You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
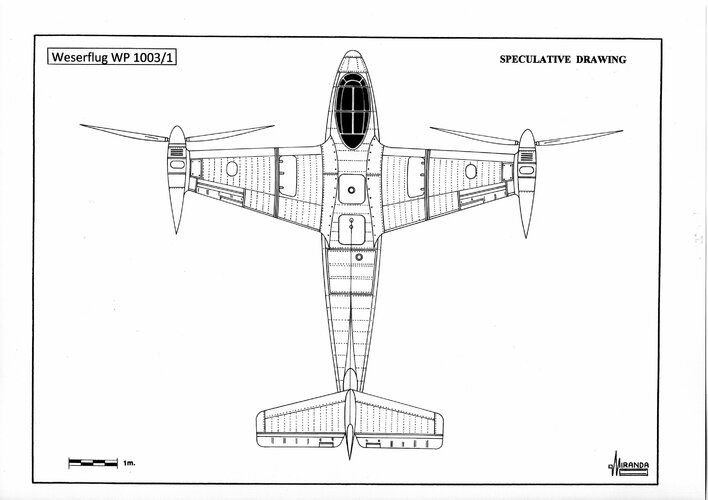
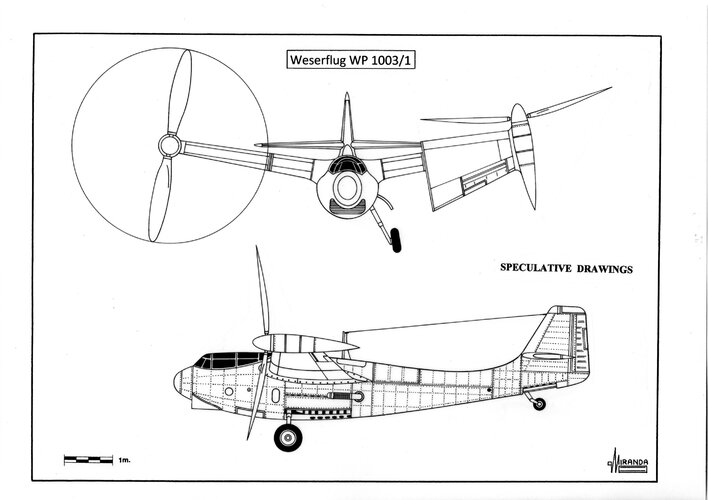
Weserflug WP 1003/I
- Thread starter Justo Miranda
- Start date
In March 1938, Weser Flugzeugbau G.m.b.H. proposed the construction of the WP 1003/1 convertiplane fitted with tilt rotors and tilt wings based on the technology developed during the construction of the Bf 163 SV1 prototype (D-IUCY).Does anyone know how this thing was supposed to be controlled in vertical flight?
The aircraft had VTOL characteristics without the restrictions of fixed rotor types.
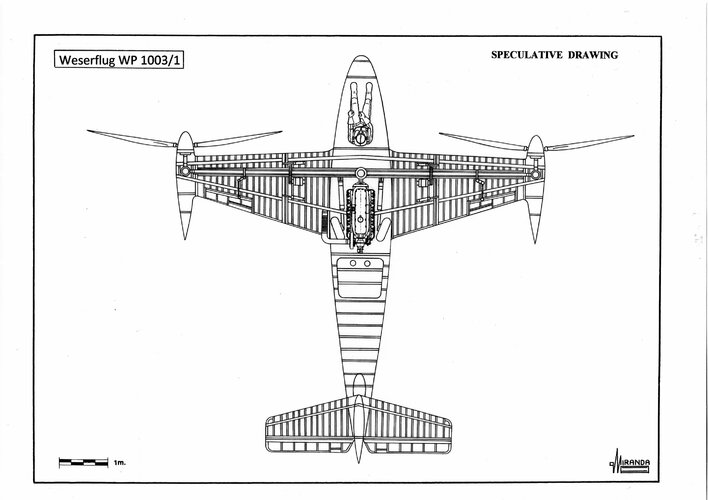
The rotor blades had been developed specifically for use as tiltrotors both in helicopter mode at 250 rpm and in the propeller mode at 600 rpm, but the cross-shifting and gearboxes between propellers not tolerate wing flexing.
The WP 1003/1 was expected to reach a speed of 650 km/h powered by a DB 600. The issue was the new engine had 900 hp. and that was just too much for the gearbox design and materials.
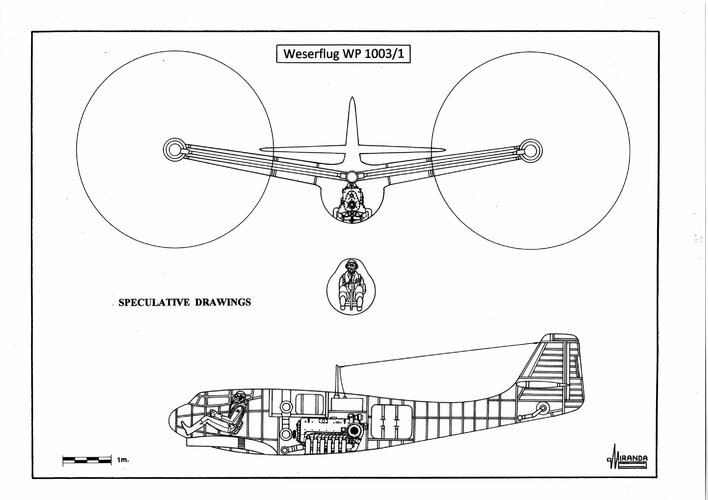
Control in hover was by means of longitudinal cyclic pitch on the rotors, roll would be controlled by differences in collective pitch.
Propellers are mounted in line along the wing and cannot provide control in pitch, so an additional rotor-control must be added. Starboard propeller rotated a clockwise direction and port propeller rotated counterclockwise producing symmetric slipstream effect over the wing areas behind the propellers and also gave better airflow over the center portion of the wing.
During the transition the rotors forcing air at high speed over wings , keeping the wing lifting at low speeds and reducing the stall speed. This helps to support aircraft weight.
The ailerons are tilted with the wings and change their function from roll control in level flight to yaw control in hover.
The full control over the aircraft throughout the entire range of speeds, from hovering to maximum, was too complex for its time and the aircraft was never built.
The Boeing VZ-2 was the first tilt wing aircraft to successfully complete a VTOL transition on August 13, 1957.
The refinement of the VTOL flight control system required a five-year development period, with an initial investment of $3 million, before the Vought XC-142A made its maiden flight on September 24, 1964.
But its VTOL technology was expensive when compared with the STOL transport Lockheed Hercules, which could carry three times the XC-142A payload over twice the distance.
Weserflug WP 1003/1 technical data
Wingspan with rotors: 11 m, length: 8.3 m, height: 3.1 m, rotors diameter: 4 m, power plant: one fuselage mounted Daimler Benz DB 600, 12 cylinders, inverted Vee, liquid cooled engine rated at 900 hp. with drive shafts transferring power to two rotor assemblies mounted on the wingtips to tilt 90-degrees from vertical to horizontal, max weight: 2,000 kg, max speed: 650 km/h.
Similar threads
-
-
Ambrosini S.1003 Twin-Engined Light Airplane Project
- Started by hesham
- Replies: 1
-
GERMAN CONCEPT PLANES VOLUME FIVE - VTOL 1933-1945
- Started by Justo Miranda
- Replies: 3
-
Dassault Etendard Prototypes and Projects
- Started by Jemiba
- Replies: 88
-