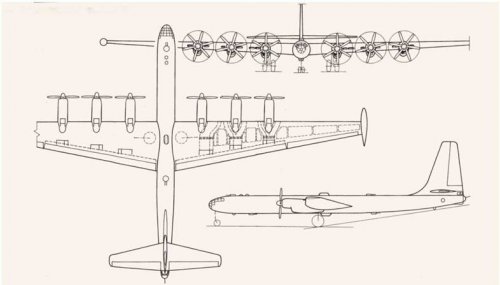
There's a photo of a model of the Il-26 bomber in Buttler's Soviet Secret Projects, but very little dimensional info. I guess it to have been in the Tu-85 or B-36 size, based on its powerplants & wing area. Anyone have a 3 view &/or dimensions on this proposal? I did a search thru here but came up empty.
You are using an out of date browser. It may not display this or other websites correctly.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
You should upgrade or use an alternative browser.
Looking for Ilyushin Il-26 info
- Thread starter frank
- Start date
Regrettably in OKB Ilyushin was not such archivist, as V.RIGMANT in OKB Tupolev. In available publicly press until it was published neither drawings, nor exact sizes Il-26.
The Known me only that in 1947-1948 in OKB-240 (Ilyushin) parallel with OKB-156 (Tupolev) were winnowed studies on plane of the class long-range heavy strategic bomber with four and six times engine. The Project OKB-240 was executed on classical scheme, as midwing with stright wing of the big lengthening. For increase of range of the flight in project was an aplying carriage with additional thrown after take-off under wings wheel-strut, allowing reduce the mass to designs of the bomber.
Work on project discontinued in 1948, given project has terminated work Ilyushin on distant bomber with piston engine.
Crew - 8-11
Mass of the combat load - 20000kg.
Engines - V.KLIMOV's (4200 hs) or M-51 M.MASLENNIKOV's (4000 hs).
max speed 650km/h, cruise 400km/h.
Range before 12000km.
service ceiling 11000km.
Source: S.GANIN A.KARPENKO V.KOLNOGOROV " Bastion "part 1, str.59.
The Known me only that in 1947-1948 in OKB-240 (Ilyushin) parallel with OKB-156 (Tupolev) were winnowed studies on plane of the class long-range heavy strategic bomber with four and six times engine. The Project OKB-240 was executed on classical scheme, as midwing with stright wing of the big lengthening. For increase of range of the flight in project was an aplying carriage with additional thrown after take-off under wings wheel-strut, allowing reduce the mass to designs of the bomber.
Work on project discontinued in 1948, given project has terminated work Ilyushin on distant bomber with piston engine.
Crew - 8-11
Mass of the combat load - 20000kg.
Engines - V.KLIMOV's (4200 hs) or M-51 M.MASLENNIKOV's (4000 hs).
max speed 650km/h, cruise 400km/h.
Range before 12000km.
service ceiling 11000km.
Source: S.GANIN A.KARPENKO V.KOLNOGOROV " Bastion "part 1, str.59.
Dear Frank and Borovik!
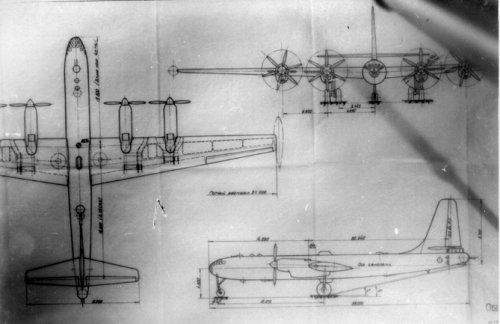
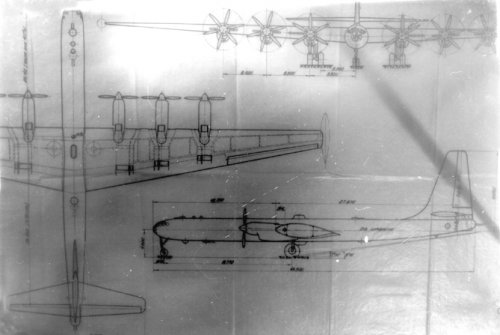
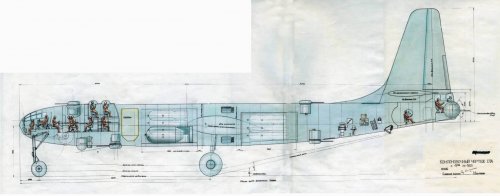
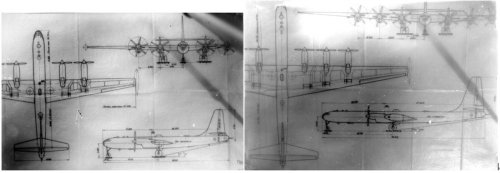
There are several copies from original OKB drawings of Il-26 in my archiev. It was a project of long-range bomber in three variants equipped with 4 and 6 engines.
Images will follow.
There are several copies from original OKB drawings of Il-26 in my archiev. It was a project of long-range bomber in three variants equipped with 4 and 6 engines.
Images will follow.
Holy cow! Thanks! And welcome! 
ucon said:Thank you, Borovik!
Here two attch. of Il-26 as promissed.
Regards.
Thank you, Frank!
Any questions about Il and MDB - welcome!
Regards
Any questions about Il and MDB - welcome!
Regards
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,752
- Reaction score
- 26,437
Given their success with the Il-28, how did Ilyushin end up in transports and civil aircraft exclusively? Politics, or poor performance (e.g. Il-40, Il-54?)
Pure politics
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,752
- Reaction score
- 26,437
It has been said that Yakovlev owed their continued existence to pure politics, and Sukhoi people have claimed that MiG owed their pre-eminence to the Mikoyan family's communist party connections.
Dear Overscan, what blue and yellow stars mean in profile?
- Joined
- 27 December 2005
- Messages
- 17,752
- Reaction score
- 26,437
Yellow stars just mean number of posts. Lots of yellow stars means you post a lot.
Moderators have blue stars, Administrators have red stars.
Two blue stars means you are recognised as a "Senior Member". This means the administrators deem you to be a person with particularly interesting posts.
Moderators have blue stars, Administrators have red stars.
Two blue stars means you are recognised as a "Senior Member". This means the administrators deem you to be a person with particularly interesting posts.
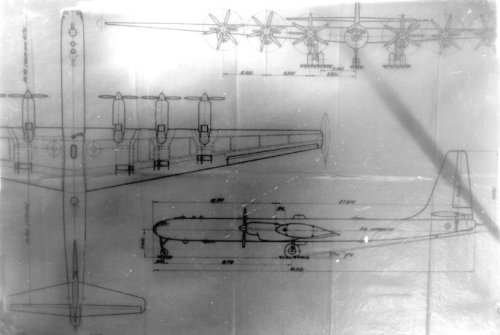
I think I only knew of the 6 engined version. Were the 4 & 6 engined versions developed in parallel to different specifications or was the 4 engined version ruled out altogether in favor of the 6 engined one? The dimensions are a bit difficult to read, but I think the dimension in the side view of the 4 engine version, the dimension from the nose to the wing leading edge, is 14,500. If I do read that correctly, then I can go further from there. Thanks again for these drawings.
ucon said:Thank you, Frank!
Any questions about Il and MDB - welcome!
Regards
Dear Thomas!
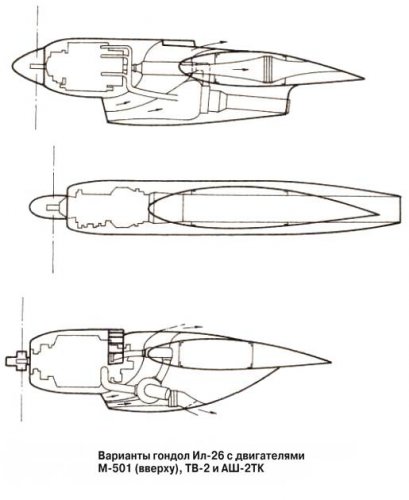
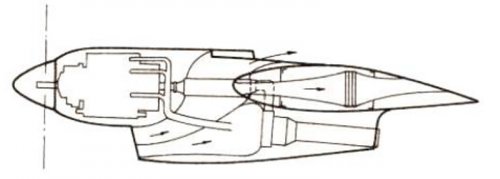
Il-26 project last only two years (1947-1948) and in Il DB they have studied 3 variants with the following engines:
piston ASh-2TK;
disel M-501;
purtoprop VK-2.
Regards
Il-26 project last only two years (1947-1948) and in Il DB they have studied 3 variants with the following engines:
piston ASh-2TK;
disel M-501;
purtoprop VK-2.
Regards
- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 34,911
- Reaction score
- 15,789
Attachments
Nice design,seems that the Russians had some inspiration with the B-29 and G10N Fugakuucon said:one more
nevertheless its a good looking design,I certain know Stalin was pleased when it was build!
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
ASh-2TK and ASh-2K (ASh-4K) – Four-row versions of the ASh-82, developed in the late '40s. The engine concept was similar to the Pratt & Whitney R-4360. The Shvetsov design bureau took into consideration all available information about the R-4360 and developed an engine with less maintenance operations, longer time between overhaul, direct fuel injection and a simpler supercharging system. The ASh-2TK had a two-stage two-speed supercharging system with intercooler (similar to the ASh-73) that compromised the engine's long TBO. Finally the ASh-2TK was discarded and a new version was developed, the ASh-4K, with an experimental variable-speed turbocharger and after-cooler, which allowed a cruising altitude of 11,000 m (36,089 ft). The engine had 82.4 litres (5,030 cu in) and 4,000 HP (2,985 kW) at 2,600 RPM (dry). The Ash-2K (ASh-4K) version had 4,700 HP (3,507 kW) wet, with a water-methanol system. For political reasons, these engines were prematurely installed in Tupolev Tu-4LL testbeds at the end of 1950, when the prototypes' initial tests had barely begun. The engines had various teething and overheating problems, and required a long testing period. Most of the flaws were fixed in the mid-fifties, but the production was cancelled: in those days, the priority for the Soviet Air Force were the turboprop and jet engines.[7]ucon said:Dear Thomas!
Il-26 project last only two years (1947-1948) and in Il DB they have studied 3 variants with the following engines:
piston ASh-2TK;
disel M-501;
purtoprop VK-2.
Regards
Yakolev slowed down work before this, believing his M-501 diesel engine would be better for long-range bombers. Apparently this engine went on into series production for marine work - seven blocks in radial, 42 cylinders. Sounds like another very interesting design!
Factory No.500 was headed by V. M. Yakovlev (no relation to the aircraft designer), who was hard at work on his own large diesel aircraft engine—the 6,200 hp (4,620 kW), 8,760 cu in (143.6 L), 42-cylinder M-501.Yakovlev was critical of the work done on the M-224; he felt that the engine took resources away from the M-501. With little progress on the M-224, Yakovlev was able to convince Soviet officials that his engine had the greater potential, and all development on the M-224 was stopped in mid-1948.
Attachments
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
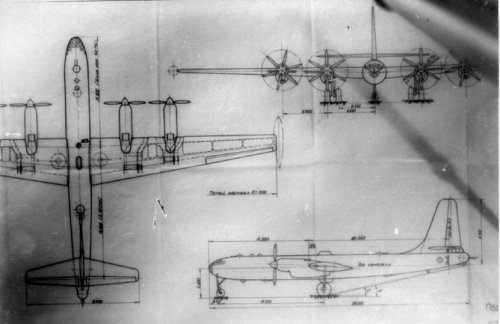
So these drawings are the design with M-501 diesel engine?
We can see radiators in these drawings.
If Il26 had 4 M-501 engine, total power was 24,800HP.
If Il26 had 6 M-501 engine, total power was 37,200HP.
We can see radiators in these drawings.
If Il26 had 4 M-501 engine, total power was 24,800HP.
If Il26 had 6 M-501 engine, total power was 37,200HP.
Attachments
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
Shvetsov Ash-82T two stage supercharged air cooling radial engine take off power is 1900HP.
If Il-26 had 6 Ash-2TK engine, total takeoff power is 22,800HP? (1900×2×6)
Shvetsov Ash-2TK air cooling radial 28 cylinder engine : 3800HP?
Factory No.500 (headed by V. M. Yakovlev) designed M-501 seven blocks in radial, 42 cylindersdiesel engine : 6200HP?
VK-2 turbo prop engine : 4800HP?
If Il-26 had 6 Ash-2TK engine, total takeoff power is 22,800HP? (1900×2×6)
Shvetsov Ash-2TK air cooling radial 28 cylinder engine : 3800HP?
Factory No.500 (headed by V. M. Yakovlev) designed M-501 seven blocks in radial, 42 cylindersdiesel engine : 6200HP?
VK-2 turbo prop engine : 4800HP?
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
Thanks a lot. Amazing drawings!!
M-501 engine looks like air cooling radial engine, but it's a liquid cooling seven blocks in radial diesel engine.
TB-2 is VK-2?
We can see turbo charged M-501 and ASh-2TK.
4×M-501 engine aircraft size is different from 6×M-501 engine aircraft size.
We want to see the drawing of Il26 bomber with air cooling ASh-2TK engine.
M-501 engine looks like air cooling radial engine, but it's a liquid cooling seven blocks in radial diesel engine.
TB-2 is VK-2?
We can see turbo charged M-501 and ASh-2TK.
4×M-501 engine aircraft size is different from 6×M-501 engine aircraft size.
We want to see the drawing of Il26 bomber with air cooling ASh-2TK engine.
Attachments
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
"For increase of range of the flight in project was an aplying carriage with additional thrown after take-off under wings wheel-strut, allowing reduce the mass to designs of the bomber."
Same as Fugaku
I read that 4×M-501 engine type overall length is 38m from these drawings.
If it's correct, propeller diameter is 6m. Wing span is 57.5m. Height is 15m.
6×M-501 engine type overall length is 48.5m. Wing span is 75m. Height is 18m
How about these values, borovik-san?
Same as Fugaku
I read that 4×M-501 engine type overall length is 38m from these drawings.
If it's correct, propeller diameter is 6m. Wing span is 57.5m. Height is 15m.
6×M-501 engine type overall length is 48.5m. Wing span is 75m. Height is 18m
How about these values, borovik-san?
blackkitefamvburg said:Thanks for all of these! Any basic dimensions found?
+How about these values,
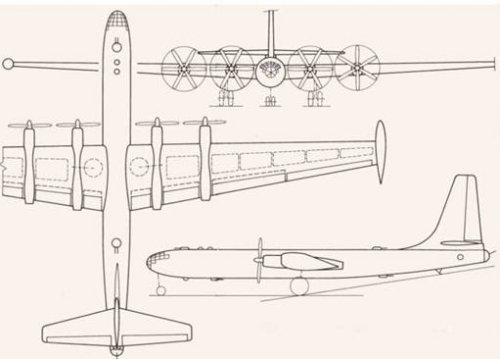
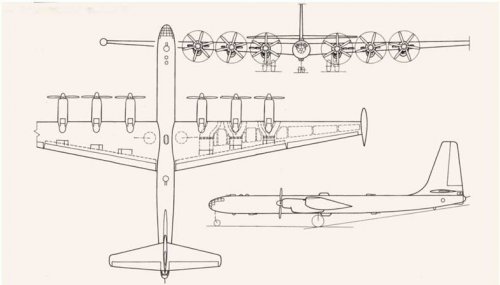
In addition, the available data In one embodiment:
Engine type -VK-2
Take-off power, hp -6x5,000
Wing area, m' (sq tt) -475 (5,113)
Crew -12
All-up weight, kg (Ib)
normal -190,000 (418,950)
Maximum speed, km/h (mph):
at sea level -545 (339)
at 9,300 m(30,510 tt) -560 (348)
Practical ceiling, m(tt) -10,000 (32,800)
Range, km (miles) with a5,000-kg (11,025-lb)
bomb load -11,560 (7,185)
Take-off run, m(tt) -1,520 (4,987)
Bomb load, kg (Ib)
normal -5,000 (11,025)
maximum -12,000 (26,460)
Defensive armament (cannon), mm - 10 x23
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
Thanks a lot borovik-san. Great information.
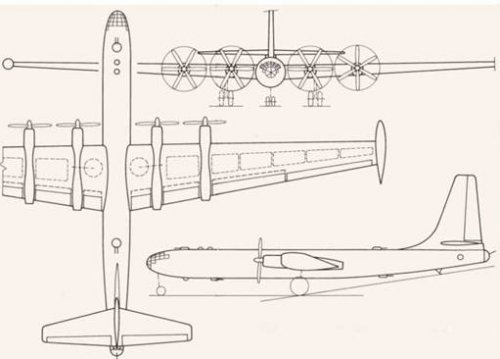
I guess following dimension for Il26 VK-2 version.
Wing span(Including wing tip fuel tanks) : 61m, Except wing tip fuel tanks : 59m
Overall length : 39m
Height : 13.7m
Fuselage diameter : 3.5m
Propeller diameter : 5.2m
How about these value, borovik-san?
I guess following dimension for Il26 VK-2 version.
Wing span(Including wing tip fuel tanks) : 61m, Except wing tip fuel tanks : 59m
Overall length : 39m
Height : 13.7m
Fuselage diameter : 3.5m
Propeller diameter : 5.2m
How about these value, borovik-san?
- Joined
- 27 March 2006
- Messages
- 1,874
- Reaction score
- 1,621
blackkite said:Yakolev slowed down work before this, believing his M-501 diesel engine would be better for long-range bombers. Apparently this engine went on into series production for marine work - seven blocks in radial, 42 cylinders. Sounds like another very interesting design!
I assume this engine formed the basis for the diesel that powered the Osa class missile boats... they were also 7 bank radial diesels.
blackkite
Don't laugh, don't cry, don't even curse, but.....
- Joined
- 31 May 2007
- Messages
- 8,819
- Reaction score
- 7,718
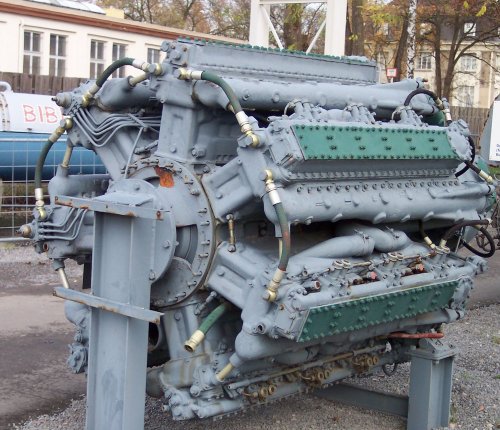
Oh thanks a lot. We want to see the drawing and picture of surprising M-501 diesel engine. 
Soviet union succeeded to develop such a surprising engine.
Specifications (Zvezda M503A)
M503A is rather small engine compared with powerful M-501 6,000HP engine.
General characteristics
Type: 42-cylinder Liquid cooled 7 bank, 6 cylinder per bank diesel radial engine
Bore: 160 mm (6.29 in)
Stroke: 170 mm (6.69 in)
Displacement: 143.6 L (8,763 in³)
Length: 3700 mm (145.66 in)
Diameter: 1560 mm (61.41 in)
Dry weight: 5450 kg (12,015 lb) (dry)
Components
Valvetrain: 7 overhead cam shafts, one per bank.
Fuel type: Diesel fuel
Cooling system: Liquid-cooled
Performance
Power output: 3,942 hp (2,940 kW, 3,997 PS) at 2,200 rpm
Specific power: 20.47 kW/L (0.44 hp/in³)
Power-to-weight ratio: 0.53 kW/kg (0.32 hp/lb)
Soviet union succeeded to develop such a surprising engine.
Specifications (Zvezda M503A)
M503A is rather small engine compared with powerful M-501 6,000HP engine.
General characteristics
Type: 42-cylinder Liquid cooled 7 bank, 6 cylinder per bank diesel radial engine
Bore: 160 mm (6.29 in)
Stroke: 170 mm (6.69 in)
Displacement: 143.6 L (8,763 in³)
Length: 3700 mm (145.66 in)
Diameter: 1560 mm (61.41 in)
Dry weight: 5450 kg (12,015 lb) (dry)
Components
Valvetrain: 7 overhead cam shafts, one per bank.
Fuel type: Diesel fuel
Cooling system: Liquid-cooled
Performance
Power output: 3,942 hp (2,940 kW, 3,997 PS) at 2,200 rpm
Specific power: 20.47 kW/L (0.44 hp/in³)
Power-to-weight ratio: 0.53 kW/kg (0.32 hp/lb)
Attachments
- Joined
- 27 March 2006
- Messages
- 1,874
- Reaction score
- 1,621
I'm simply assuming they're linked, due to the configuration, but I thought I would mention it as the description of the M501 rang a bell and reminded me of the naval M503 diesel in the Osa class missile boats from roughly the same era.
They're both diesels with the same configuration, same amount of banks, same amount of cylinders, same displacement.....and in your one post it is mentioned the design went further into production for marine work.
If the engines do indeed have a link, a navalised development would have differences I'm sure. Not least of which would be weight. The marine M503 is way too heavy for aviation uses.
Somebody with better knowledge of the engine or Zvezda would shed more light on the matter, and the relationship between the engines, than I could.
They're both diesels with the same configuration, same amount of banks, same amount of cylinders, same displacement.....and in your one post it is mentioned the design went further into production for marine work.
If the engines do indeed have a link, a navalised development would have differences I'm sure. Not least of which would be weight. The marine M503 is way too heavy for aviation uses.
Somebody with better knowledge of the engine or Zvezda would shed more light on the matter, and the relationship between the engines, than I could.
Similar threads
-
-
Looking for infos about the Ilyushin IL 40 Brawny
- Started by XB-35
- Replies: 3
-
-
NATO reporting names for Soviet/Chinese aircraft and missiles
- Started by Stargazer
- Replies: 12
-