- Joined
- 26 May 2006
- Messages
- 32,643
- Reaction score
- 11,821
Mikhael said:Yak-125B
Nice find Mikhael.
Mikhael said:Yak-125B
hesham said:visvirtusvoluntas said:Yak-40 designed between January and June 1948. It was a single seat fighter powered by two 850 kgp ramjet engines mounted at the wingtips. The aircraft was 7.5 m long, with a wingspan of 5.05 m and an all-up weight of 1800 kg. Normally the fighter was to take off from a wheeled launch dolly accelerated by solid fuel rocket, landing on a centerline skid. Yakovlev OKB suggested using Yak-40 as parasite fighter to be suspended under Tu-4 wings in number of 6 (see image). The Yak-40A introduced a bicycle retractable landing gear and two rocket boosters for take off. Not built.
From; Аэрокосмическое обозрение №06 (67) 2013
here is again Yak-40 drawings in colors.
borovik said:Several options for preliminary designs of OKB-115, the first jet fighter with the engine JUMO-004, before finally was chosen scheme Yak-RD / Yak-15.
(from : N.Yakubovich-"Jet firstborn")
hesham said:Hi,
here is a strange Yak-9V with modifications,maybe remained a Project ?.
Все самолеты-разведчики СССР: "Глаза" армии и Флота
blackkite said:Hi! Yakovlev LFI.
http://translate.google.fr/translate?hl=fr&sl=auto&tl=en&u=http%3A%2F%2Fwww.hitechweb.genezis.eu%2FfightersSF02.htm
Paralay-san's super site.
http://paralay.com/lfsyak.html
http://translate.google.fr/translate?hl=fr&sl=ru&tl=en&u=http%3A%2F%2Fparalay.com%2Flfsyak.html&sandbox=1
CiTrus90 said:Checked my copy of Buttler & Gordon Soviet Secret Projects: fighters since 1945. On page 101 is mentioned a pre-Yak-41 study with semi circular side intakes, twin fins and cranked delta wing a la Yak-45. I think this is our culprit.
Regards.
PlanesPictures said:from old archives
hesham said:Hi,
The Yak-V project for VTOL experimental aircraft of early of 1960s.
ucon said:I wonder, what is the source about A-8 Yakovlev bomber? ???
werewolf0001 said:some concept plane from Saratov aviation plant
Definitely not a Yak-141, nice catch Kaiserbill
Regards.

Hi all,
Yak-29 and Yak-40 are both described in "Early Soviet Jet Fighters" by Yefim Gordon & Dmitriy Komissarov (2014) as well as Yak-U and Yak-M. Yak-50/60/70 are described in "Storia ed Evoluzione dei Caccia Sovietici a Reazione, 1945-55" by Alberto Trevisan (2013).
Yak-29 was developed between July and October 1947 as a light fighter. Powered by a RD-500 turbojet, the machine had a wingspan of 6.3 m, lenght of 8.64 m, and a wing area of 8.0 sqm. The all-up weight was 2300 kg and the armament consisted of 2x23 mm cannons in conformal underwing pods. Not built.
Yak-30 is well known.
Yak-40 designed between January and June 1948. It was a single seat fighter powered by two 850 kgp ramjet engines mounted at the wingtips. The aircraft was 7.5 m long, with a wingspan of 5.05 m and an all-up weight of 1800 kg. Normally the fighter was to take off from a wheeled launch dolly accelerated by solid fuel rocket, landing on a centerline skid. Yakovlev OKB suggested using Yak-40 as parasite fighter to be suspended under Tu-4 wings in number of 6 (see image). The Yak-40A introduced a bicycle retractable landing gear and two rocket boosters for take off. Not built.
Yak-50 is well known also.
Yak-60 was an intermediate project between Yak-50 and Yak-120 (the series built Yak-25). Approved by Yakovlev in 1948 November 20. General aspect as Yak-50, VK-1 engine, 45° swept wings, tricycle landing gear, underwing drop tanks. Between 1948 and 1949 several wing tunnel (TsAGI T-106) tests were conducted. A second version of Yak-60 had bicycle landing gear and bullet radome above air intake. Limited range as interceptor led to cancellation. Twin engined Yak-120 was preferred.
Yak-70 was a supersonic single seat fighter designed in 1950. Powered by a TR-3 engine (4500 kgp), butterfly tail, bicycle landing gear, 15,24 m long. Second version radar equipped.
Yak-M was a single seat light fighter
Yak-U single seat twin engined fighter
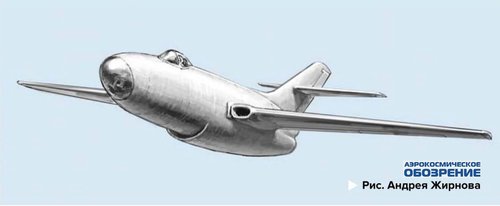
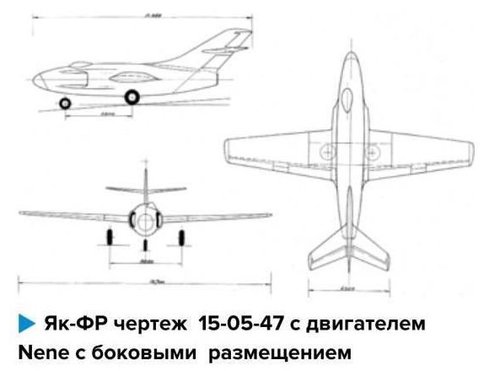
Проект реактивного самолёта разведчика Як-ФР (СССР)
Появление в СССР первых лицензионных английских двигателей Rolls - Royce Nene и Dervent V позволило резко активизировать проектные работы по созданию реактивных боевых самолетов в советских авиационных КБ. В стране, сразу по окончанию войны развернулись активные работы по развитию отечественного реактивного двигателестроения, но до появления отработанных образцов таких двигателей требовалось некоторое время, поэтому закупка в Англии у фирмы Rolls-Royce небольшой партии серийных реактивных двигателей и лицензии на их производство была, как нельзя кстати. Работы ОКБ А.С. Яковлева по реактивной истребительной тематике Як-1Б, Як-17, Як-19, Як-23, Як-25 (первый) второй половины 40-х годов, достаточно хорошо известны, а о малоизвестных проектах и модификациях рассказывалось в предыдущих статьях этой серии. Тем не менее, удалось обнаружить сведения о совершенно не упоминаемом проекте реактивного фоторазведчика Як-ФР начала 1947 года.
Проект этого самолета, хотя и не получил развития, стал своеобразным родоначальником таких известных и строившихся серийно самолетов - разведчиков Як-25Р, Як-25МР (опытные), ЯК-2БРВ, Як-27Р и Як-28Р, которые длительное время составляли основу разведывательной фронтовой авиации ВВС СССР. Сейчас уже трудно выяснить причины отказа от постройки фоторазведчика по яковлевскому проекту, но совершенно очевидно, что Як-ФР в конце 40-х годов мог бы занять достойное место в строю советских ВВС. В те годы, основу фронтовой разведывательной авиации составляли самолеты с поршневыми двигателями - модификации серийных истребителей и бомбардировщиков. А в условиях массового принятия на вооружение реактивных истребителей вероятным противником, шансы успешного выполнения боевых задач советскими поршневыми разведчиками были невелики. К тому же, Як-ФР мог бы стать отличным фоторазведчиком на период переходного этапа к появлению более скоростных и совершенных самолетов.
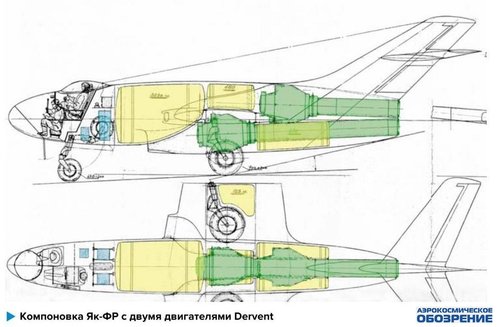
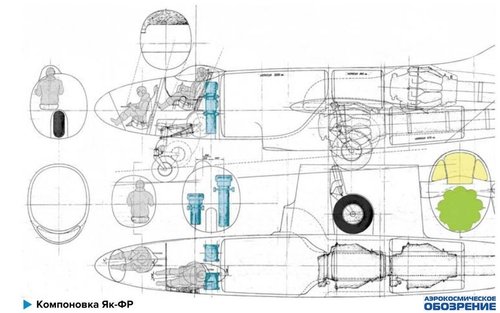
Так, что же представлял из себя проект двухместного фоторазведчика Як-ФР. Первый чертеж проработки этого самолета датируется 10 марта 1947 года, его подписал главный компоновщик (по - современному дизайнер) ОКБ Яковлева - Леон Шехтер. Уже 29 марта он же выпустил очередной чертеж, несколько доработанного варианта фоторазведчика, была удлинена носовая часть, для более комфортного расположения членов экипажа. Самолет имел, по сравнению с первыми реактивными истребителями ОКБ, довольно внушительные размеры - его полная длина составляла 13,6 м, длина фюзеляжа 10,9 м, размах прямого крыла 12,7 м. Совершенно оригинальной стала его общая компоновка - самолет имел в хвостовой части два двигателя с центробежным компрессором РД-500 (Dervent V) тягой по 1590 кгс каждый, расположенные друг над другом. Для уменьшения миделя фюзеляжа, учитывая особенности габаритов этих двигателей, их расположили уступом, нижний двигатель был смещен вперед и, следовательно, удлинена труба его сопла.
Воздухозаборники в передней кромке корневых частей крыла питали воздухом верхний двигатель, а для нижнего двигателя служил подфюзеляжный воздухозаборник. Вертикальное и горизонтальное оперение были стреловидными. Компоновка носовой части фюзеляжа стала прообразом конструкции разведчиков Як-27Р и Як-28Р, да и бомбардировщиков - ЯК-25Б, Як-26 и семейства Як-28. В носовой части Як-ФР располагалось рабочее место штурмана-оператора, смещенное вправо от продольной оси самолета, носовая часть имела беспереплетное остекление большой площади, что обеспечивало штурману достаточный обзор вперед-вниз. Вход в кабину осуществлялся через люк над головой штурмана. Рабочее место пилота самолета было смещено влево от продольной оси самолета и находилось сразу за креслом штурмана, беспереплетный фонарь кабины летчика, каплевидной формы, имел небольшие размеры и также был смещен к левому борту. Вход в кабину летчика осуществлялся через бортовой люк. Сразу за кабиной экипажа располагался отсек фотооборудования, включавший в себя два фотоаппарата АФА-ЗС-500 и АФА-ЗС-1000. Фюзеляж самолета имел овальную форму высотой 1.7 м, а в районе нижнего воздухозаборника его высота составляла два метра.
Внутренние объемы фюзеляжа и крыла позволяли разместить большое количество топлива: в трех фюзеляжных баках размещалось 3250 кг + 485 кг + 670 кг соответственно, в двух крыльевых баках - 2 х 125 кг. Суммарный запас авиационного керосина, таким образом, составлял около 5820 литров и позволял фоторазведчику выполнять задачу на большую глубину. Предусматривалось размещение дополнительных баков в отъемных частях крыла и использование дополнительных подвесных топливных баков, а это еще больше увеличивало расчетную дальность полета. Шасси самолета трехстоечное, все колеса имели большие размеры, что позволяло осуществлять взлет с грунтовых аэродромов. Колеса тормозные: носовое колесо - 650 х 200 мм убиралось назад в подкабинный отсек, колеса основных стоек шасси - 960 х 300 мм, убирались в крыло. Колея шасси 3,85 м, база шасси - 3,5 м.
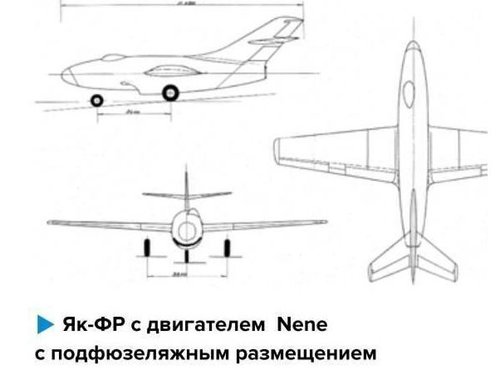
Следующим вариантом фоторазведчика Як-ФР стала проработка его однодвигательной компоновки с использованием двигателя РД-45 (Nene). Это позволило несколько уменьшить длину фюзеляжа при сохранении того же крыла и конструкции вертикального и горизонтального оперения. Причем на двух чертежах, датированных 15-05-47 г. и подписанных Леоном Шехтером, разное размещение воздухозаборников - в первом варианте он подфюзеляжный, во втором - воздухозаборники боковые. Конструкция кабин и размещение экипажа самолета, шасси аналогичны первым вариантам Як-ФР. Интересный момент, один из чертежей с двигателем Nene имеет название выполненное тушью Як-, а после тире стоит четко видимый аккуратный контур цифры 20, выдавленный на кальке. На носовой части нанесен номер 54, а на киле цифра 2. Очевидно, что в это время рассматривался вопрос присвоения проекту фоторазведчика названия Як-20 (первый с таким индексом) и была надежда постройки опытного самолета. Позднее, осенью 1949 года проходил испытания учебно-пилотажный легкий одномоторный самолет Як-20, но в серии не строился.
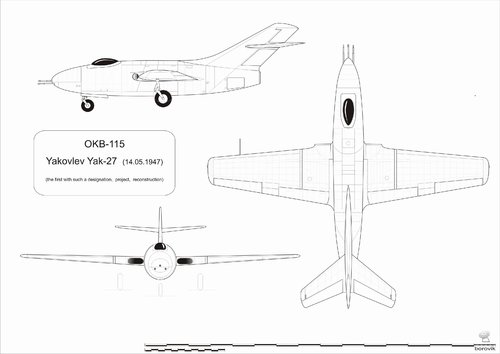
Третьим проектом, разработанным на базе однодвигательного фоторазведчика Як-ФР, стал одноместный истребитель Як-27 (первый с таким названием, чертеж датирован 14-05-47 г.) Конструкция самолета, при тех же размерах, имела следующие отличия от варианта фоторазведчика: воздухозаборники перемещены в корневые части крыла и несколько выступали вперед относительно его передней кромки, в носовой части самолета был размещен отсек с пушечным вооружением, с легким и удобным доступом для перезарядки и обслуживания. Пушечное вооружение состояло из одной пушки Н-37 калибра 37 мм и двух пушек НС-23 калибра 23 мм, стволы пушек выступали на 700 мм вперед из носового обтекателя фюзеляжа. Конструкция фонаря кабины летчика осталась без изменений, только фонарь, естественно, разместился строго по оси самолета.
Автор Виктор ДРУШЛЯКОВ
The project of the reconnaissance jet aircraft Yak-FR (USSR)
The appearance in the USSR of the first licensed English Rolls-Royce Nene and Dervent V engines made it possible to sharply intensify design work on the creation of jet combat aircraft in Soviet aviation design bureaus. In the country, immediately after the war, active work began on the development of domestic jet engine building, but it took some time before the appearance of the developed samples of such engines, so the purchase of a small batch of serial jet engines in England from Rolls-Royce and the license for their production were impossible by the way. Work OKB A.S. Yakovleva on jet fighter subjects Yak-1B, Yak-17, Yak-19, Yak-23, Yak-25 (first) of the second half of the 40s, are well known, and about little-known projects and modifications were described in previous articles of this series . Nevertheless, it was possible to find information about the completely unreported project of the Yak-FR reactive photo reconnaissance in early 1947.
The project of this aircraft, although it did not receive development, became a kind of ancestor of such well-known and mass-built aircraft - reconnaissance aircraft Yak-25R, Yak-25MR (experimental), Yak-2BRV, Yak-27R and Yak-28R, which for a long time formed the basis of reconnaissance Air Force of the USSR Air Force. It is now difficult to find out the reasons for the refusal to build a photo reconnaissance according to the Yakovlev project, but it is clear that the Yak-FR in the late 40s could take its rightful place in the ranks of the Soviet Air Force. In those years, the basis of front-line reconnaissance aviation was aircraft with piston engines — modifications of serial fighters and bombers. And in the conditions of the mass adoption of jet fighters as a possible adversary, the chances of successful fulfillment of combat missions by Soviet piston reconnaissance officers were slim. In addition, the Yak-FR could be an excellent photo reconnaissance for the transition period to the emergence of more high-speed and advanced aircraft.
So, what was the project of a two-seater photo reconnaissance Yak-FR. The first drawing of the development of this aircraft dates back to March 10, 1947, it was signed by the main linker (according to the modern designer) Yakovlev Design Bureau - Leon Shekhter. Already on March 29, he also released another drawing, a somewhat modified version of the photo reconnaissance, the bow was lengthened, for a more comfortable arrangement of crew members. The aircraft, in comparison with the first OKB fighter jets, had rather impressive dimensions — its full length was 13.6 m, the fuselage length was 10.9 m, and the wingspan of the forward wing was 12.7 m. Its general layout became completely original — the aircraft had a tail parts two engines with a centrifugal compressor RD-500 (Dervent V) with a thrust of 1590 kgf each, located one above the other. To reduce the midsection of the fuselage, taking into account the particular dimensions of these engines, they were positioned with a ledge, the lower engine was shifted forward and, therefore, the pipe of its nozzle was lengthened.
The air intakes at the leading edge of the root parts of the wing fed air to the upper engine, while the lower engine served as the ventral air intake. The vertical and horizontal plumage were swept. The layout of the nose of the fuselage became a prototype of the design of the scouts Yak-27R and Yak-28R, and bombers - Yak-25B, Yak-26 and the Yak-28 family. In the bow of the Yak-FR there was a workstation of the navigator-operator, shifted to the right of the longitudinal axis of the aircraft, the bow had glazing without glazing over a large area, which provided the navigator with a sufficient forward-downward view. Entrance to the cabin was through a hatch above the head of the navigator. The aircraft pilot's workplace was shifted to the left of the longitudinal axis of the aircraft and was immediately behind the navigator’s seat, the tear-free pilot's taillight was small in size and was also shifted to the port side. Entrance to the cockpit was through the side hatch. Immediately behind the cockpit there was a photographic equipment compartment, which included two AFA-ZS-500 and AFA-ZS-1000 cameras. The fuselage of the aircraft had an oval shape with a height of 1.7 m, and in the area of the lower air intake its height was two meters.
The internal volumes of the fuselage and wing made it possible to accommodate a large amount of fuel: 3250 kg + 485 kg + 670 kg, respectively, were located in three fuselage tanks, respectively, 2 x 125 kg in two wing tanks. The total supply of aviation kerosene, thus, amounted to about 5820 liters and allowed the photo reconnaissance to carry out the task to great depths. It was planned to place additional tanks in detachable parts of the wing and to use additional suspended fuel tanks, and this further increased the estimated flight range. The aircraft’s landing gear is three-post, all wheels were large, which made it possible to take off from unpaved airfields. Brake wheels: the nose wheel - 650 x 200 mm was retracted back into the pod compartment, the wheels of the main landing gear - 960 x 300 mm, were retracted into the wing. Chassis track 3.85 m, chassis base 3.5 m.
The next version of the Yak-FR photo reconnaissance was the development of its single-engine layout using the RD-45 engine (Nene). This made it possible to slightly reduce the length of the fuselage while maintaining the same wing and the design of vertical and horizontal plumage. Moreover, in two drawings dated 15-05-47 and signed by Leon Schechter, the different arrangement of the air intakes is in the first embodiment, it is ventral, in the second - side air intakes. The design of the cabins and the placement of the aircraft crew, landing gear are similar to the first options of the Yak-FR. An interesting point, one of the drawings with the Nene engine has the name made by Yak- ink, and after the dash there is a clearly visible neat outline of the number 20, squeezed out on tracing paper. The number 54 is marked on the bow, and the number 2 on the keel. Obviously, at that time the issue of assigning the name Yak-20 (the first with such an index) to the photo reconnaissance project was considered and there was hope of building an experimental aircraft. Later, in the fall of 1949, the Yak-20 light pilot single-engine aircraft was tested, but was not built in the series.
The third project, developed on the basis of the Yak-FR single-engine photo reconnaissance, was the Yak-27 single-seat fighter (the first with the same name, the drawing is dated 14-05-47). The aircraft design, with the same dimensions, had the following differences from the photo reconnaissance option: air intakes moved to the root parts of the wing and protruded somewhat relative to its leading edge; a cannon armament compartment was placed in the nose of the aircraft, with easy and convenient access for reloading and maintenance. The cannon armament consisted of one N-37 cannon of 37 mm caliber and two NS-23 cannons of 23 mm caliber, gun barrels protruding 700 mm forward from the nose fairing of the fuselage. The design of the lamp of the cockpit remained unchanged, only the lamp, of course, was placed strictly along the axis of the aircraft.
Author Victor DRUSHLYAKOV
