scalp and SDB (not all are supported right now)?
And there were cheap upgrade variants (and still are for that matter, as Russia or Belarus didn't discontinue), but MIG-29 is not cheap in operation due to being twin engined light/medium fighter. And it is main issue that made it unpopular.
aonestudio
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 11 March 2018
- Messages
- 2,964
- Reaction score
- 7,493
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,628
- Reaction score
- 14,304
Am I seeing the "Air Recognition" markings correctly?
Yellow wingtips, blue flaps and LE slats, tail forward section blue and aft section yellow, divided on the spar line?
Or is it just yellow ailerons?
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,628
- Reaction score
- 14,304
Thank you!Technically, LE slats appear to be Blue and Yellow. Yellow on the outboard section.
Notice that this particular aircraft carries no AAM.
Can't trust my half-colorblind eyes on things like that...
I may have to build a model of one of the Ukrainian MiG29s with those Ground ID markings.
Kiltonge
Greetings Earthling
- Joined
- 24 January 2013
- Messages
- 634
- Reaction score
- 1,186
The problem with using colours for visual ID is that they depend on good lighting, which often won't be available on the underside of an aircraft.
Contrasting patterns, such as D-Day / Suez stripes or those on USAAF form-up bombers, are much more effective.
Contrasting patterns, such as D-Day / Suez stripes or those on USAAF form-up bombers, are much more effective.
F.L.
ACCESS: Top Secret
I found this on X, is it real or a photoshop ?!! Edited : it's a photoshop.
View: https://x.com/Macaskeel/status/1800064075080356344?t=wpfNoYIZa2mDmFQK2zsfKg&s=19
View: https://x.com/Macaskeel/status/1800064075080356344?t=wpfNoYIZa2mDmFQK2zsfKg&s=19
Attachments
Last edited:
Life of Tyo
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 23 January 2022
- Messages
- 71
- Reaction score
- 231
I found this on X, is it real or a photoshop ?!! Edited : it's a photoshop.
View: https://x.com/Macaskeel/status/1800064075080356344?t=wpfNoYIZa2mDmFQK2zsfKg&s=19[I found this on X, is it real or a photoshop ?!! Edited : it's a photoshop.
[URL='https://x.com/Macaskeel/status/1800064075080356344?t=wpfNoYIZa2mDmFQK2zsfKg&s=19']View: https://x.com/Macaskeel/status/1800064075080356344?t=wpfNoYIZa2mDmFQK2zsfKg&s=19
Photoshop we don,t have Mig-29 only Su-27/30 was Russia fighter can fly today
aonestudio
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 11 March 2018
- Messages
- 2,964
- Reaction score
- 7,493
jsport
what do you know about surfing Major? you're from-
- Joined
- 27 July 2011
- Messages
- 7,732
- Reaction score
- 5,750

Slovakia’s F-16 top-up plans reopen political battles over Ukraine aid
The country's Moscow-friendly government has walked back on a combat-helicopter deal for Bell AH-1Z Vipers, championed by the previous Cabinet.
aonestudio
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 11 March 2018
- Messages
- 2,964
- Reaction score
- 7,493
aonestudio
I really should change my personal text
- Joined
- 11 March 2018
- Messages
- 2,964
- Reaction score
- 7,493
- Joined
- 22 January 2006
- Messages
- 4,213
- Reaction score
- 2,010
This is not related with the the thread. This thread isn't about MiG-29 general news, as a possible aircraf transference from Slovakia to Ukraine, it's about improvements or technical modifications on existing MiG-29 models.
Slovakia’s F-16 top-up plans reopen political battles over Ukraine aid
The country's Moscow-friendly government has walked back on a combat-helicopter deal for Bell AH-1Z Vipers, championed by the previous Cabinet.www.defensenews.com
Ukrainian MiG-29 modified to accept Western hardware could be, to at some debatable extent, relevant here.
Please read the tittles and try to adjust to it. Otherwise, if you think you have a relevant information not related to any existing thread, feel free to open a new specific thread.
Similar threads
-
-
Anti-F-15: The Soviet PFI Program
- Started by overscan (PaulMM)
- Replies: 12
-
NVLAD by Joint Soviet Fighter
- Started by Joint Soviet Fighter
- Replies: 5
-
Article Related to Some of Russian Air Launched Missile Programme
- Started by ocay
- Replies: 0
-
Alt USAAC/AAF fighters, 1937-45
- Started by tomo pauk
- Replies: 0