You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Yakovlev Yak-45 & Yak-47
- Thread starter lozko
- Start date
Hi, Lozko!
Could you please mention the source?
Thank you
Could you please mention the source?
Thank you
Matej
Multiuniversal creator
I am curious if it is the official model from Yak or if it is the only one of the wooden models that were made for the illustrating of modern books.
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,897
- Reaction score
- 15,759
Attachments
lozko
ACCESS: Restricted
- Joined
- 14 August 2008
- Messages
- 3
- Reaction score
- 0
The author of the Polish article is Tomasz Szulc (drawings as well).
Considering the fact that I don't speak Polish that well (but do Russian), I compared both articles, and seems to me that they are not identical.
More so, mr.Szulc claims that among other sources that were used for the article, were his stenographs from conversations with Yakovlev OKB members, pilots, etc.
Considering the fact that I don't speak Polish that well (but do Russian), I compared both articles, and seems to me that they are not identical.
More so, mr.Szulc claims that among other sources that were used for the article, were his stenographs from conversations with Yakovlev OKB members, pilots, etc.
- Joined
- 21 May 2006
- Messages
- 3,002
- Reaction score
- 2,278
hs1216
ACCESS: Confidential
- Joined
- 4 October 2006
- Messages
- 110
- Reaction score
- 28
I wonder if the Yak-45 is related to the the Yak-35mv low altitude fighter-bomber project of the early 60's. The Yak-35mv was described as a twin engined delta wing aircraft with versions for both fighter and strike. Perhaps Yak okb used some of material developed for that aircraft for the later yak-45.
- Joined
- 12 July 2006
- Messages
- 948
- Reaction score
- 749
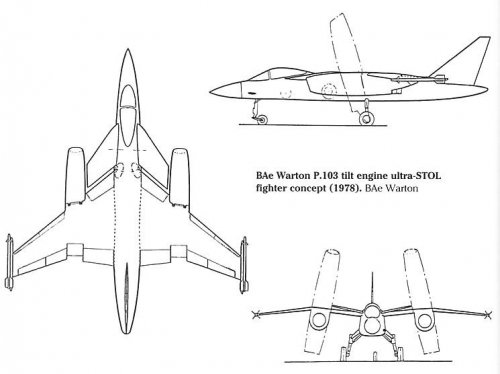
Pioneer said:Not much different in layout and concept to the BAe P.103 supersonic ASTOVL fighter project!
Which came first?
Regards
Pioneer
The position of the engines in nacelles in the middle of the wing is a continuity in fighter design at Yakovlev - see Yak-25/-26/-27/-28.
- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,753
- Reaction score
- 6,145
Sure!Pioneer said:Not much different in layout and concept to the BAe P.103 supersonic ASTOVL fighter project!
Which came first?
Regards
Pioneer
BAE P.103's secrets were stolen from Minister John Profumo by a female KGB agent in 1961...
- Joined
- 12 July 2006
- Messages
- 948
- Reaction score
- 749
stargazer said:Sure!
BAE P.103's secrets were stolen from Minister John Profumo by a female KGB agent in 1961...
P.103 "started in about 1977" (see Tony Buttler, BSP Jet Fighters, page 146) ... British Aerospace is a child of 1977 too ...
Matej
Multiuniversal creator
So now I am totally confused. Had the REAL Yak-45 proposal the engines positioned in the middle of the wing or below it??
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
There were several Yak-45 designs. First was the MiG-27 type ground attack design with middle mounted wings. Then there was a derived fighter which was competing in PFI competition along with the scaled up Yak-47. Lastly there was a derived VTOL fighter design which had underwing engines.
Attachments
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
http://www.airwar.ru/enc/attack/yak45.html
The Vietnam War forced both combatants to draw definite conclusions. First of all, it affected aircraft, and its use as a tactic, and the types of aircraft. Widely used in support of ground troops subsonic attack aircraft A-1, A-4, A-6, OV-10A and multipurpose supersonic fighter F-105 and F-4 had a low survivability and a number of qualities are not able to effectively perform the functions of attack aircraft. United States made several attempts to rectify the situation, elaborating planes "right in the system." However, field modification of existing aircraft did not bring the desired result.
Can be considered the most successful completion under conditions of guerrilla war subsonic jet trainer aircraft Cessna T-37. Cockpit partially protected by armor, but from the inside covered with quilts synthetic mats. The fuel tanks are self-sealing and filled with polyurethane foam. Machine equipment complemented simple sighting system. Arms placed on the outer nodes under the wing. To prevent the ingress of dirt into the air intakes are located close to the ground, they closed the nets that were removed simultaneously with the landing gear. A small unit of these small and maneuverable aircraft performed several thousand combat missions without losing a single machine. It was a stunning figure, given the intensity of the fire, according to the storming of the land. However, the threat of the aircraft from the air almost was not.
In the domestic aviation up to that time there was also a specialized attack aircraft. Fire support to ground troops on the battlefield should have a supersonic multi-role fighters MiG-21 and Su-7B, as well as the subsonic MiG-17. Such a doctrine decided to check the fall of 1967 during a large-scale maneuvers "Dnepr" in Belarus. It turned out that the task of supporting ground troops latest supersonic fighters decide worse than the subsonic MiG-17. MiG-17 pilots quickly find the target, time to recognize it and destroy the first approach. High levels of speed MiG-21 and Su-7B and poor visibility from the cockpit made it difficult to search, detection, identification and tracking of targets. Frequent flier just lost visual contact with the target for re-entering it, was forced to limit the time of the shooting and bombing. The possibility of the operation of such aircraft ground, elementary prepared airfields also proved problematic. The efficiency decreased due to the lack of security and aircraft - they lacked booking cabs, vital units were also not sufficiently protected against fire from the ground.
All this forced the generals and designers to think about the creation of a specialized aircraft capable of effectively meet the challenges of the immediate support of troops on the battlefield. What was needed was the IL-2 with a modern edge.
Attempts to create such a machine have made shortly after the war. It was the Tu-91 and IL-40, But by the time they are born - at the end of 1949 - Tu-91 was already decked dive bomber, torpedo. Soon, however, a new military-political leadership of the Soviet Union, is considered ocean-going fleet and its large ships undue and useless burden to the country and its armed forces, decided to cut the military shipbuilding program. As a result of the design work on the aircraft carriers and carrier-based aircraft rolled. However, the Tu-91 was successfully flight tested, including for operational use. But the plan of the MAP pas production of combat aircraft in the years 1956-1960. Tu-91 is still deleted.
It is equally sad fate and IL-40. The plane has been praised by test pilots, it was recommended in the mass production and for service. However, in the military leadership of the country has matured opinion that domestic Air Force attack aircraft today are not needed, and she de date by definition, and do it in a nuclear war on the battle fields of the future is simply nothing. April 13, 1956 the Government issued a decree to lift Il-40 series and the cessation of all work on it "due to the equipment of the Soviet Army with new kinds of" weapons. "After a week, the Minister of Defense of the USSR Georgy Zhukov its order finally destroyed the Soviet assault aviation. recyclable, even a relatively new attack aircraft IL-10 and IL-10M.
And now, ten years later, the Air Force again until the plane made a similar, this simple idea, however, it is difficult to push its way. The military believed that every new aircraft should fly faster, higher and further than his predecessors. Ideas enthusiasts, who started at their own risk on its own initiative to design a similar aircraft, became Colonel Ivan Savchenko (VVA Gagarin), deputy chief of the brigade general types of Sukhoi Design Bureau Oleg Samoylovich and Dmitry Gorbachev Leading Engineer of efficiency and combat use of the Sukhoi Design Bureau.
In February 1968, completed the first sketches to the modern attack aircraft TTT - specialized aircraft to the battlefield. In May, the work reported Sukhoi, and two months later chief designer of the project reported the Minister of Aviation Industry of the USSR P.V.Dementevu. Not all project gunship went down well. At the conclusion of the General Staff of the STC, for example, stated that this aircraft the Air Force is not needed.
And yet, at the beginning of 1969, Defense Minister Grechko P.V.Dementevu approached with a proposal to hold a design competition a light attack aircraft (LSSH). TTT appeared to him March 19, 1969 participated in the competition four CB: Ilyushin, Mikoyan, Sukhoi and Yakovlev.
In July 1969, the Commission considered the proposals of the Air Force. After a lengthy discussion, projects double IL-42 and Yak-28LSH rejected. The match continued to attack aircraft T-8 and MiG-21LSH. Probably considered the project and attack aircraft Yak-45 .
In the U.S., work on specialized stormtroopers started a little earlier, in 1966, were formed first TTT direct support to the aircraft. The program is called AX, and of the 12 contestants to the stage of flight models came only two firms - Fairchild-Republic and Northrop. Experienced stormtroopers of these companies took to the skies for the first time in May 1972.
But Vietnam and gave another, no less important lesson. Experience with the U.S. aircraft there demanded a radical revision of the whole concept of the future fighter. Phantom, has a powerful and effective missile-radar, had the advantage over the MiG-21 in large and medium ranges, but were defeated by lighter and more maneuverable "MiG" in the melee. The new fighter was not supposed to have such a shortage.
One of these fighters created in the U.S. under the FX, begun in 1966, was the result of the work plane F-15. But do not forget about the creation of a light fighter: in the early 70's the U.S. Air Force has come to the conclusion that both heavy and light aircraft in its class, and in 1972 it was announced the beginning of the program LWF (Light Weight Fighter).
At the same time, and in the Soviet Union to work to create a fighter of 4th generation. In 1971, the Air Force formulated the TTT for new aircraft - a promising front-line fighter (PFI). To the program involved all fighter KB countries - Mikoyan, Sukhoi and Yakovlev.
PFI had to fight with the fighters in close air combat maneuvering (using SD and guns), intercept airborne targets at long range when you move from the ground or autonomously and to dogfight at medium ranges, covering troops and infrastructure from attack from the air, and to oppose means of aerial reconnaissance, escort heavy aircraft and to protect them from fighters, to conduct aerial reconnaissance, to destroy small-size ground targets in the field of vision. The main opponents of the aircraft initially considered promising American fighter F-15, P.530 and the YF-17 (later F-18).
In 1971, the institutions of the industry and the Air Force began to study the formation of the concept of building the park fighter aircraft. As a result, it was concluded (the same as in the U.S.), which requires two types of aircraft - heavy and light. Easy front-line fighter (LFS) was designed to operate on its territory and within the tactical depth.
In 1972, the Air Force reviewed the preliminary design of advanced fighter aircraft, made in the Mikoyan design bureau, Sukhoi and Yakovlev. These were projects light fighters MiG-29 and Yak-45 heavy fighters and designs T-10 and Yak-47. Yakovlev Design Bureau, taking part in the competition for the creation of promising fighter and attack aircraft, it is likely to create offered all three types of aircraft on a single aerodynamic configuration. This has significantly reduced the cost of the study of aerodynamics and design. Moreover, attack aircraft and light fighter is different in practice only the equipment. On the one hand, it was profitable and Air Force - so close "relationship" would greatly simplify and training pilots, and maintenance of the fleet.
Today it is well known, the completed contests. The life cycle of the winners have already passed for the second half, and replace them must come new aircraft. However, detailed and reliable information about the project Yak-45 has been available for the first time. With the permission of OKB Yakovlev we publish materials on the draft of this machine.
Preliminary design of the first versions of the Yak-45 was completed in July 1970 he whole "recipient" in one book - a little more than 50 pages and began with these words: "In view of the war in the Middle East and in Vietnam, we have developed the Yak-45 version of the fighter and attack aircraft. aircraft is characterized by a large excess thrust, vertical exceptional maneuverability, which in combination with the small dimension of the aircraft, long range and supersonic flight at low altitude makes it possible to successfully carry out his mission as an assault on, and on fighter operations. Given similarity requirements for flight performance, the ability to mass-produced aircraft, simplification and cost reduction operation, both versions have the same design and aerodynamic configuration. differences lie in the weapons sighting and navigation equipment. "
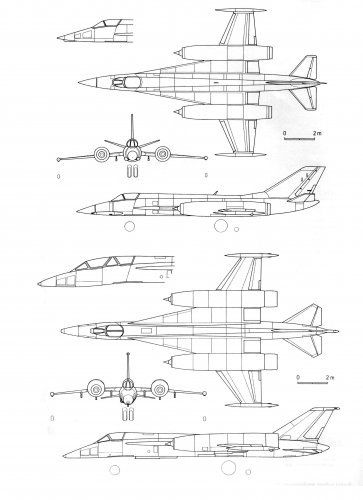
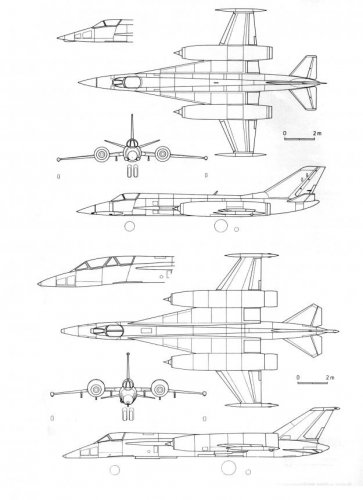
Yak-45 was a twin-engine single midwing normal aerodynamic configuration with a single vertical tail and bicycle landing gear. Engines were located in almost half the wingspan, the two main wing spar in this place took the form of half-ring motors covering the bottom. This arrangement gave certain advantages. First, this arrangement greatly increased engine durability machine, reducing the chance of damage to both of the two motors. Second, simplify maintenance, opening the approach to engines with virtually any party. In addition, simply solved issues replacement engines. There were also the aerodynamic advantages: it reduces the loss of inlet air intakes and at the nozzle exit.
Axially symmetric head-adjustable air vents to the outside shell and braking had bypass flap motors feeding on the ground to coordinate the work of engines and air intakes at low speeds. The aft nacelle positioned brake pads.
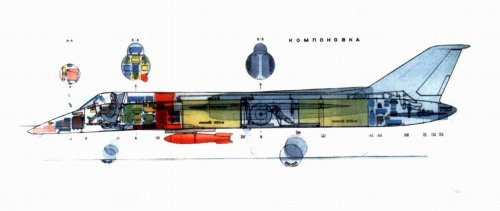
Fuselage-monocoque has a circular cross section with a maximum diameter of 1.2 m main construction material - aluminum alloys in the form of extrusions, forgings and plates. Structurally and technologically fuselage was divided into several compartments. In the front was located cockpit, radar, niche nose landing gear, equipment bays. The pilot's cockpit accommodates two built-gun GS-23 with a total 400 rounds ammunition. At the same caisson installed directly in front of the cockpit, thus protecting the pilot from the front. 2nd and 4th compartments were the fuel tanks. Power supply engines were split, but in emergency situations, and the left and right engines could receive fuel from both tanks. In the 3rd compartment formed by the force of the wing mounting frames, a niche was the main landing gear, hydraulic units and air conditioning systems. The aft compartment to which was attached tail, housed airborne equipment and braking parachute. The wing with the relative thickness of the profile 5% had developed an influx into the root of the sweep angle from 79 ╟. Console moderate sweep - 25 ╟. At the rear edge of the wing between the fuselage and engine nacelles were installed retractable flaps, and on the wings - the ailerons. In addition, along the leading edge of consoles located automatic slats. The design of the wing - mnogolonzheronnaya, mainly of aluminum alloy, with extensive use of punching and chemical milling.
Plumage - the usual pattern, stabilizer - resettable in flight, with elevators. The design of the keel and stabilizer - two-spar, aluminum alloy. The stabilizer had a significant cross-V -18 ╟, to work outside the exhaust jet engines.
Another feature of the Yak-45 was a bike rack. This scheme gave him the opportunity to land normally even when damaged one of the tires of each of the supports. The main landing gear wheel - brake, release and cleaning racks produced by a hydraulic system. Aircraft landing gear provided on unpaved airfields with the strength of the soil at least 6 kgf / cm ² (although, TTT Air Force needed a landing on the ground with a strength of 5 kgf / cm ²). For the stability of the aircraft taxiing on the wing tips were installed additional supports, closed fairing.
Control of the aircraft - a hard, in the channels of the elevators and ailerons are set hydroamplifiers irreversible type trimmer effect mechanisms and spring mechanisms boot knob.
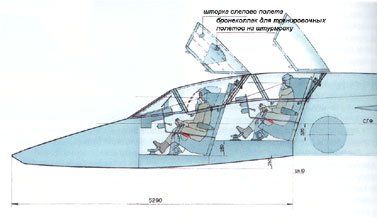
Cockpit - sealed, ventilation type. Ejection seat "Altai" was to provide rescue pilot in all flight modes, including on the run. All operations of the bailout had to happen automatically, including the withdrawal of the cockpit seat, stabilization and separation with the introduction of the pilot parachute system.
The hydraulic system consists of two independent systems: booster (main and emergency) system and actuators, intended for the production and the landing gear, flaps, air brakes, turn the nose landing gear to move the air intake cones, rudder stabilizer. Working pressure of hydraulic fluid AMG-10 was 150 kg / cm ². In case of emergency resurfacing stabilizer, landing gear and flaps was carried out with the help of pneumatic system.
Light Fighter Yak-45I intended to "protect ground forces from air attack and destroy enemy fighters at low and medium altitudes in visual visibility." The conquest of the air superiority was carried out "by means of autonomous action using airborne sighting systems, as well as pre-targeting."
Attack aircraft Yak-45 was designed to destroy the group and single small and mobile ground targets in the tactical and operational depth of the enemy. In this assault actions he could speak only in visual contact with the target.
Basic flight data planes were determined on the basis of experimental studies of model aircraft in wind tunnels T112 and T113 TsAGI. In these tubes were shooting characteristics of stability and controllability of the aircraft. Calculations showed that he had satisfactory performance throughout the operating range of altitudes and speeds and satisfies the basic requirements of the Air Force.
Equipment Yak-45I included the ASP-17 gunsight, radio station "Buk-10", the IFF system "Ozon", "Sirena-3M" radar warning receiver, a system of short-range navigation "Radikal" (with terrain avoidance) finder " Olenyok, "altimeter" A Reper-M. On account of the payload can be hung containers Jammer "Geran" and IPP-26M flare dispenser.
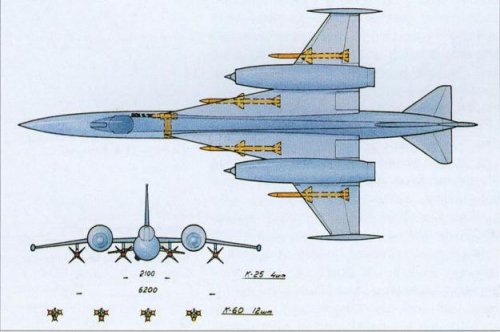
Fighter armament was placed on two pylons under the wing between the fuselage and the engine nacelles. They can be hung two short range AAM R-3S or six K-60 (three on each pylon). Built artvooruzheniya - staffing.
Ground attack bombsight PBK-3 and a laser range finder "Fon". Means of passive protection "Barrier" and jammer "Geran". In addition, the attack planned to equip DISS "Poisk". Total weight of the equipment reached 1000 kg. Gunsight ASP-17, coupled with quantum optical rangefinder and sight RBK-3, was to provide a bombing in horizontal flight, pitching and dive into the field of vision or purpose of a guide, as well as the firing of artillery and unguided rocket weapon against air and ground targets. For guidance UR X-23 air-to-surface provided for the suspension container with equipment "Delta-N".
Bomber weapons housed in the five universal beam holders of third weight group - four under the wing and one under the fuselage. Instead, a unit can be fitted Multi Lock Holders beam and underneath the fuselage - the same carrier, but the second group. For universal holders could hang bombs caliber 50-500 kg or incendiary tanks ST-500. Ventral holder designed for special items. Multi Lock Holders third the weight of the suspension provided or six bombs caliber 100 kg, or three calibers of 250 kg, or 500 kg of the same caliber. On the holder of the 2nd group could hang four bombs caliber 100 kg. Thus, the aircraft can be hung 28 bombs caliber 100 kg bombs or 13 caliber 250 kg or five bombs caliber 500 kg. Maximum payload mass was 3840 kg.
Missiles included UR Kh-23 air-to-surface (2 pcs.), SD R-3S air-to-air (4 pcs.), 240-mm high-explosive rockets S-24 (5 pcs.), 80-mm shells of the family of S-8 (100 pcs. in five 20-barrel cannon blocks B-8M) or 57-mm projectiles family of C-5 (160 pcs. in five 32-barrel cannon blocks UB-32 ). Artvooruzheniya consisted of one gun GS-23 machine gun with 400 rounds of ammunition in the forward fuselage front of the cabin. In addition, an external load the aircraft could carry up to five containers with guns GS-23 (supplied with each - 250 rounds).
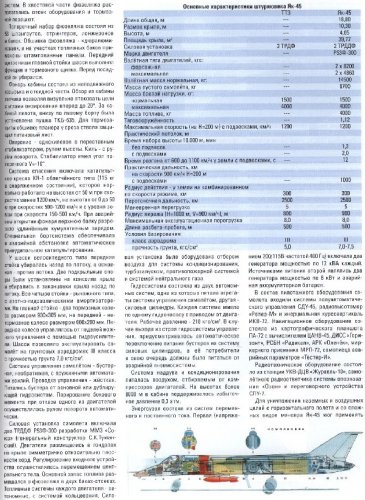
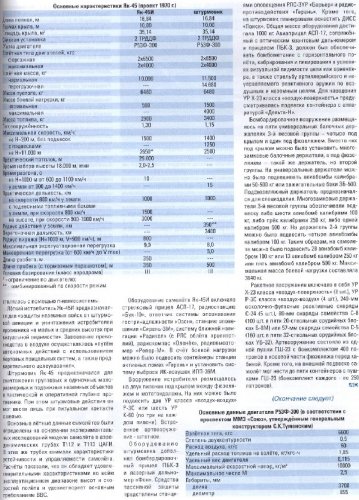
The main characteristics of the Yak-45 Yak-45I
Overall length, m 16.84 16.84
Wing span, m 10.00 10.00
Wing area, m ² 35.14 35.14
Power plant 2 x Turbofans 2 x Тurbofans
Engine specification R53F-300 R53F-300
Takeoff thrust engines, kgf
afterburner 2 x 6500 2 x 6500
Maximum 2 x 4000 2 x 4000
Take-off weight, kg
normal 10000 11500
Overload - 14680
Empty weight, kg 6480 6480
Mass of payload, kg
normal 500 1500
Maximum - 4000
Fuel weight, kg 2900 3400
Thrust-to-weight 1.3 1.15
Maximum speed, km / h:
at H = 200 m, without stores 1500 1400
with stores - 1250
at H = 11,000m 2650 2500
Service ceiling, m 25000 -
Time to climb to 18,000 m, min 2-2.5 -
Acceleration time, with
at H = 1000 м от 600 до 1100 км/ч 10 -
at ground level from 900 to 1400 km / h - 15
Range, km
at a speed of 800 km / h at sea 1000 1000
with external fuel tanks
from the earth at a speed of 800 km / h 1500 -
at altitude, velocity 900-1000 km / h 3000 -
Range near the ground, km - 350**
Ferry range, km - 3400
Радиус виража ( H = 1000 м, V = 900 км/ч), м 800 -
The maximum operating load 9 8
Manëvrennaâ overload (from 600 km / h to V max ) - 5
Take-off run, m 350 -
The mean free path (with brake parachute), m 350 500
Terms bases (class airport) III III
* - Limited engine:
** - combined speed mode.
Engine data R53F-300 (according to the prospectus MMZ "Union", approved by the General Designer S.K.Tumanskim)
Takeoff Thrust, kgf 6600
Bypass ratio 0.5
Flow rate, kg / s 60
Fuel consumption on the rise, kg / kg x h 1.85
The specific weight of the engine 0.115
The maximum dynamic pressure, kg / m ² 10000
The maximum number of M 2.5
Dimensions in mm
length 3700
diameter 855
A year later, in May 1971, a preliminary design has been prepared by attack aircraft Yak-45, and a light tactical fighter Yak-45I. While in the materials of the project, it was noted that the Yak-45I "is designed based on a light attack aircraft Yak-45." Now it was no longer a book, and as many as eight, seven of them were dedicated attack aircraft.
A light attack aircraft Yak-45 was designed to defeat moving and stationary ground targets in the tactical and immediate operational depth (up to 200 km behind the front line) in the field of vision. The materials of the project said that "high maneuverability and acceleration capabilities allow the aircraft to successfully overcome the front line of enemy air defenses at low altitudes."
This is what initially and demanded the military in 1971, TTT, realizing that maximum speed largely determines the shape of the aircraft. On the one hand a large flight speed increases the likelihood of overcoming the defense, on the other - reducing the likelihood of visual detection of small targets, increasing requirements for the qualification of pilots. Nevertheless, the customer would receive a Forward maximum speed of 1200 km / h at the surface (four blocks cannon NAR 80 mm C-8 on the outer suspension). It was at this time in the Sukhoi Design Bureau project was born of attack aircraft based interceptor (!) Su-15.
In the introduction to the project, which Yakovlev was signed July 22, 1971 (two months later than the fighter project), said that the Yak-45 "has the following characteristics: high maneuverability, high values of the maximum speed at all heights, the ability to use elementary prepared airfields, ease and speed of maintenance, relatively low cost of production, speed of action on call and timeliness of the attack. "
The selected circuit wing sweep having a large root compartment and relatively low in consoles allow without additional complications for good bearing properties as runways and at supersonic speeds, low inductance and light focus shift in going from subsonic to supersonic speed.
Diversity powerplant provides the minimum losses in the inlet and the nozzle engine, as well as provide certain advantages in maintenance, in the further modernization of aircraft and vitality. To reduce the cost of the machine, its assumed glider manufactured from common, mainly dyuralyumievyh alloys.
Aerodynamic design and layout of the machines have not fundamentally changed. However, the wing was split and lifted it slightly relative to the fuselage. The root of the wing now had no cross-V, and rejected the console down by 7 ╟. Several reduced sweep influx (73 ╟), and sweep angle brackets increased to 29 ╟. In this case, the root of the wing has a thin (3%). Airfoil - TSAGI P53-M with the relative thickness of 3-5% by the influx and 5% on the consoles. It is equipped with drooping ailerons, flaps and pull-automatic slats. The frame consisted of a main wing and rear spars, beams, stringers and ribs.
Fuselage - stringer monocoque circular with a diameter of 1.2 m in the tail section of the fuselage passed into an oval. In the forward part of the fuselage housed the front bay equipment, pressurized cockpit and pilot recess nose landing gear. In the middle part - zakabinny equipment compartment, two fuel compartments (tanks ╧ ╧ 1 and 2) and a niche main landing gear, which placed additional units, hydraulic and fuel systems. In the rear fuselage housed the equipment compartment and the brake parachute.
A set of cross-fuselage consisted of 53 frames, stringers, spars and beams. Fuselage - "dyuralyuminovaya" and in the areas of fuel tanks used stamped panel. Front panel niche main landing gear and served as a brake flap. Before planting, it was cleaned.
The canopy consists of a fixed canopy and folding parts. Overview of the cockpit allows you to visually engage targets with angles of sight ahead to 20 ╟. For the cockpit, at the bottom on the left side was installed gun TKB-635. For thermal lining glider at the muzzle defended titanium sheet.
Plumage - odnokilevym with adjustable stabilizer, elevator. Kiel - with rudder. The stabilizer had an angle cross-V -10 ╟.
The rescue system included ejection seat QW-1 lightweight type (115 kg curb weight), which worked fine on the heights of 50 m at speeds of less than 1200 km / h at an altitude of 0 to 50 m at speeds of 500-1200 km / h and from ground level at a speed of 150-500 km / h An abnormal opening of the upper beam of light sliced through an elongated shaped charge. Special bortsistema provide emergency automatic enforcement bailout.
In front bicycle landing gear strut was removed back in the flow, and the main - upstream. Two underwing supports were installed on the wing and wing tips were cleaned by back flow. All four stands - lever-type with nitrogen-hydraulic shock absorbers. On the home front - two brake tire size 930 ∙ 305 mm, non-braking on the front-wheel size 660 ∙ 200 mm. The front wheel was driven by foot pedals control with steering. Chassis allowed to operate the aircraft on unpaved airfields with Class III soil strength 7 kgf / cm 2 .;
Aircraft control system - booster, irreversible, with spring guns efforts. Control wiring - tough. Fed from the main boosters or redundant hydraulic systems. Parry side at the moment of failure of one engine carried rudder automatically.
The power plant consisted of two aircraft turbofan R53F-300 development MMZ "Union" (chief designer S.K.Tumansky). Engines housed in nacelles on the wing of the plane of symmetry of the chords. Regulation of the input device performs the movement of the central body. The main fuel tank in the fuselage housed in two tanks, compartments. Each engine fuel systems - self-contained, with a system of banding. The power plant was equipped with a selection of air conditioning systems, turbozapuskom, fire system and the neutral gas.
The hydraulic system consists of two independent systems, one of which is powered aircraft control system units, the other - power cylinders. Each system has one hydraulic pump driven by the engine. Operating pressure - 210 kgf / cm 2 .; In the event of failure of the hydraulic system control provides automatic switching power boosters on the system actuators, and its consumers, in turn, were to be powered by an emergency air system.
Turbocharging and air fed bleed air from the engine compressor. At altitudes of over 8,000 m in the cabin maintained pressure 0.3 atm.
Power unit consisted of a system of alternating and direct current. The first (voltage 200/115 V and frequency of 400 Hz) included two generators with a capacity of 12 kVA each. The sources of supply were the second two generators with a capacity of 8 kW and the emergency battery.
The structure of the aircraft navigation equipment consisted of semi-automatic control of the CDS-45 radar altimeter, "A frame-M" and inertial and heading SCR-72. Navigation equipment consisted of mapping the tablet PA-72-45 calculator TSANV, Diss "Horizon" RSBN "Radical" ARC "Olenyok" marker receiver MRP-72 recorder fault parameters "Tester-I".
Radio equipment consisted of a VHF-UHF station "Crane-10" aircraft transponder identification system "Ozone" and intercom SPU-7.
To destroy ground and air targets from level flight and maneuver with complex types of Yak-45 could apply bombing (including spetsboepripasov), rocket (managed and unmanaged), and artillery weapons.
By plane was provided for seven points of the suspension on the universal holders 3rd and 4th groups, as well as on the Multi Lock beam holders. Universal holders of the third group of CDD-have established a wing panels (4 pcs), and under the fuselage (1 pc.) They can be hung bombs gauges from 50 to 500 kg, incendiary tanks, universal gun pods, launchers with guided missiles and cannon blocks NAR. Two universal holder group 4 BD4-U installed between the pods under the wings and fuselage, another - under the fuselage instead of universal holders BDZ-U. They hung bombs caliber 1500 kg, special items and, in addition, under the wing - drop tanks with a capacity of 1300 liters each.
Under the fuselage and engine nacelles with spetsuzlov can be installed holders Multi Lock beamed third group MBDZ-K and to suspend or by six bombs caliber 50-100 kg, or three 250 kg bombs caliber model 62 or 54 in four models, or by two bombs caliber 500 kg.
Thus, bomber aircraft armament suspension provided:
Type Number, pcs
bombs caliber 50-100 10..22
bombs caliber 250 5..16
bombs caliber 500 3..8
bombs caliber 1500 1..2
incendiary tanks ST-250 3..5
spetsaviabomba 1..3
Aircraft missile guided weapons included SD air-to-surface and "air-to-air." Two missiles X-23 APU-68 were intended to hit small moving and stationary targets in the field of vision. The system of control - single-loop, hand, teamwork, according to the method of three points. Teams from the aircraft to the missile transmitted by radio command station "Delta-H" placed in a hanging container. More sophisticated missiles X-25 had a system of control and guidance with a laser.
UR K-13M was designed to destroy air targets in IMC and SMU. They hung on the wing holders with APU-13MT. Takeover target IR seeker pilot controlled to change the beep tone in the headset. SD K-60 (for the defeat actively maneuvering aircraft in close air combat) hung on the wing beam holders with APU-60.
Jet aircraft armament consisted of one hundred 80-mm rockets family of C-8 in five 20-barrel cannon blocks B-8M or four 420/266-mm (or 340/266-mm) NAR family of C-25 in the singly charged O-starting devices 25. Blocks B-8M can be suspended from all universal holders, and G-25 - only wing holders.
Artvooruzheniya aircraft included a fixed gun TKB-635 on the left side with ammunition 300 rounds of ammunition. Besides, under the wing can be hung four universal container SPPU-gun 22. In each container was placed deflected down to 30 ╟ automatic gun GS-23 with 260 rounds ammunition.
On account of the payload, the aircraft was provided for suspension of special removable container station "Geranium-UV" system clutter type PPIs and BPD command radio "Delta-H" system of laser illumination purposes "Spotlight" finder "Blizzard" (for SD-class "air-to-radar" X-58).
With the support of ground troops fighting the main objectives of the Yak-45 attack aircraft were to become a nuclear artillery, missile systems, tactical and operational-tactical and warehouses of ammunition and fuel, manual, platoon strong points, planes at airfields, radar stations control systems missiles and fighter aircraft , the troops in concentration areas and on the march, Hawk SAM battery and Nike Hercules, avtobronetehnika, etc. Most of these objectives will incapacitate conventional weapons. For precision bombing on a plane provided sighting aerobatic display IPP-72 onboard computer on the basis of "Orbit-15", a laser range finder "Background." Sighting and navigation system provided a bombing in level flight in a dive and pitch up. The yield of the target pilot carried out visually.
The efficiency of the Yak-45 in bombing (22 bombs caliber 100 kg bombs or 12 caliber 250 kg), and the combined use of various weapons (12 caliber bombs or four 100 kg bombs caliber 250kg and four containers with guns GS-23L) in a single flight was determined on the basis of two approaches for the same purpose. The estimated probability of hitting small targets bombs caliber 100 or 250 kg was 0.7-0.85 (except armored targets). The long goal (crossing, r / w compositions and columns) bombs caliber 100 and 250 kg - with a probability of 0.43-0.58 and 0.37-0.58, respectively. Theoretically, two Yak-45 main square and linear targets (infantry company and parking of aircraft, artillery and mortar batteries, a company of tanks and infantry on the march) caused damage to at least 30%.
By launching rockets S-25-O, the calculated probability of hitting small targets in non-armored one go was 0.85-0.97, and the shells of the family C-80 0.40-0.58. With the shooting of guns GS-23 is a danger of these goals in two Sunset was 0.85-0.96. Probability of defeat BMP or 20.3-cm howitzers in one go was 0.52-0.59. Application deflected downward GS-23 guns in pods SPPU-22 in one go ensured the defeat of small front-line targets queue length 2 with a probability of 0.92. TKB-635 gun hit small targets unarmoured with probability 0.5-0.7, and armored - with a probability of 0.43-0.46. The use of different weapons (eg, bombs and guns GS-23M) in an attack comes in two model the probability of hitting small targets increased and amounted to 0.8-0.93.
In combat missions in the tactical and operational-tactical areas of the Yak-45 could overcome jointly combat missiles and air defense fighter with a probability of 0.55-0.64. Combat use of special items on ground targets ensured at all altitudes and speeds in level flight, as well as pitching and dive.
Expected likelihood of ur X-23 cockpit radar at start in level flight was estimated as 0.4, and at the start of dive - 0.5-0.6. At the Kh-25 at the start of dive (25-40 ╟) circular error probability was estimated at 5-8 m using illumination station "Spotlight." To enhance the combat capabilities of SD X-25 in the future on an airplane is supposed to establish LTPS "Cairo".
To engage employees included the use of ground radar homing UR X-25MP and X-58. To search, target acquisition and start-up for undiscovered purposes served by direct radio direction finder board defense "Birch" (if it is matched with the GOS SD) or finder "Blizzard" in a hanging container. Range shooting ensured the defeat of the station Hawk missiles without entering its coverage.
The Yak-45 provides for special measures to enhance survivability. Attack aircraft fuselage consisted of separate, isolated compartments, and the layout of the compartments themselves screened vital units less important or less vulnerable units. Spaced along the wing engines reduced the probability of their simultaneous decommissioning of the fuel is also housed in two separated compartments. In emergency motors can be powered by any of them. To protect the fuel compartments of water hammer and reduce the loss of fuel through the holes, the inner surface of the compartments intended to cover a two-layer coating. Furthermore, as the production of fuel tanks have been filled with nitrogen. Landing gear provides a normal landing at one of the tires of lumbago. To protect the pilot's cabin has been welded from steel armor plates with a thickness of 4 to 8.5 mm. In addition, front and rear of its bottom-screened various hardware units. Hood canopy front protected bulletproof glass thickness of 45 mm, tilting of the lantern closed two-layer armor (outer layer - 3 mm steel, internal - 5-mm titanium).
At the preliminary design stage of the quantitative reliability of assemblies and systems Yak-45 were determined on the basis of statistical processing of information on failures and defects arising in aggregates and systems of Yak-28P. The reliability of the system and save the ejection seat QW-1 had already been proved by tests. The basic aircraft systems were backed up.
Calculations showed that the mean time between failures on equipment is 13 hours, mean time to failure on the airframe - 180-200 hours on the engine - 250 hours, and the aircraft as a whole (with one embodiment of the equipment) - 8-10 pm These figures correspond to reliability indicators of front-line fighters of those years on 4-5th year of operation.
Characteristics engine R53F-300 (1971)
Takeoff Thrust, kgf
afterburner 8200
Maximum 4860
Bypass ratio 0.5
Flow rate, kg / s 72
Specific fuel consumption, kg / kgf ∙ h
afterburner 1.97
the maximum 0.725
The specific weight of the engine 0.11
Weight, kg 900
The new version of light tactical fighter (in the first version of such a term was not yet) Yak-45I intended for "of air combat with enemy fighters and destroying its strike aircraft mainly on small and medium altitudes in all weather conditions, day and night." In addition, the aircraft could intercept air targets at prompting it to land, and destroy mobile and small-size ground targets.
It was noted that "feature of the aircraft is the small unit load on the wing and high power-to." The advantages of the machines were large supersonic speed, high agility, mobility, ease of maintenance, the possibility to operate from unpaved airfields with minimal facilities and supplies.
In the introduction to the project, signed by Alexander Yakovlev May 6, 1971, noted that "the Yak-45I is designed on the basis of a light attack aircraft Yak-45, which significantly reduces the cost of designing and manufacturing aircraft. Structurally, the planes are almost identical and differ in mainly the composition of equipment and weapons. "
The Yak-45I is to put the sighting and navigation system of radar "Pearl", coupled with the finders and TV-optical reticle. The complex provides a semi-automatic control of the aircraft in combat, on the route and landing, as well as an indication of flight parameters on the instruments panel-72 PNP-72 and the display on the windshield. Radar "Pearl" provided detection and target acquisition, target designation betrayed finders, optical-electronic bearing and homing missiles. The pilot also possessed a second channel targeting weapons systems from the helmet visor.
Information polukompas, part of the control system of director, figured autonomous landing trajectory and provide semi-automatic flight at low altitude (200 m) above the ground with a slope of relief to 10-15 ╟.
Navigation system provides fixes the aircraft relative to ground-based radio beacons in the polar coordinate system, piloting on the drive and broadcast radio stations and radio beacons, as well as the release of information to the ATC system.
Communications equipment provided bespodstroechnuyu link on VHF-UHF-band (radio station "Crane 10") and issue a response in the identification gosprinadlezhnosti (the defendant "Ozone").
Defense system signaled the pilot of irradiated ground and airborne radar with the issuance of the bearing (station "Birch-L") and defended the plane creating a launch-leading away of active and passive radio (station active jamming "Geranium-FSA" in container), as well as an IR interference (means of dipole emission and IR interference established in the bill of payload).
Built-in control electronics provide automatic control of aircraft systems and emergency registration parameters (recorder "Tester-I"). Total weight of the equipment was 1460 kg.
Two guns GS-23 23-mm cannon replaced by a TKB-645 30-mm. In this artvooruzheniya "moved" from the nose of the fuselage in zakabinny compartment and shifted to starboard. Box of 200 cartridges installed directly in front of the front fuselage fuel tank. In addition, under the wing could hang four containers of the CPC-23 GS-23 guns. Under the wing provided a four-point suspension of SD air-to-air melee K-60 (6 pcs.) Or K-55 (4 pcs.) Or K-13 (4 pcs.). To "work on ground targets" fighter weapons complemented bombs, incendiary rockets and tanks. The aircraft could carry up to four bombs caliber up to 500 kg, four 20-barrel gun unit 80-mm rockets family of C-8 (or pyatistvolnyh artillery unit 122-mm rockets S-13 family of four or NAR family of C-25).
All this, according to developers, enable easy front-line fighter Yak-45I successfully conduct a visual maneuverable air combat with enemy fighters and destroy its strike aircraft at low and medium altitudes in the PMU and SMU day and night. The materials of the project said that "the most important factor that ensured the Yak-45I fighter to win air superiority is its greater flexibility, which is achieved due to the large installed power, relatively low wing loading and the availability of effective air brakes."
It was especially noted that "to ensure air superiority at all heights and depths across the front line action Yak-45I should be complemented by an all-weather fighter with sophisticated weapons systems and equipment." That is exactly what happened. By the Air Force of the USSR as a result of the adoption of two types of fighters: easy MiG-29 and Su-27 heavy. Yakovlev Design Bureau also participated in the competition for the heavy fighter, and we hope that there is still an opportunity to tell our readers about the car and that was called the Yak-47.
Modification Yak-45 (attack) Yak-45I (fighter)
Wing span, m 10.30 10.30
Length, m 18.80 18.52
Height, m 4.65 4.60
Wing area m2 39.77 40.00
Mass, kg
Empty 8700 8830
Normal 14500 13900
Fuel 4000 4100
Engine Type 2 x R53F-300 2 x R53F-300
Thrust kgf
afterburner 2 х 8200 2 х 8200
Maximum 2 x 4860
Maximum speed, km / h
at height 1440 1200
sea level
Ferry range, km 2500
Range, km
at the ground 1000 1000
at cruising speed 2500
Range, km 300
Service ceiling, m 11000 11000
Max. G loading 8 9
Crew 1 1
Armament: combat load of up to 1,500 kg
(maximum - 4000 kg) 30 mm gun TKB-645
combat load of 620 kg on four
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
I'll keep tidying this translation up.
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
Andrei Yurgenson's original two part article attached in low res form.
Source:
Andrei Jurgenson, Yak-45: Attack aircraft & fighter (Аэрокосмическое обозрение Issue 5 & 6, 2005)
Source:
Andrei Jurgenson, Yak-45: Attack aircraft & fighter (Аэрокосмическое обозрение Issue 5 & 6, 2005)
Attachments
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
- Joined
- 21 May 2006
- Messages
- 3,002
- Reaction score
- 2,278
Thanks for the translation Overscan Could somebody please explain to me what TTT [
Regards
Pioneer
Is this similar to the U.S. Request for Proposal (RfP)?In 1971, the Air Force formulated the TTT for new aircraft - a promising front-line fighter (PFI). To the program involved all fighter KB countries - Mikoyan, Sukhoi and Yakovlev.
Regards
Pioneer
Last edited:
otxentero
Первым делом самолеты
- Joined
- 1 December 2012
- Messages
- 7
- Reaction score
- 1
Pioneer said:Thanks for the translation Overscan Could somebody please explain to me what TTT [] equates to? Is this similar to the U.S. Request for Proposal (RfP)? RegardsPioneerIn 1971, the Air Force formulated the TTT for new aircraft - a promising front-line fighter (PFI). To the program involved all fighter KB countries - Mikoyan, Sukhoi and Yakovlev.
Dear Sir, TTT stands for Тактико-технические требования / Taktiko-tekhnicheskoe trebovaniya, which is the Tactical & Technical Requirements.
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
Hi!
https://www.e-reading.club/chapter.php/1010126/52/Yakubovich_-_Neizvestnyy_Yakovlev._Zheleznyy_aviakonstruktor.html
http://airspot.ru/catalogue/item/yakovlev-yak-45
"In 1972, the Air Force considered the advance designs of advanced fighters made in the OKB Mikoyan, Sukhoi and Yakovlev. These were the projects of light fighters MiG-29 and Yak-45 and projects of heavy fighters T-10 and Yak-47. OKB AS Yakovlev, participating in the competition for the creation of a ground-attack aircraft and advanced fighters, probably suggested the creation of all three types of aircraft according to one aerodynamic scheme. This significantly reduced the costs of aerodynamic research and design. Moreover, the attack aircraft and the light fighter differed only in the composition of the equipment. On the one hand, it was profitable and the Air Force - such a close "kinship" would greatly simplify the training of pilots and the operation of a fleet of aircraft.
Today it is well known that the competitions ended. The life cycle of the winners has already passed for the second half, and they should be replaced by new aircraft. However, detailed and reliable information about the Yak-45 project became available for the first time. With the permission of the OKB named after AS Yakovlev, we publish materials on the project of this machine.
The outline design of the first Yak-45 variants was completed in July 1970. All of it was "contained" in one book - just over 50 pages and began with these words: "Taking into account the war in the Middle East and Vietnam, we developed a Yak-45 aircraft in The aircraft is characterized by large excess thrust, exceptional vertical maneuverability, which in combination with the small dimension of the aircraft, a large radius of action and supersonic flight speed at low altitude makes it possible to successfully carry out the combat mission as an assault, Taking into account the similarity of requirements for flight characteristics, the possibility of mass production of aircraft, simplification and cheapening of operation, both versions have the same design and aerodynamic configuration .The differences are in the composition of weapons, sighting and navigation equipment. "
Yak-45 was a single twin-engine mid-plane normal aerodynamic scheme with single-keystone and a bicycle-type chassis. The engines were located almost at half the span of the wing, and the two main wing spars in this place had the shape of a half ring, covering the motors from below. This arrangement gave certain advantages. First, this arrangement of engines significantly increased the survivability of the machine, reducing the likelihood of damage to two motors simultaneously. Secondly, maintenance was simplified, opening the approach to engines from almost any side. In addition, the issues of engine replacement were solved quite simply. There were also aerodynamic advantages: the losses at the inlet to the air intakes and on the nozzle cut were reduced."
"The light fighter Yak-45I was designed to "protect ground troops from assault aviation and destroy enemy fighters at small and medium altitudes with visual visibility." The conquest of superiority in the air was carried out "through autonomous actions using onboard targeting systems, as well as preliminary designation."
The Yak-45 attack aircraft was intended for the destruction of group and single small-sized and mobile ground targets in the tactical and operational depth of the enemy. At the same time he could conduct assault actions only with visual contact with the target. "
Yak-45 (attack aircraft) Yak-45I (fighter)
Wing span, m 10.30 10.30
Length of aircraft, m 18.80 18.52
Aircraft height, m 4.65 4.60
Wing area, m2 39.77 40.00
Weight, kg
Empty aircraft 8700 8830
Normal take-off 14500 13900
Of fuel 4000 4100
engine's type 2 TRDDF P53F-300 2 TRDDF P53F-300
Thrust kgf
Afterburner 2 x 8200 2 x 8200
Maximum speed, km / h
on high 1440 1200
Distance range, km 2500
Practical range, km
At the ground 1000 1000
At cruising speed 2500
Radius of action, km 300
Practical ceiling, m 11000 11000
Max. Operational overload 8 9
Crew, people 1 1
Armament(attack aircraft): Combat load up to 1500 kg , (Maximum - 4000 kg)
Armament(fighter): 30 mm gun TKB-645 , Combat load 620 kg per 4 suspension points
https://www.e-reading.club/chapter.php/1010126/52/Yakubovich_-_Neizvestnyy_Yakovlev._Zheleznyy_aviakonstruktor.html
http://airspot.ru/catalogue/item/yakovlev-yak-45
"In 1972, the Air Force considered the advance designs of advanced fighters made in the OKB Mikoyan, Sukhoi and Yakovlev. These were the projects of light fighters MiG-29 and Yak-45 and projects of heavy fighters T-10 and Yak-47. OKB AS Yakovlev, participating in the competition for the creation of a ground-attack aircraft and advanced fighters, probably suggested the creation of all three types of aircraft according to one aerodynamic scheme. This significantly reduced the costs of aerodynamic research and design. Moreover, the attack aircraft and the light fighter differed only in the composition of the equipment. On the one hand, it was profitable and the Air Force - such a close "kinship" would greatly simplify the training of pilots and the operation of a fleet of aircraft.
Today it is well known that the competitions ended. The life cycle of the winners has already passed for the second half, and they should be replaced by new aircraft. However, detailed and reliable information about the Yak-45 project became available for the first time. With the permission of the OKB named after AS Yakovlev, we publish materials on the project of this machine.
The outline design of the first Yak-45 variants was completed in July 1970. All of it was "contained" in one book - just over 50 pages and began with these words: "Taking into account the war in the Middle East and Vietnam, we developed a Yak-45 aircraft in The aircraft is characterized by large excess thrust, exceptional vertical maneuverability, which in combination with the small dimension of the aircraft, a large radius of action and supersonic flight speed at low altitude makes it possible to successfully carry out the combat mission as an assault, Taking into account the similarity of requirements for flight characteristics, the possibility of mass production of aircraft, simplification and cheapening of operation, both versions have the same design and aerodynamic configuration .The differences are in the composition of weapons, sighting and navigation equipment. "
Yak-45 was a single twin-engine mid-plane normal aerodynamic scheme with single-keystone and a bicycle-type chassis. The engines were located almost at half the span of the wing, and the two main wing spars in this place had the shape of a half ring, covering the motors from below. This arrangement gave certain advantages. First, this arrangement of engines significantly increased the survivability of the machine, reducing the likelihood of damage to two motors simultaneously. Secondly, maintenance was simplified, opening the approach to engines from almost any side. In addition, the issues of engine replacement were solved quite simply. There were also aerodynamic advantages: the losses at the inlet to the air intakes and on the nozzle cut were reduced."
"The light fighter Yak-45I was designed to "protect ground troops from assault aviation and destroy enemy fighters at small and medium altitudes with visual visibility." The conquest of superiority in the air was carried out "through autonomous actions using onboard targeting systems, as well as preliminary designation."
The Yak-45 attack aircraft was intended for the destruction of group and single small-sized and mobile ground targets in the tactical and operational depth of the enemy. At the same time he could conduct assault actions only with visual contact with the target. "
Yak-45 (attack aircraft) Yak-45I (fighter)
Wing span, m 10.30 10.30
Length of aircraft, m 18.80 18.52
Aircraft height, m 4.65 4.60
Wing area, m2 39.77 40.00
Weight, kg
Empty aircraft 8700 8830
Normal take-off 14500 13900
Of fuel 4000 4100
engine's type 2 TRDDF P53F-300 2 TRDDF P53F-300
Thrust kgf
Afterburner 2 x 8200 2 x 8200
Maximum speed, km / h
on high 1440 1200
Distance range, km 2500
Practical range, km
At the ground 1000 1000
At cruising speed 2500
Radius of action, km 300
Practical ceiling, m 11000 11000
Max. Operational overload 8 9
Crew, people 1 1
Armament(attack aircraft): Combat load up to 1500 kg , (Maximum - 4000 kg)
Armament(fighter): 30 mm gun TKB-645 , Combat load 620 kg per 4 suspension points
Attachments
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
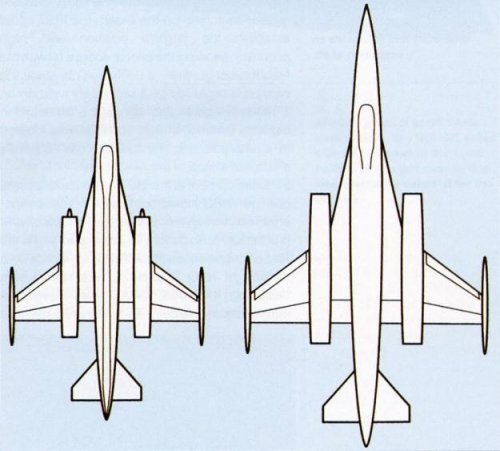
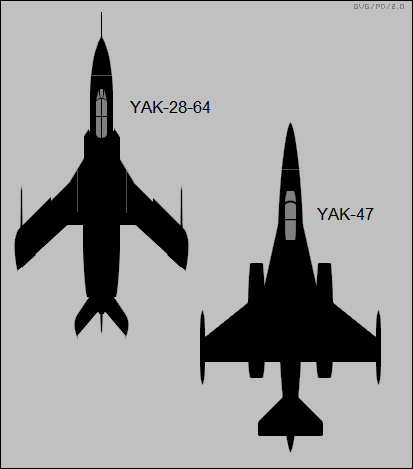
Yak-45 and Yak-47.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=193661;image
Yak-47.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=193663;image
http://alternathistory.com/samolet-yakovleva-yak-45-tak-i-ne-sostoyavshayasya-alternativa-su-27-i-mig-29
http://www.airvectors.net/avyak25.html
"The Yak offerings consisted of the lightweight "Yak-45" and the heavyweight "Yak-47", which were very similar configurationally, featuring twin engines and with something of a design flavor of the earlier Yak twinjet fighters. The requirements were actually met by the lightweight Mikoyan MiG-29 and the heavyweight Sukhoi Su-27. "
Yak-45/47 something looks like Republic F-15 proposal.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=193661;image
Yak-47.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=193663;image
http://alternathistory.com/samolet-yakovleva-yak-45-tak-i-ne-sostoyavshayasya-alternativa-su-27-i-mig-29
http://www.airvectors.net/avyak25.html
"The Yak offerings consisted of the lightweight "Yak-45" and the heavyweight "Yak-47", which were very similar configurationally, featuring twin engines and with something of a design flavor of the earlier Yak twinjet fighters. The requirements were actually met by the lightweight Mikoyan MiG-29 and the heavyweight Sukhoi Su-27. "
Yak-45/47 something looks like Republic F-15 proposal.
Attachments
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
Matej
Multiuniversal creator
blackkite said:Hi! Yak-45I. Engines are located under the wing.
http://warfiles.ru/show-64630-opytnyy-istrebitel-yak-45i-proekt-1972-g-rossiya.html
This drawing is mine. I even forgot I made it
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
Oh thanks a lot. Excellent drawing!! 
How do you think about this Yak-47 drawing which contributed by Lozko-san?
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=67140;image
I measured this drawing.
If top aircraft is Yak-45, Span=9.83m, Length=16.67m
If bottom aircraft is Yak-47, Span=10.28m, Length=18.61m
Do you have the size data of Yak-47?
How do you think about this Yak-47 drawing which contributed by Lozko-san?
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=67140;image
I measured this drawing.
If top aircraft is Yak-45, Span=9.83m, Length=16.67m
If bottom aircraft is Yak-47, Span=10.28m, Length=18.61m
Do you have the size data of Yak-47?
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
If Yak-28-64's span is 12.5m, Yak-47's span is 13m, length is 23.74m.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=582855;image
I believe in following data.
Yak-45 (attack aircraft) Yak-45I (fighter)
Wing span, m 10.30 10.30
Length of aircraft, m 18.80 18.52
Aircraft height, m 4.65 4.60
Wing area, m2 39.77 40.00
So I think that Yak-47's span is 13m, length is around 24m.
http://www.secretprojects.co.uk/forum/index.php?action=dlattach;topic=6288.0;attach=582855;image
I believe in following data.
Yak-45 (attack aircraft) Yak-45I (fighter)
Wing span, m 10.30 10.30
Length of aircraft, m 18.80 18.52
Aircraft height, m 4.65 4.60
Wing area, m2 39.77 40.00
So I think that Yak-47's span is 13m, length is around 24m.
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,748
- Reaction score
- 26,409
blackkite said:Oh thanks a lot. Excellent drawing!!
How do you think about this Yak-47 drawing which contributed by Lozko-san?
I measured this drawing.
If top aircraft is Yak-45, Span=9.83m, Length=16.67m
If bottom aircraft is Yak-47, Span=10.28m, Length=18.61m
Do you have the size data of Yak-47?
If you wanr to calculate the size of the Yak-47, start with an actual image of the Yak-47:
K-25 length is known, so its a relatively simple calculation.
Last edited:
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,716
K-25 was AIM-7. (Span : 1.02m, Length : 3.66m)
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/attachments/yak-47_1_0-jpg.193663/
https://www.secretprojects.co.uk/attachments/yak-47_1_0-jpg.193663/
Last edited:
Similar threads
-
-
-
-
Various Post-War Yakovlev (Yak) Projects & Prototypes
- Started by hesham
- Replies: 198
-