Blitzer9856
ACCESS: Restricted
- Joined
- 13 August 2019
- Messages
- 48
- Reaction score
- 66
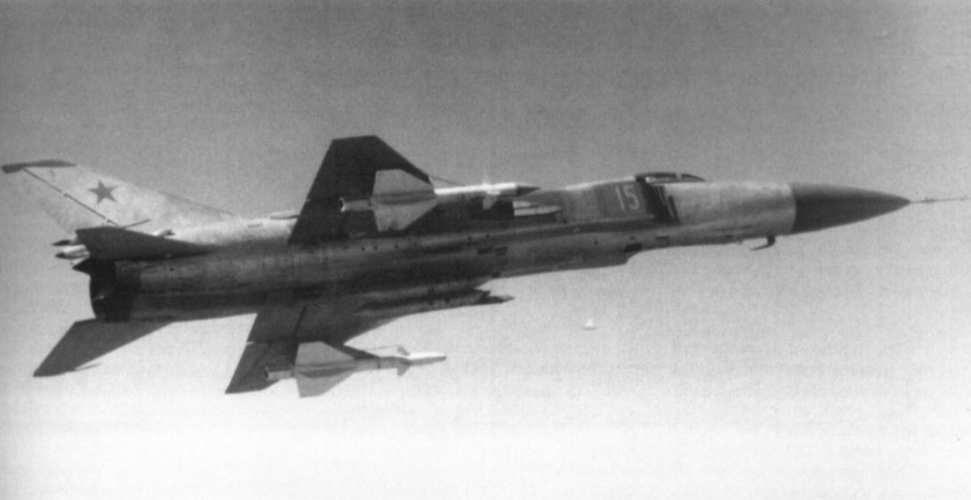

(R-98MR under the right wing, R-98MT under the left wing)
I was kind of surprised when I didn't find a thread on this missile. I decided to compile the information I personally know about it and start a thread.
From my personal writing:
The R-98 used to be the main weapon of the Su-15TM Flagon interceptor. Its semi-active radar-homing derivative was the one used to shoot down the Korean Airliner during the year of 1983.
Originally conceived as the R-8, it was soon modified to the R-8M ("M" for "modifitseerovannaya" (modified)), made compatible with aircraft equipped with the Oyrol radar, mostly used on the Sukhoi Su-11 interceptor.
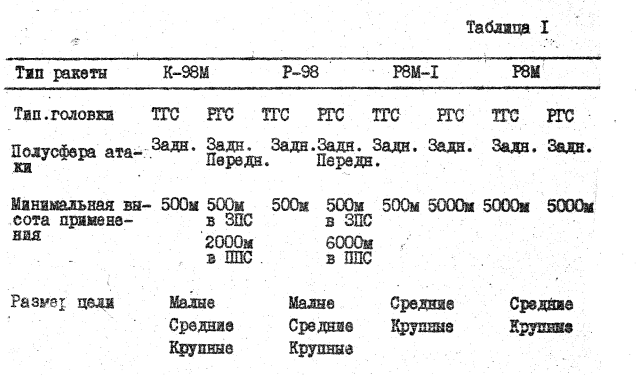
The R-8M, also came in 1961 in two variants: the R-8MT, and the R-8MR (IR and SARH respectively). Those were also improved into the R-8MT1 and R-8MR1, which saw an increased operational altitude envelope, to 300 m - 23,000 m and it is thanks to the improved autopilot and newer seeker heads; especially the R-8MT1, the new IR seeker head gave it round-the-clock capability. Changes have also been made to the missiles' airframes, featuring reinforced wings enabling them to turn tighter at low altitudes.
Two years later (in 1963), the R-98 was conceived as the main weapon of the Su-15. Based on the older R-8, new models of each the IR and SARH deriatives were conceived. The objective was to improve on their reliability and nose immunity to countermeasures, as well as increasing their power supply. The changes that ocurred were promising; the IR version became all-aspect (beat the US by 15 years in all-aspect IR missile seekers!), featuring the new TGS-14T seeker-head, while the SARH version received the more reliable PARG-14-VV. The autopilot and fuse were also improved, and the rear-fairing was reshaped to become perfectly cylindrical instead of the tapered design. The new missiles were designated R-98R and R-98T. Another important change was the new PRD-143 rocket motor, which unlike the older PRD-141 of the R-8, produced 13,400 kgf of thrust instead of 11,200 kgf.
As the Su-15 interceptor evolved into the Su-15TM, so did the R-98. A new PARG-16 semi-active radar-homing seeker head was installed in the R-98R which improved its reliability. Other than that however, not much changed. The new missiles were designated R-98MR and R-98MT (SARH and IR respectively). The main changes were to make the previous R-98s compatible with the Taifoon-M radar of the Su-15TM.
The R-98MR was capable of engaging targets from 2,000 - 21,000 m in head-on mode, and from 500 m - 24,000 m in pursuit mode, and its maximum kill range was 24 km in head-on and 16 km in pursuit.
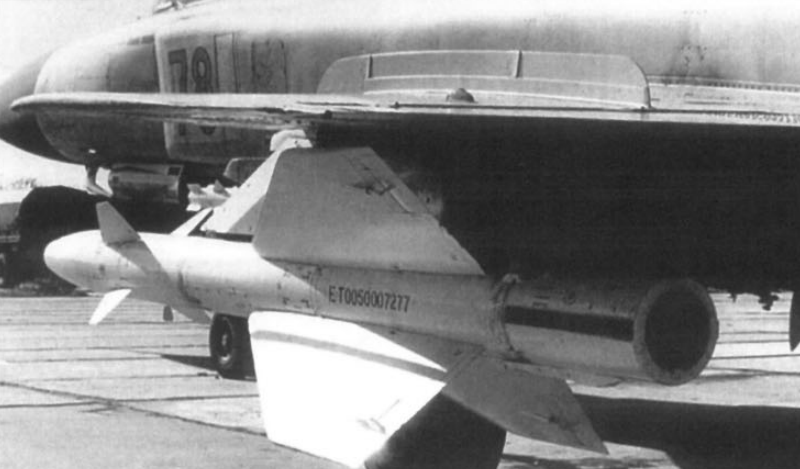
These missiles were usually loaded under PU-2-8 racks. The usual setup was two GSh-23 guns in two gunpods, R-60/R-60M dogfight missiles and two R-98MR or R-98MT AAMs or one of each (so 2 x R-60/R-60M + 1 x R-98MR + 1 x R-98MT sometimes).

Quoting:
The usual setup was two R-60/R-60M dogfight missiles and two R-98MR or R-98MT AAMs or one of each (so 2 x R-60/R-60M + 1 x R-98MR + 1 x R-98MT sometimes).
Despite this, in some cases the Su-15TM had the APU-60-2 / APU-60-II launchers which allowed it to carry four R-60/R-60Ms and two R-98s, bringing the count to six missiles.
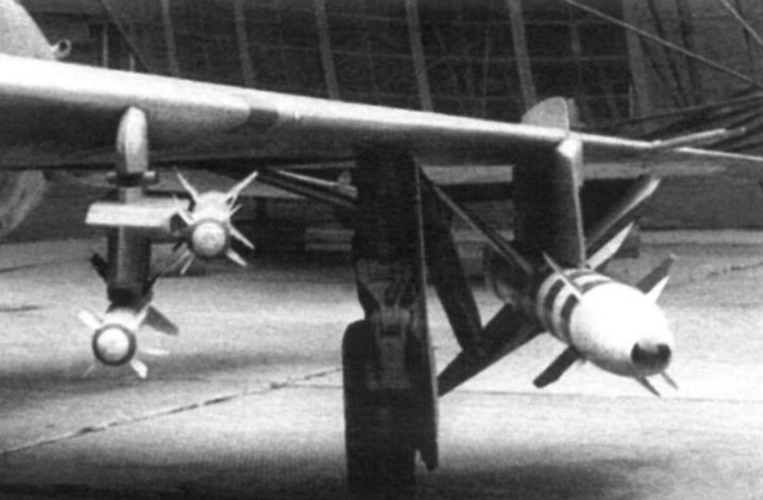

I think it's impressive that the USSR had all-aspect heat-seeking missiles in 1963, although possibly the worst ones in history.
The specifications for the R-98MR are as follows, from my information:
- Length: 4.18 m (164.56 in)
- Wingspan: 1.22 m (48 in)
- Body Diameter: 275 mm (12.2 in)
- Weight: 285 kg (628 lb)
- Speed: Mach 2
- Burn time: 2.5 - 6s
- Flight time: 40s
- Propulsion: PRD-143 single-stage solid rocket propellant motor (thrust: 13,400 kgf)
- Warhead: 40 kg (88 lb) HE
- Guidance: Semi-Active Radar-Homing
- Range: 24 km max (15 mi)
- G overload (launch limit): 3G
- G overload (target): 3G
- G overload (Air): 14G
- IRCM: No
- ECCM: No
- Aspect: All-Aspect
Last edited: