- Joined
- 25 June 2009
- Messages
- 14,754
- Reaction score
- 6,155
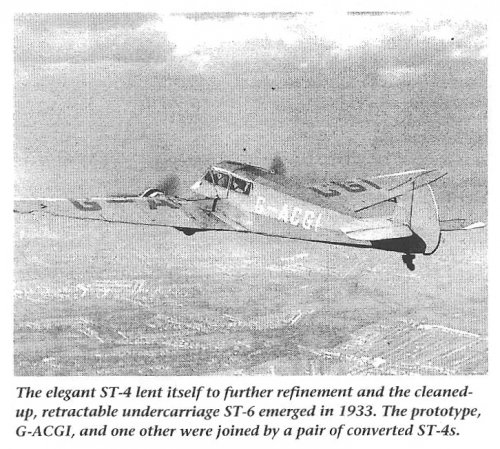
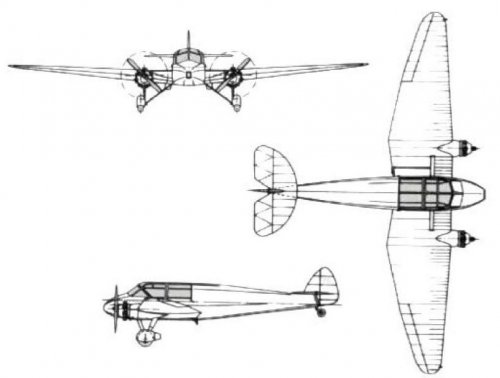
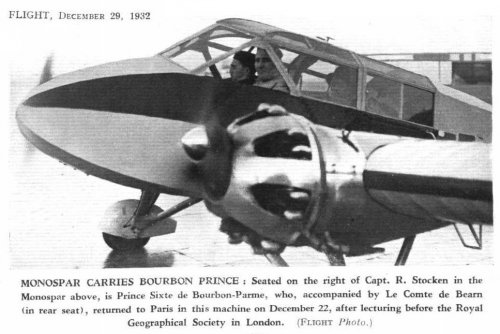
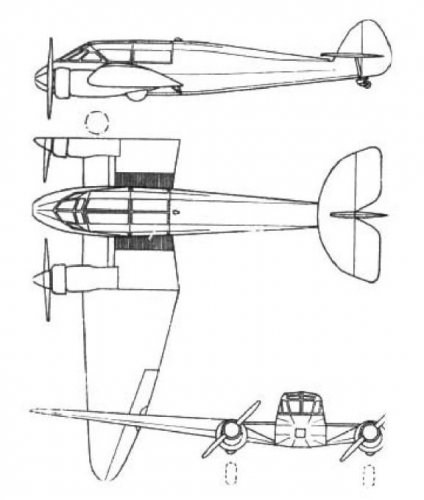
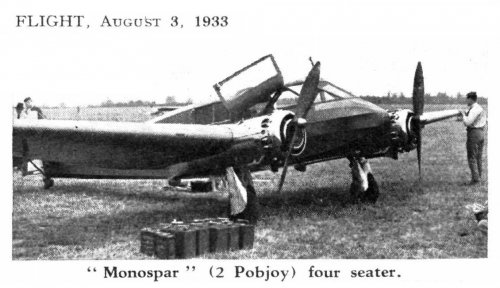
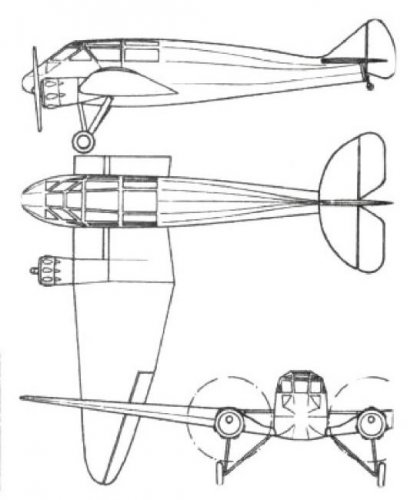
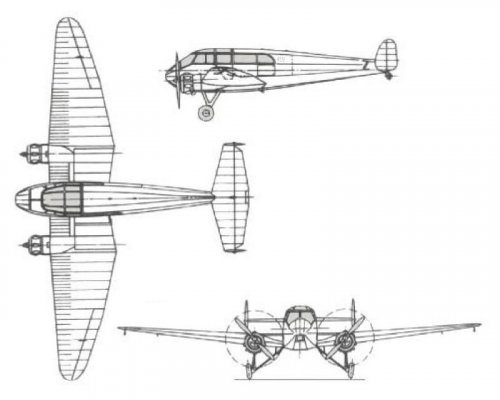
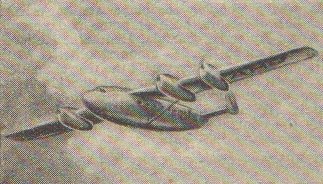
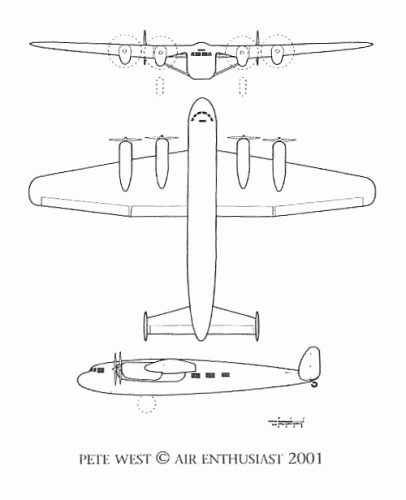
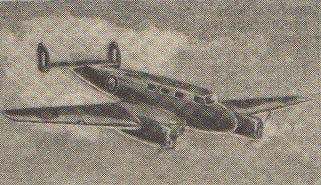
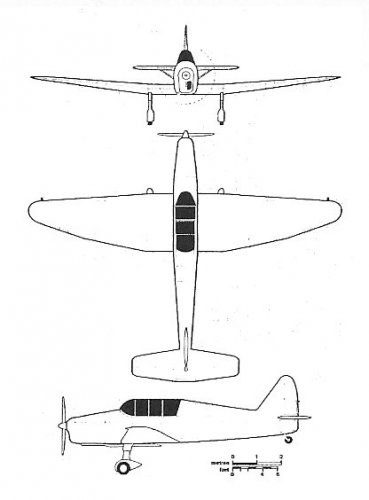
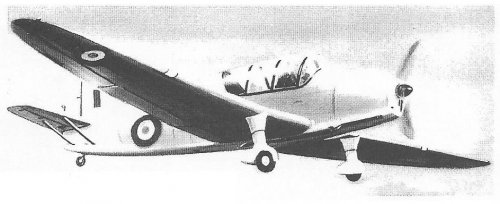
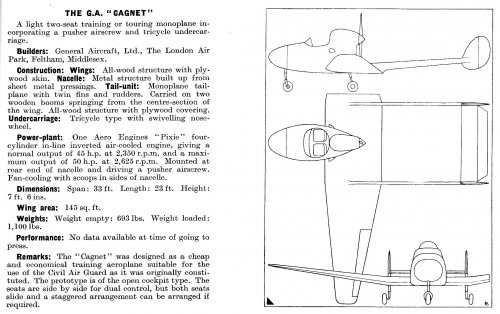
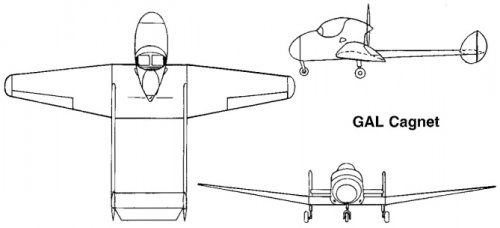
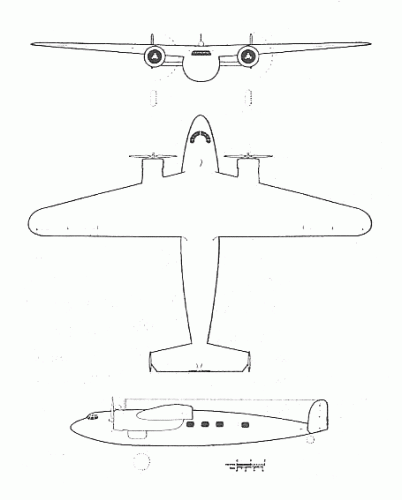
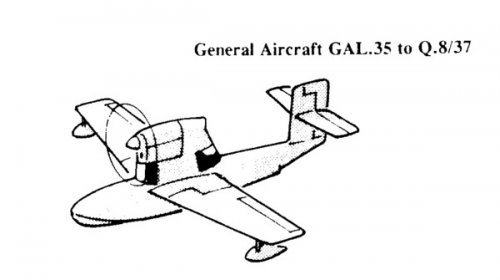
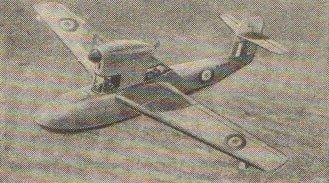
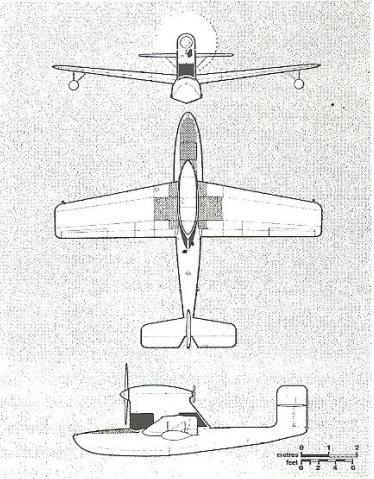
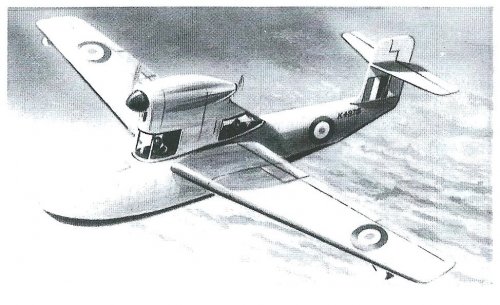
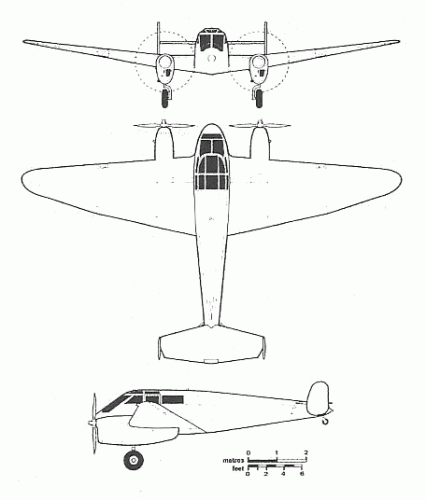
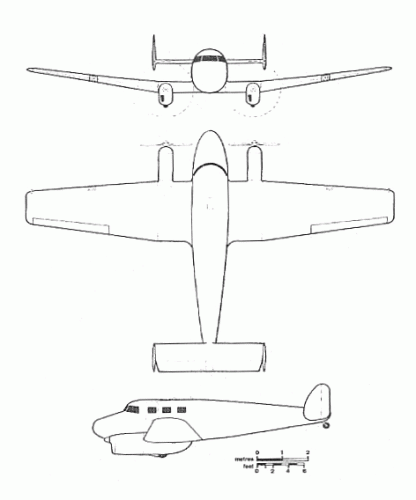
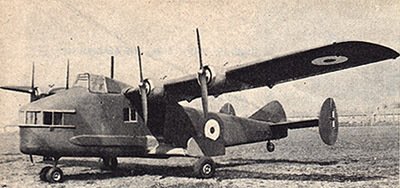
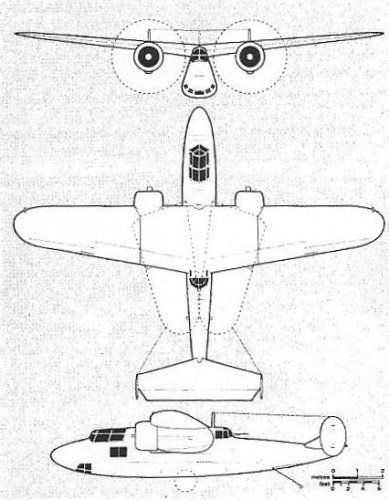
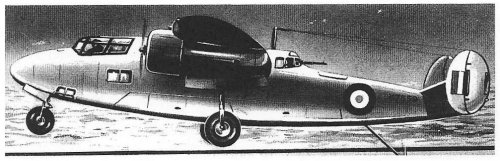
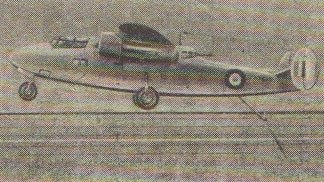
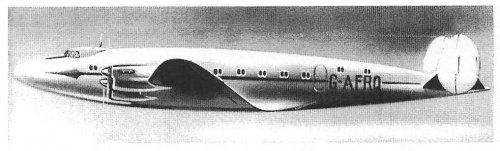
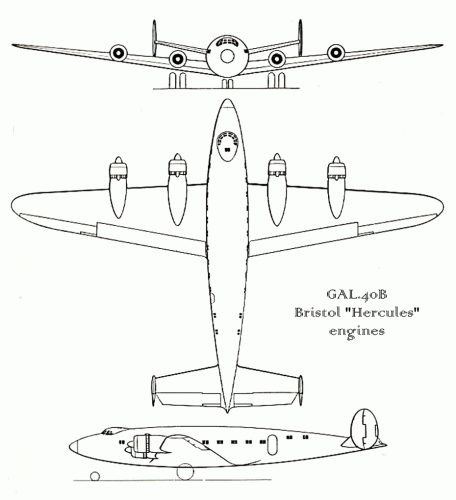
The Mono-Spar Co., Ltd., was formed in London in 1929 by Swiss-born inventor Helmut J. Steiger to design and build aircraft wings according to a new technique he had developed. Then on 27 February 1931 he formed The General Aircraft Co., Ltd., the purpose of which was to undertake production of aircraft using his 'Monospar' wing design.
All the aircraft that were produced under Stieger's helm were developed by his Mono-spar company but built by his General Aircraft company. All carried the name commercial "Monospar" and used "ST." designations to denote Stieger designs. For instance, design ST.4 was casually refered to as the "Monospar ST.4", or design ST.25 as the "Monospar ST.25 Universal", without it actually referring to a company name, as has often been thought. They were actually the General Aircraft ST.4 "Monospar" and General Aircraft ST.25 "Monospar Universal", which is evidenced notably by (1) period advertisements, (2) the absence of a hyphen in the word "Monospar" (indicating the commercial name and not the designing company's name) and also (3) civil register entries.
In the following pages, some decisions were made for clarity purposes: the early Stieger designations used Roman numerals (ST.I, ST.II etc.) have been replaced by Arabic numerals (ST.1, ST.2, etc.) as was customary in period publications, anyway; the "G.A.L." designations have been simplified as "GAL.", both for readability purposes and also better indexation in search engines; and measure units were simplified in specification figures ("lb" instead of "lbs.", "mph" instead of "m.p.h.", etc.).
ST.1
Type: Monospar wing
Built: 1929
Built by: The Mono-Spar Co., Ltd., London
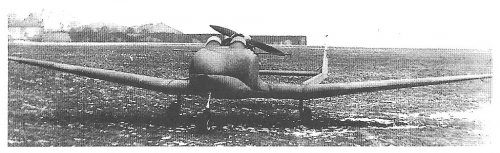
The ST.1 was a new type of cantilever wing developed by Swiss-born H. J. Stieger. It was ordered for testing by the British Air Ministry.
All the aircraft that were produced under Stieger's helm were developed by his Mono-spar company but built by his General Aircraft company. All carried the name commercial "Monospar" and used "ST." designations to denote Stieger designs. For instance, design ST.4 was casually refered to as the "Monospar ST.4", or design ST.25 as the "Monospar ST.25 Universal", without it actually referring to a company name, as has often been thought. They were actually the General Aircraft ST.4 "Monospar" and General Aircraft ST.25 "Monospar Universal", which is evidenced notably by (1) period advertisements, (2) the absence of a hyphen in the word "Monospar" (indicating the commercial name and not the designing company's name) and also (3) civil register entries.
In the following pages, some decisions were made for clarity purposes: the early Stieger designations used Roman numerals (ST.I, ST.II etc.) have been replaced by Arabic numerals (ST.1, ST.2, etc.) as was customary in period publications, anyway; the "G.A.L." designations have been simplified as "GAL.", both for readability purposes and also better indexation in search engines; and measure units were simplified in specification figures ("lb" instead of "lbs.", "mph" instead of "m.p.h.", etc.).
ST.1
Type: Monospar wing
Built: 1929
Built by: The Mono-Spar Co., Ltd., London
The ST.1 was a new type of cantilever wing developed by Swiss-born H. J. Stieger. It was ordered for testing by the British Air Ministry.







![ST.3 [G-AARP].jpg](/data/attachments/91/91668-55b2744f5db7d89b206d2e335df14634.jpg)