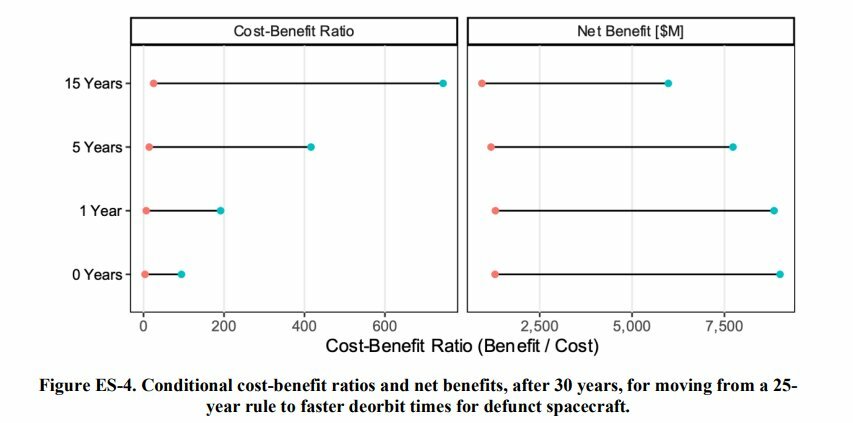
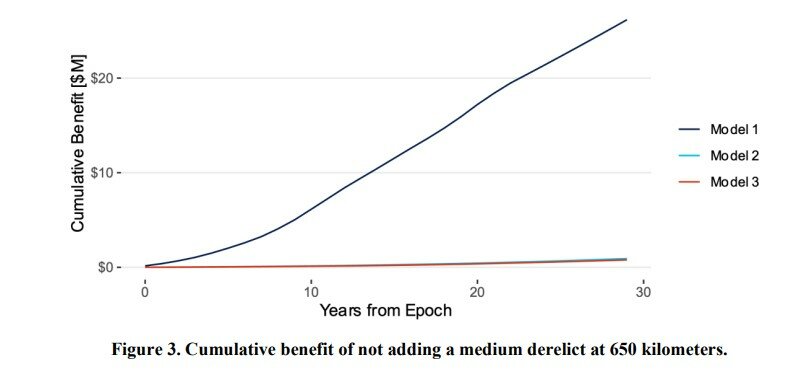
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
The Space Junk Agency we need
- Thread starter TomcatViP
- Start date
There’s already an anime of that; forgot the name.
I think ultimately the only cost effective solution will be huge solar farms with lasers the can impart thrust by burning the top surfaces of satellites as them come into range. It would be a slow process but it wouldn’t involve much reaction mass or energy input once you had the platforms set up. Slow constant burns should eventually push junk downwards over a long enough time frame. Anything super high risk that needs to be moved in a hurry would require a more hands on, less energy efficient mechanism.
I think ultimately the only cost effective solution will be huge solar farms with lasers the can impart thrust by burning the top surfaces of satellites as them come into range. It would be a slow process but it wouldn’t involve much reaction mass or energy input once you had the platforms set up. Slow constant burns should eventually push junk downwards over a long enough time frame. Anything super high risk that needs to be moved in a hurry would require a more hands on, less energy efficient mechanism.
- Joined
- 11 March 2012
- Messages
- 3,250
- Reaction score
- 3,179
There’s already an anime of that; forgot the name.
I think ultimately the only cost effective solution will be huge solar farms with lasers the can impart thrust by burning the top surfaces of satellites as them come into range. It would be a slow process but it wouldn’t involve much reaction mass or energy input once you had the platforms set up. Slow constant burns should eventually push junk downwards over a long enough time frame. Anything super high risk that needs to be moved in a hurry would require a more hands on, less energy efficient mechanism.
Are you saying that conventional explosives would not work well in space?
Would they provide too great a range of size of chunks of debris?
... running the risk that a few remaining bits of debris would be big enough to penetrate the atmosphere and hit the earth's surface intact?
What about clamping on retro-rockets to de-orbit space junk?
Last edited:
- Joined
- 11 March 2012
- Messages
- 3,250
- Reaction score
- 3,179
I found the "Space Sweepers" trailers on Netflix and they look interesting.
Thanks for the suggestion. I enjoyed "Space Sweepers." Parts may have been a bit corny, but overall it was a rollicking piece of space opera.
Last edited:
SpaceX has long emphasized the ability of its Starlink satellites to autonomously maneuver to avoid conjunctions. The company said that, between December 2021 and May 2022, Starlink satellites performed nearly 7,000 collision avoidance maneuvers, of which 1,700 were linked to Russian ASAT debris.
While SpaceX may be able to manage those conjunctions with its technology, it may be more difficult for other operators of satellite constellations. “If you didn’t have that automated system taking care of a spike like this, it could be really challenging to work it though,” he said.

Starlink satellites encounter Russian ASAT debris squalls - SpaceNews
Debris from a Russian ASAT test that caused “squalls” of close approaches to satellites earlier this year is now affecting Starlink satellites.
Biden-Harris administration on the right path to create an US Space Junk agency:
Link originally by @Forest Green in the US Space Force thread:

 breakingdefense.com
breakingdefense.com
We believe the new space age needs new rules. Because here on the ground, the regulatory frameworks we rely on to shape space policy were largely built for another era,” FCC Chair Jessica Rosenworcel, said in a press release accompanying the vote.
It is important to remember that while Rosenworcel joined Harris at the meeting in Oakland today, the FCC by law is an independent entity that does not answer to the White House.
As a first step, the FCC issued a “notice of inquiry” that “will examine the opportunities and challenges of space missions like satellite refueling, inspecting and repairing in-orbit spacecraft, capturing and removing debris, and transforming materials through manufacturing while in space.”
Link originally by @Forest Green in the US Space Force thread:

White House crafting rules framework for emerging space activities - Breaking Defense
The White House announcement comes after the FCC indicated it was wading into the murky regulatory waters of space-space services like satellite repair and refueling.
Last edited:
- Joined
- 9 October 2009
- Messages
- 21,979
- Reaction score
- 13,640
Startups Envision Lucrative Space Reentry Industry | Aviation Week Network
Companies say satellites could be refurbished and reused, addressing both costs and environmental concerns.aviationweek.com

The U.S. is getting serious about space junk
The FCC will force satellites to deorbit after five years, and a growing private industry around space junk is picking up steam.
- Joined
- 9 October 2009
- Messages
- 21,979
- Reaction score
- 13,640

Joint Commerce, STRATCOM commercial SSA pilot planned for December - Breaking Defense
That pilot project will use SPACECOM's Unified Data Library (UDL) as a data base, DalBello said, because Commerce is still in the early stages of creating its own cloud-based data storage capability, called the Open Architecture Data Repository (OADR).breakingdefense.com
shin_getter
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 1 June 2019
- Messages
- 1,110
- Reaction score
- 1,496

Britain’s first garbage truck for space could clear up junk with bear hug
Two UK firms are developing technologies to track down and capture the growing number of defunct satellites orbiting the planet.
If it is anime, there is planetesThere’s already an anime of that; forgot the name.
More Chinese debrits:

 www.space.com
www.space.com

Chinese rocket body disintegrates into big cloud of space junk
A Long March 6A upper stage has deteriorated into 350 pieces of debris following a Nov. 12 breakup event.

Space debris expert: Orbits will be lost—and people will die—later this decade
"Flexing geopolitical muscles in space to harm others has already happened."
Predicted near miss at 250m (800ft):

 www.space.com
www.space.com

Russian space debris forces space station to dodge, cancels US spacewalk
The Russian space junk is part of an old Fregat upper stage and will pass within a quarter-mile of the station at 11:17 a.m. ET.

Mysterious Russian satellite breaks up in orbit, generating cloud of debris
Kosmos 2499 broke apart in early January, according to the U.S. Space Force.
According to the European Space Agency(opens in new tab), about 36,500 pieces of space junk at least 4 inches (10 centimeters) wide zoom around our planet. And those are just the objects big enough to be tracked; Earth orbit likely hosts more than 130 million objects at least 1 millimeter across
southwestforests
ACCESS: Top Secret
- Joined
- 28 June 2012
- Messages
- 758
- Reaction score
- 1,229
Just keeps getting messier and messier up there. At orbital speeds even those 1mm fragments do damage.And those are just the objects big enough to be tracked; Earth orbit likely hosts more than 130 million objects at least 1 millimeter across
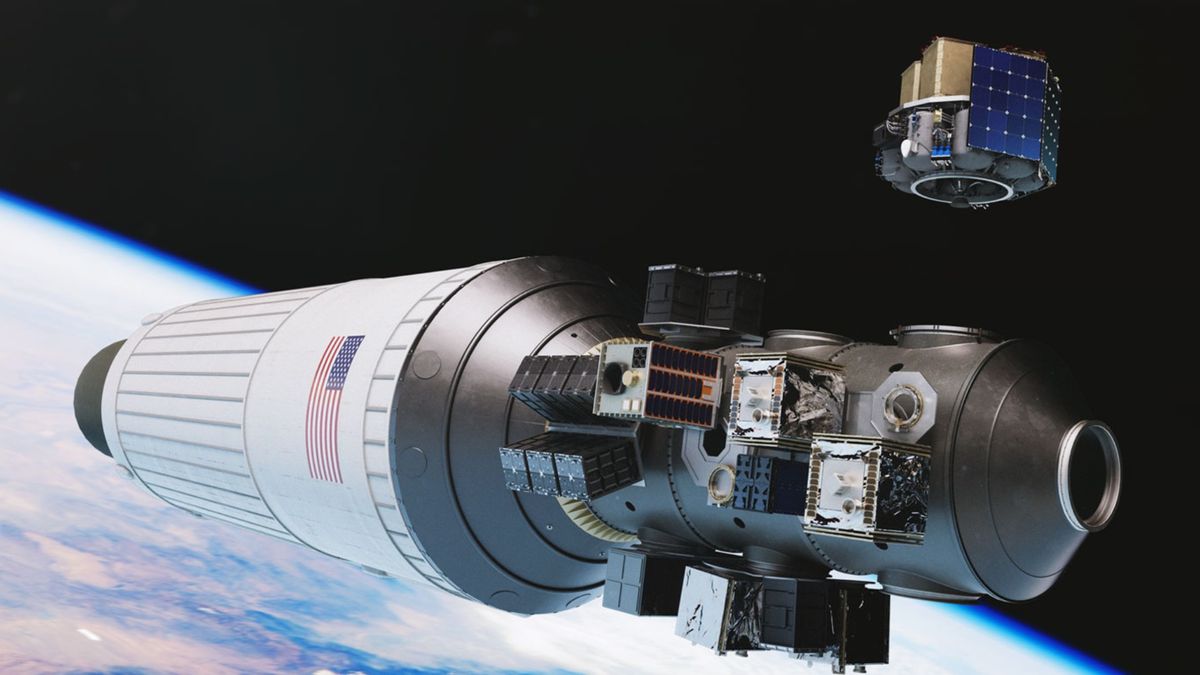
1st private Launcher space tug fails after launching on SpaceX rocket
Launcher plans to launch additional missions later this year, on SpaceX's Transporter-8 in June and Transporter-9 in October.
Let's hope that someone got a firm eye on this one (high energetic materials)

1st private Launcher space tug fails after launching on SpaceX rocket
Launcher plans to launch additional missions later this year, on SpaceX's Transporter-8 in June and Transporter-9 in October.www.space.com
Let's hope that someone got a firm eye on this one (high energetic materials)
So all they managed to do is add one more piece of junk…
France just last week became the ninth nation to publicly join the moratorium — following Canada, New Zealand, Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, South Korea, Switzerland, and Australia.

US call for halting kinetic anti-satellite tests gets boost from UN vote - Breaking Defense
France just last week became the ninth nation to publicly join the moratorium — following Canada, New Zealand, Germany, Japan, the United Kingdom, South Korea, Switzerland, and Australia.
TransAstra and Think Orbital propose launching capture bags in TransAstra Worker Bee spacecraft. After moving into the orbit of the targeted debris, the Worker Bee would transport the debris to ThinkOrbital’s ThinkPlatform.
The proposed ThinkPlatform would be about 37 meters in diameter with a volume of 4,000 cubic meters. ThinkOrbital plans to equip the ThinkPlatform with tools for inspecting, repairing and recycling objects.

TransAstra claims NASA contract for debris capture bag
Space logistics startup TransAstra won a NASA contract to manufacture a bag to capture orbital debris.
 spacenews.com
spacenews.com
Satellite television company Dish Network has been hit with a $150,000 fine for failing to properly dispose of one of its satellites, marking the first time federal regulators have issued such a penalty.
Nearly 10% of all large sulfuric acid particles, the main component of aerosols formed in the stratosphere, contained anthropogenic space metal hitchhikers. “That’s a big number, considering we didn’t know it would be abundant at all,” Abou-Ghanem said.
According to a collaborative report by McKinsey & Company and the World Economic Forum, the number of satellites orbiting Earth could triple in the next decade. At that rate, 50% of sulfuric acid particles could be contaminated, Abou-Ghanem said.

Spacecraft Are Sprinkling the Stratosphere with Metal - Eos
Metals from spacecraft reentry don’t simply vaporize and vanish. Scientists found them in the stratosphere.
 eos.org
eos.org
Researchers release open-source space debris model
MIT's Astrodynamics, Space Robotics, and Controls Laboratory (ARCLab) announced the public beta release of the MIT Orbital Capacity Assessment Tool (MOCAT) during the 2023 Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD) Space Forum Workshop on Dec. 14. MOCAT enables users to model...
phys.org
- Joined
- 21 January 2015
- Messages
- 12,157
- Reaction score
- 16,376
View: https://twitter.com/RocketLab/status/1759269717137842603
There it goes! ️
ADRAS-J is now in orbit, ready to start its mission of rendezvousing with an aging piece of space debris and observing it closely to determine whether it can be deorbited in the future.
Proud to be part of this innovative
@astroscale_HQ
mission studying ways to clean up space.
- Joined
- 21 January 2015
- Messages
- 12,157
- Reaction score
- 16,376
- Joined
- 21 January 2015
- Messages
- 12,157
- Reaction score
- 16,376
— UPDATE 21 FEBRUARY, 17:45 CET —
This is likely the final update prior to the reentry and break up of ERS-2. Consider following @esaoperations on X (formerly Twitter) for any further info.
ESA’s Space Debris Office currently predicts that the reentry of ESA’s ERS-2 satellite will take place at:
17:05 UTC (18:05 CET) on 21 February 2024
The uncertainty in this prediction is now just +/- 0.55 hours.

Connecting the Dots | Making light work of space junk removal
As inter-satellite laser links fuel the expansion of the largest constellations to date, a traditional satellite operator wants to use stronger lasers to clear the debris LEO megaconstellations leave behind.
 spacenews.com
spacenews.com
- Joined
- 11 February 2007
- Messages
- 2,570
- Reaction score
- 4,383
PhD scholarship looking at low cost de-orbit techniques:

 www.birmingham.ac.uk
www.birmingham.ac.uk

125th Anniversary Scholarships for Black British Researchers - University of Birmingham
This new scholarship scheme will fund up to 12 talented Black students who want to pursue a postgraduate research degree in Autumn 2024.
Read also here for the first embryonic development of a typical SJA:
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,663
- Reaction score
- 14,371
Someone has already beaten me to posting a link to Planetes/Debris Section...
Just no fatalities yet.
We've already had hits to the ISS!I think the loss of a high priority satellite or two would be enough once costs come down, but certainly a hit to the ISS would press the need home. All other human activity in space is sufficiently fleeting in significantly small platforms that the probability seem extremely low compared to the threat to satellites.
Just no fatalities yet.
I'm not sure it'd be possible to salvage a satellite without the owner knowing it. But I'm sure Spook types would be all over trying to pull it off.Good idea.
Even if we get orbiting trash trucks before some one dies ... the incentive might be high-value (think nuclear reactor) or very sensitive, next generation recce instruments. CIA will gladly pay a few million dollars for the latest Chinese spy camera. Bonus points if the orbiting trash truck can capture a Chinese spy satellite without the Chinese realizing that it has been "salvaged."
But the biggest hassle is matching trajectory and speed with the space junk you are trying to capture.
And may I suggest that final capture is best done with nets held out on arms away from the hull of the orbiting trash truck? Worst case scenario, during a poorly-timed capture, you burst a hole in a capture net, but damage misses the hull. This might be better done by small, net-slinging, un-manned drones matching orbit with space junk, netting it, then flying it back to the mother of all orbiting trash trucks. Trash trucks then sort various space junk into different nets until they have a large enough cargo to re-cycle (in orbit), de-orbit for burn-up on re-entry, or slow descent to an earth-based salvage yard. I suspect that the last option will be reserved for the most "sensitive" bit of space junk (e.g. the latest Chinese spy camera).
As mentioned, that anime is Planetes. It's GOOD and highly accurate about how physics works. Even goes into the horrors of a Kessler Cascade!I can foresee a rollicking (fictional) space-opera starring a multi-national crew flying a rattle-trap orbiting trash truck while conducting "salvage" operations of dubious legality and selling space junk to the highest bidder, whether that bidder be an orbiting salvage yard feeding raw materials to an orbiting shipyard building the next generation of freighters to Mars or an earth-bound spy agency trying to get their hand son the latest Chinese spy camera. Add in conflicting corporate agendas and you can create plenty of tension between characters.
- Joined
- 9 October 2009
- Messages
- 21,979
- Reaction score
- 13,640
Nasa ‘shocked’ by how close Russian spacecraft came to hitting satellite
A Russian satellite was just metres from hitting a Nasa counterpart in a “shocking” near-miss that could have put lives at risk, the US space agency has claimed.
- Joined
- 9 October 2009
- Messages
- 21,979
- Reaction score
- 13,640
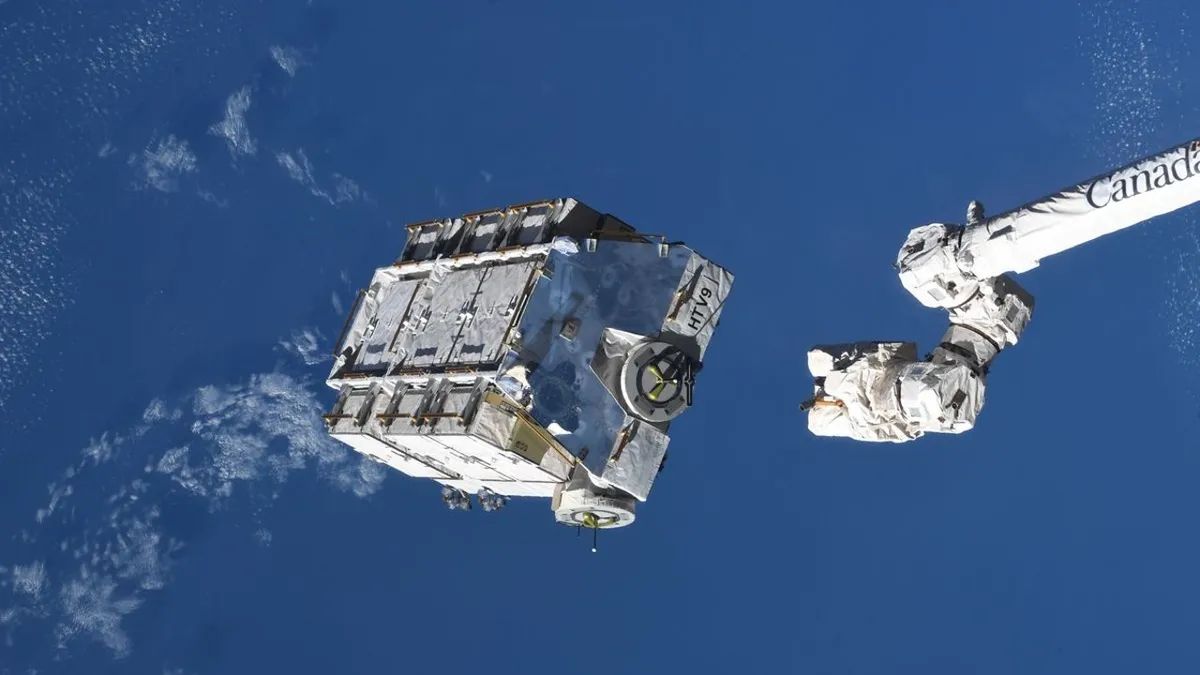

Object that slammed into Florida home was indeed space junk from ISS, NASA confirms
It was part of a pallet jettisoned along with 5,800 pounds of aging batteries back in March 2021.
Scott Kenny
ACCESS: USAP
- Joined
- 15 May 2023
- Messages
- 11,663
- Reaction score
- 14,371
Oops!
Object that slammed into Florida home was indeed space junk from ISS, NASA confirms
It was part of a pallet jettisoned along with 5,800 pounds of aging batteries back in March 2021.www.space.com
Guess NASA gets to foot the bill for this one...

France funds small satellite capture and inspection mission
France has awarded a Thales Alenia Space-led group a contract to capture and inspect a small satellite in a demonstration mission slated toward the end of the decade.
 spacenews.com
spacenews.com

Chinese satellite launch rocket breaks into hundred of pieces in orbit
Washington DC (UPI) Aug 10, 2024 - A Chinese Long March 6A rocket broke apart in low-Earth orbit and formed a debris field with hundreds of pieces, confirmed by U.S. Space Command. USSPACECOM has observed no immediate threats
www.spacedaily.com
Satellite monitoring company LeoLabs estimated there were at least 700 fragments created by the rocket's break-up.
While there's no immediate danger, it's possible that the fragments could eventually descend to where the space station and SpaceX's Starlink satellites are located.
Slingshot Aerospace said debris from the rocket poses "a significant hazard to LEO [low-Earth orbit] constellations below 800 km altitude."
"If even a fraction of the launches required to field this Chinese mega-constellation generate as much debris as this first launch, the result would be an untenable addition to the space debris population in LEO,"
Forest Green
ACCESS: Above Top Secret
- Joined
- 11 June 2019
- Messages
- 9,532
- Reaction score
- 17,497

Astroscale Demonstrates Advanced Fly-Around Capabilities in Space Debris Mission
Tokyo, Japan (SPX) Aug 14, 2024 - Astroscale Japan Inc. has successfully advanced its Active Debris Removal by Astroscale-Japan (ADRAS-J) mission, marking a significant milestone in commercial space operations. The ADRAS-J satellite
www.spacewar.com
Another in the series (breakup resulting from defective battery explosion) :

 spacenews.com
spacenews.com

Retired military weather satellite breaks up
A defunct military weather satellite has broken up in orbit and created more than 50 pieces of debris, the latest in a series of similar incidents.
 spacenews.com
spacenews.com
I should have packed my umbrella

 www.al.com
www.al.com

Fireballs seen over Alabama: Were they meteors or a Chinese satellite?
Photos came from observers in a cluster of Southern states including Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, and Georgia.
- Joined
- 21 January 2015
- Messages
- 12,157
- Reaction score
- 16,376
In late March 1972, the Soviet Union's Cosmos 482 was launched. But that attempted Venus probe ran amuck during its rocket-assisted toss to the cloud-veiled world. Major elements of that failed craft remained in Earth orbit.
The upper stage of the Soyuz booster launching that Venus probe cut off prematurely, leaving the payload marooned in Earth orbit. But there is new news for this old probe: "In about two weeks from now, on or near May 9-10, an unusual uncontrolled reentry will happen." That's the report from satellite watcher Marco Langbroek of the Netherlands. He has been taking telescopic looks at the errant, Earth-circling Cosmos 482 remains for numbers of years.
What’s ahead is the reentry of the Cosmos 482 descent craft – the landing module of the errant Soviet Venera mission that failed over 53 years ago.
And one hot topic to ponder is whether that landing module intended for Venus, custom-made to withstand reentry through the thick Venus atmosphere, might survive reentry through Earth's atmosphere intact.

A failed Soviet Venus lander will fall back to Earth after being stranded for 53 years
"In about two weeks from now, on or near May 9-10, an unusual uncontrolled reentry will happen."
Similar threads
-
-
EU to build secure satellite communication constellation IRIS2
- Started by Flyaway
- Replies: 3
-
-
-
NASA, Partner Space Agencies Amass Global View of COVID-19 Impacts
- Started by Flyaway
- Replies: 0