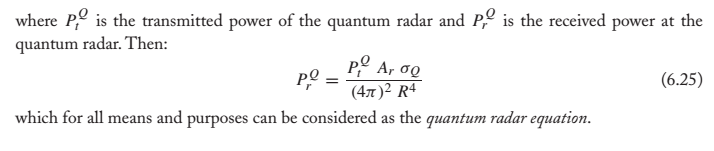antigravite said:
Hi.
This set of patent references is just the beginning of any honest elementary homework, just like the tip of the iceberg. I feel pretty comfident that browsing through peer-reviewed literature would bring up a least a hundred more references. Well… Fact checking news articles is a prerequisite. Digging up primary sources a must. Then you can listen / read / sort through online psyop operatives trying to forge the mindscape to make your mind up. That's all. And that's very simple. And yes, as always, it requires homework, i.e. a bit of sweat.
A.
When I have time, on the websites like Secretprojects my "homework" concerns :
-1 : Payen planes and the history of these planes.
I visited the Musee Delta (where I met too the daughter of M. Payen and later the french author of the aviation history Pierre Gaillard)
I visited the archives of the french Musee de l'Air in Le Bourget,
I visited the archives of the french Armée de l'Air in Vincennes near Paris,
I bought/buy/will buy books
I bought/buy/will buy magazines,
And I search, share and discuss on the net.
And reguliarly I make global search on the web to find news about this subject and to share it, here and on other websites. And I can make (and I make) mistakes too (translations, copies, misinterpretations, ...) that I correct as soon as I (can) find their.
And as you can see. It's not only "Homework". And if you want to find somebody who "sweats" more than me about this subject since 15 years, at least on the web, I think that you can made "homework" and "sweat" until the end of Eternity and beyond.
And I am not alone.
For example, to make and share Payen drawings and 3D, Jemiba is far, far, far, ahead of me ;D. On the web, Modellers (even flying modellers) build and show/share home made Payen models or what they buy by Unicraft and others. Authors (Tophe, Rico, Carbonel, ...) help the Payen fans here and/or on other websites. Other enthusiasts and amateurs here and elsewhere on the web help us and share too (I suspect sometimes that Hesham

doesn't sleep and doesn't eat and only searchs and shares aviation history on Secretprojects).
As shows the example of the Payen planes, nobody was/is/will be waiting for you to "homework" and "sweat".
When I have more time and money
-2 : delta planes, futuristic/original planes in the history of aviation and french planes.
I buy books
I buy magazines
I search and share and discuss on the net.
When I have even more time and money
-3 : other planes.
I buy magazines
I search and share and discuss on the net.
Too : I don't speak very good English. It's the same for German and Russian languages (that I learned a long time ago too). My old dictionaries for these three languages, and Google translation for these three languages too and other languages (for example the portuguese during the last fighter contest in Brazil), can be useful. But it's impossible for me to understand all these languages as in french.
And sometimes I have discussions and digress about some subjects. For example, I have sometimes discussions on a french websites about the efficiency of the stealth planes in the future. I think that this technology would have problems the day when there would be radars (and in particular airborne radars) to counter it. I think it
can be soon. Others think it
will be in a very long time.
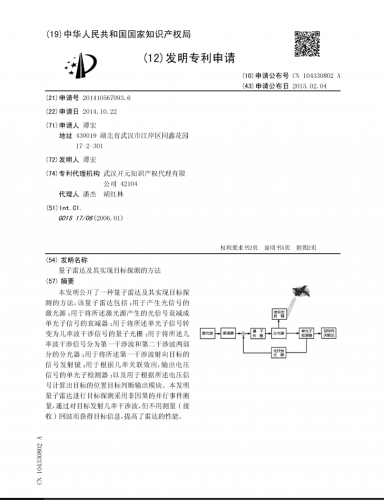
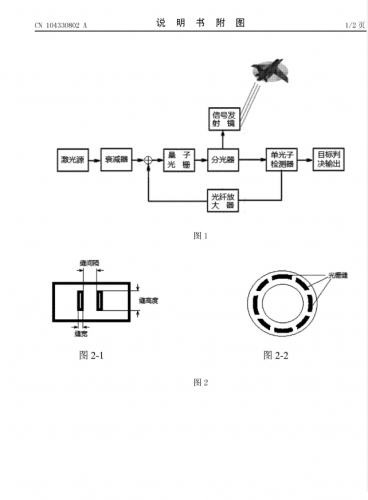
On a french magazine I recently found news (two lines...) about this chinese
quantum radar. I searched on the web in french and English about it and found tens more or less explanatory articles/files. I didn't find something concrete, and I am not a specialist. And the history, and in particular aviation and technological history, is full of announcements that were, finally, without concrete production.
I opened a topic on a french website to know the
opinion about it. And I was interested too to know what was the opinion about it on SecretProjects where contributors are from the world. That's why I opened this topic.
I follow the two discussions on the two websites about the possibility of this chinese radar to be used
really, with efficiency and in large scale. It can be interesting too to know what other lands can made too. And it can be interesting to discuss (at least for me and for the ones who like to discuss about it) about what would be the conséquences on military stealth planes (now and afterward). I wrote "discuss" and not "know" because I don't know someone who knows the Future.
All the contributions are interesting. Your second shows that, there is, in China, theoretical research, at least.
But,
nobody is forced to answer and my question is to be seen as
fun, not as existential.
And if somebody is very competent and/or very interested in this question, I hope that he will answer like I do when I answer about the Payen planes (where I am more "very interested" because of my lack of technical knowledges, even if sometimes I make "homework" and "sweat" and buy to correct it) on this website and on all the other websites where I share about the Payen planes, and like almost all the other contributors answer here and elsewhere on the web about the subjects that they like.
Once again, thanks for your second answer.