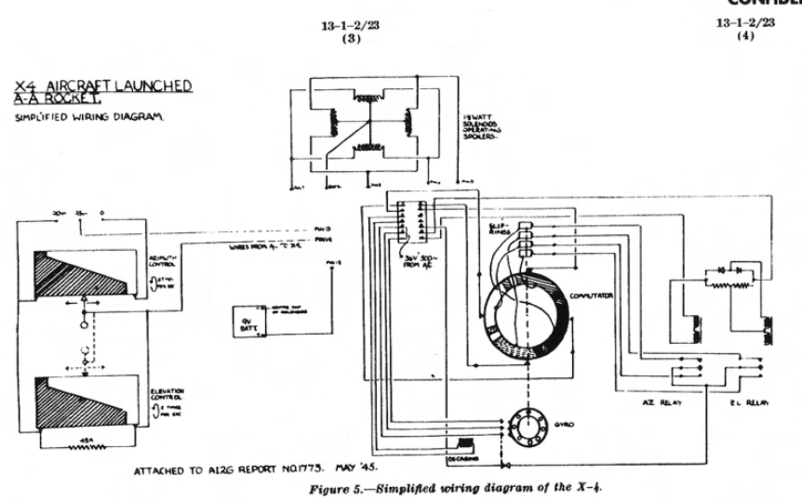
As far as its importance to development of other AAM's, the X-4 was a technological dead end that NOBODY copied in any way. The guidance system was dumped as unworkable. The Kransch acoustic proximity fuze was not proceeded on or copied by anyone. The missile being subsonic (and there's ZERO evidence to show it could exceed Mach) made it a worthless example compared to postwar development efforts into an AAM.
According to the video, the French kept on working on this design until 1950, so either the video is wrong or you. Dave_sic linked his sources, you migh go through them or bring your own evidence.
They did do some testing as the AA 10 with it. However, they found its low speed, MCLOS guidance, use of liquid fuel, and unreliability all traits they couldn't get past. See:
La Saga des Missiles Européens for example. The whole program was dropped by 1951 as far better AAM's were close to being introduced into service. Dilandu is correct in stating that any developments the French made were found to be unworkable with systems similar to the X-4.
It would be competing programs that the French did adopt for an AAM rather than use German wartime technology.
The US did look at the Kranch fuze at Wright Field briefly under one of the MX series programs (I have a list somewhere of the exact program number) but that program was brief and nothing came out of it.
As for the US, they had no reason to copy or test the X-4 as their own programs into an AAM in 1945 were ahead of the Germans in any case:
On March 8, 1945 the first live fire test against a TDC-2 target drone of a Gorgon IIA using TV MCLOS took place off Cape May NJ. The system was the same as used successfully on the Bat and Pelican guided bomb. The Navy’s project engineer, Cdr. Moulton “Molt” Taylor, reported that this guidance system was unworkable against an aerial target where closing speeds were too high for human mind and hand-eye coordination to match the speed of response needed to make it work. This launch represents the first time in history that a guided air-to-air missile had been tried in a live fire test against a target.
The USAAF, likewise adopted the NACA's test missiles into guidance at Wallops Island VA as the JB-3 Tiamat in late 1944. It too was in advance of the German missile using a variety of guidance systems like semi-active and active radar homing, TV MCLOS and MCLOS control. This was followed closely by the Ryan AAM-A-1 Firebird AAM.
The Russians immediately after the war didn't do much towards developing an AAM, and when they did it was not based on German wartime technology. The British, likewise, used homegrown technology, not captured German to develop their early AAM's.